- Key Takeaways
- Understanding the Cannabis Plant
- Understanding Cannabinoids: CBD and THC
- Psychoactive Properties and Effects
- Key Differences in Effects
- Therapeutic Potential and Medical Uses
- Medical Marijuana and CBD vs THC
- Legality and Regulation
- International Legal Framework for THC Control
- Side Effects and Risks of THC and CBD
- Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
- Practical Considerations for Use
- Latest Research Developments
- Scientific References
- Summary
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Scientific References
What’s the difference between CBD and THC, two compounds found in the cannabis sativa plant? In this article, we’ll explore their distinct effects, benefits, and uses, helping you understand how each compound can impact your health, especially in the context of C B D vs THC.
Key Takeaways
- CBD and THC, despite having the same molecular formula, differ significantly in their chemical structure and effects, with THC being psychoactive and CBD being non-psychoactive and therapeutic.
- THC is primarily used for its psychoactive effects and is beneficial for pain relief, appetite stimulation, and nausea control, while CBD offers a range of therapeutic benefits without inducing a high, making it suitable for medical applications.
- The legal status of CBD and THC varies, with CBD being more accessible under specific conditions, while THC remains a controlled substance in many regions, emphasizing the importance of understanding their legal implications.
Understanding the Cannabis Plant
The cannabis plant, also known as Cannabis sativa, is a complex species that contains over 100 different compounds known as cannabinoids. Among these, THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol) are the most well-known and extensively studied. THC is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, responsible for the “high” associated with marijuana use. In contrast, CBD is a non-psychoactive compound that has gained significant attention for its potential therapeutic applications. The diverse array of cannabinoids in the cannabis plant contributes to its wide range of effects and potential medical benefits.
Understanding Cannabinoids: CBD and THC
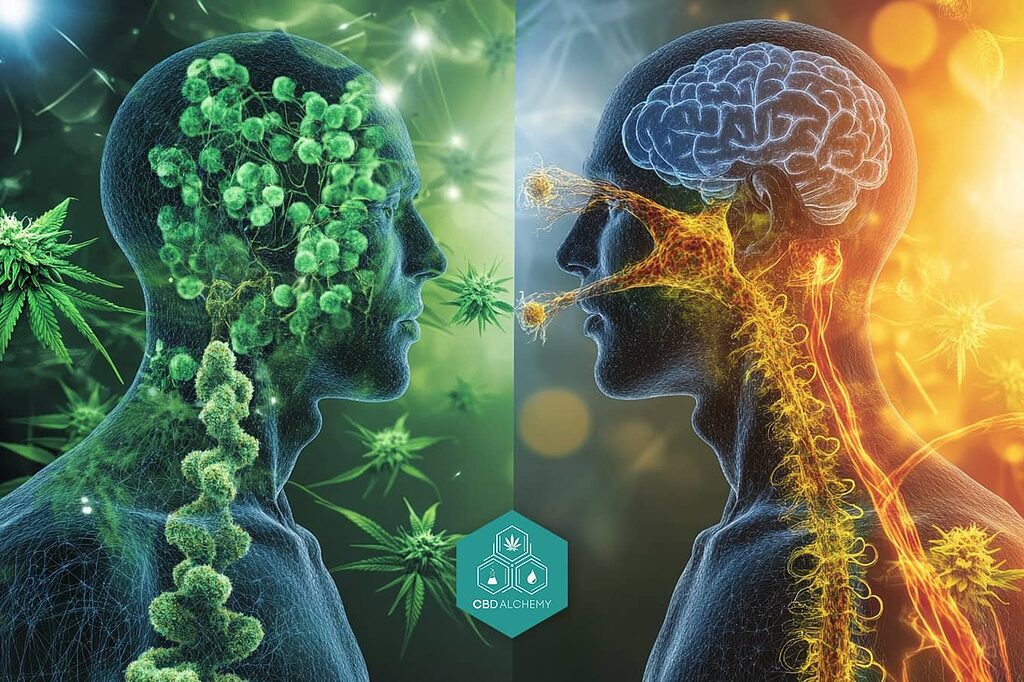

Cannabinoids are compounds that engage with our body’s cannabinoid receptors, effectively simulating the action of naturally occurring endogenous cannabinoids within us. CBD (cannabidiol) and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), among the multitude of cannabinoids present in the cannabis plant, have garnered significant attention due to their extensive research and recognition. The growing acceptance of cannabinoids is reflected in the increasing number of states that have legalized medical marijuana.
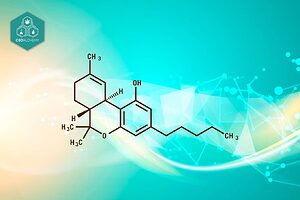
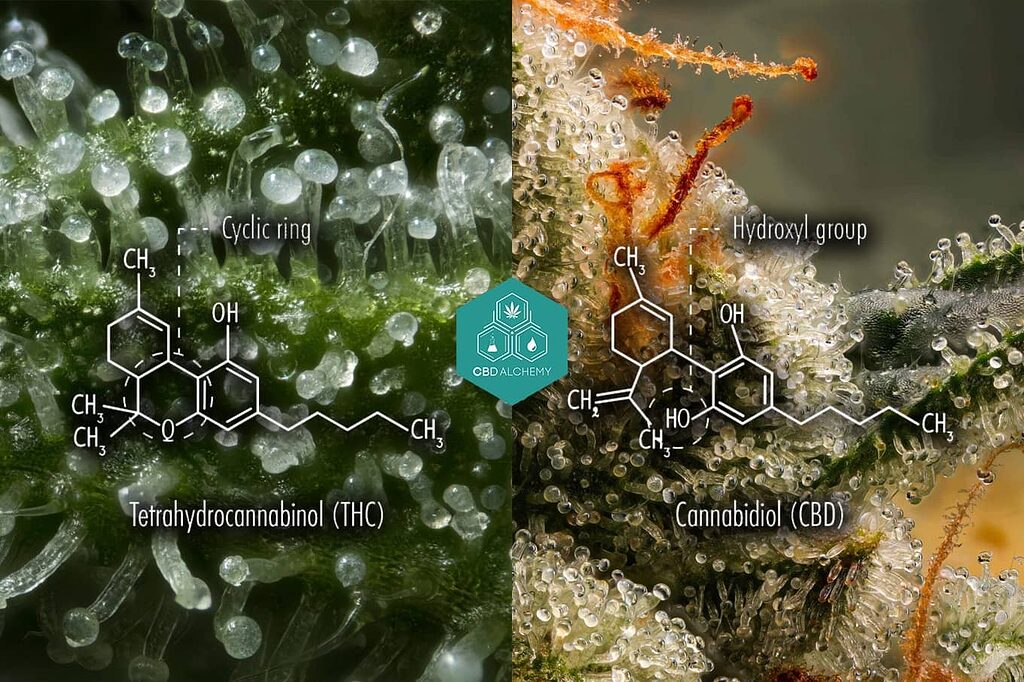
Despite both CBD and THC having an identical molecular constitution with 21 carbon atoms, 30 hydrogen atoms, and 2 oxygen atoms each—their differing chemical structures lead to unique impacts on the human system. Notably, THC is widely known for its psychoactive effects which result in a sensation of ‘high’, whereas CBD is acclaimed for its non-psychoactive benefits that offer therapeutic value.
Their varying influences stem from how they interact differently with specific cannabinoid receptors within the body. The binding affinity of THC is primarily towards CB1 receptors found heavily populated across brain areas and central nervous system regions. This attachment promotes mood alterations as well as changes in perception. Contrarily, by interacting more diversely – including affecting serotonin receptors besides other biological pathways – CBD can modulate pain perception along with mood management without inducing the high associated commonly linked to THC consumption.
What is CBD?
CBD, or cannabidiol, is a naturally occurring compound found in the cannabis plant. It is one of the many cannabinoids present in cannabis and has garnered significant attention for its potential therapeutic applications. Unlike THC, CBD does not produce a high. Instead, it interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system, which plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes, including pain sensation, inflammation, mood, and immune response. CBD influences cannabinoid receptors indirectly, leading to a range of potential therapeutic effects without the psychoactive impact associated with THC.
What is THC?
THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is a naturally occurring compound found in the cannabis plant. It is one of the most well-known cannabinoids and is primarily responsible for the psychoactive effects associated with marijuana use. When THC is consumed or inhaled, it binds to cannabinoid receptors in the brain and central nervous system, particularly the CB1 receptors. This interaction alters the release of neurotransmitters, resulting in various physiological and psychological effects. The most notable effect is the euphoric “high” commonly associated with marijuana, making THC a popular choice for both recreational and certain medical uses.
Psychoactive Properties and Effects
Substances like CBD and THC influence the body by binding with cannabinoid receptors, which are integral to the endocannabinoid system involved in regulating a host of physiological functions such as emotional state, sensation of pain, and immune response. Both elements possess potential healing properties. They vary markedly in their psychoactive effects.
THC is widely recognized for its capacity to induce an intoxicating high that is favored among users of recreational cannabis. This sensation stems chiefly from THC’s interaction with CB1 receptors in the brain, altering emotions and sensory experiences. In contrast, CBD lacks these intoxicating effects but provides numerous advantages without causing a euphoric state, offering a viable option for therapeutic use.
The differing psychoactive attributes between CBD and THC underscore their separate applications within medical treatment and leisurely consumption of cannabis products. Comprehending this distinction is critical for individuals contemplating the use of cannabis, whether it be for health-related relief or enjoyment.
Psychoactive vs. Non-Psychoactive
CBD and THC share identical molecular structures (21 carbon atoms, 30 hydrogen atoms, and 2 oxygen atoms), yet their effects on the human brain differ significantly.
THC acts as the primary psychotropic compound in cannabis, directly binding to CB1 receptors in the brain to produce euphoric effects and altered perception. This interaction triggers dopamine release, leading to the characteristic “high” associated with cannabis use.
While CBD is technically psychoactive – as evidenced by its documented effects on anxiety and FDA approval for epilepsy treatment – it does not produce intoxicating effects. Instead, CBD primarily interacts with serotonin receptors rather than CB1 receptors, influencing mood and pain regulation without causing cognitive or motor impairment. This crucial distinction makes CBD an attractive therapeutic option for those seeking medicinal benefits without THC’s mind-altering effects.
The interaction between these compounds becomes particularly interesting when used together. CBD can actually moderate THC’s psychoactive effects, potentially reducing negative effects like paranoia and anxiety. When present in higher ratios to THC, CBD promotes relaxation rather than euphoria. This modulating effect has led to growing interest in products with specific THC:CBD ratios for optimized therapeutic benefits.
Key Differences in Effects
CBD and THC exert diverse yet significant impacts on the human body and psyche. Known for its potent psychoactive effects, THC induces a state of euphoria along with perceptual alterations by activating CB1 receptors within the brain. This activation leads to variations in mood, cognitive functions, and sensory experiences.
In contrast, CBD is considered to be non-psychoactive as it does not create a high sensation. Its primary role lies in tempering the intoxicating effects of THC while fostering calmness and reducing anxiety without any euphoric outcome—thus positioning CBD as an appealing alternative for medical applications seeking cannabis’s therapeutic advantages without inducing a high.
This distinction between their influences highlights distinct uses for each compound: THC finds favor among those seeking recreational enjoyment or specific medicinal conditions that leverage its mind-altering attributes. Conversely, CBD caters to those needing relief from various ailments but with clear-headed sobriety.
Impact on Central Nervous System
THC engages with CB1 receptors in the brain, altering cognitive processes and emotional states. This interaction may dampen excitatory transmission and induce relaxation while possibly affecting cognitive abilities. When THC is inhaled, its concentration peaks rapidly in the blood, leading to swift effects.
In contrast, CBD’s effect on the central nervous system is more complex. Rodent research suggests that CBD could affect memory reconsolidation and motor control, hinting at possible uses for treating neurological disorders. Because of how it interacts with serotonin receptors, CBD could improve mood and alleviate anxiety – offering potential as a treatment option for different mental health issues.
The distinct influences of CBD and THC on the central nervous system underscore their individual therapeutic value. While THC has more noticeable immediate effects, CBD provides a gentler impact on neurologic functions but can be just as advantageous therapeutically.
Therapeutic Potential and Medical Uses

Investigations into the realm of cannabinoids have paved the way for cutting-edge therapeutic interventions applicable to an array of medical conditions. Both CBD and THC hold considerable potential in managing various ailments, including chronic pain and neurological diseases. This stems from their interaction with our endocannabinoid system, which governs assorted physiological processes.
CBD has emerged as particularly versatile, offering a broad spectrum of advantages such as mitigating pain, alleviating anxiety, reducing inflammation, and possessing anti-seizure qualities that render it instrumental in treating epilepsy.
Conversely, THC is acknowledged for its efficacy in boosting appetite and diminishing both discomfort and nausea—benefits that are especially appreciated by chemotherapy patients.
When used together, CBD and THC can amplify each other’s remedial impacts through what is known as the entourage effect. Their combined application may yield a more robust treatment response for issues like chronic pain or epilepsy.
CBD Benefits
CBD is widely recognized for its non-intoxicating effects and its diverse therapeutic potential. Research has demonstrated that CBD can effectively alleviate symptoms associated with anxiety, depression, and epilepsy. Notably, the FDA has endorsed CBD’s anti-seizure capabilities by approving it for use in certain types of treatment-resistant epilepsies.
Due to interactions with the central nervous system (CNS), CBD shows promise in improving memory function as well as motor skills, which may benefit individuals dealing with neurological disorders. Its abilities to reduce anxiety and combat psychosis Bolster its profile as a multifaceted candidate for medical therapy.
With an ability to mitigate inflammation and address pain management issues, CBD emerges as a compelling choice for those suffering from chronic pain or inflammatory conditions. The expansive scope of advantages tied to using CBD solidifies its status as a significant tool within the realm of therapeutics.
THC Therapeutic Applications
The therapeutic potential of THC is well-established, most notably for its effectiveness in enhancing appetite and reducing nausea, which is crucial for chemotherapy patients. Its pain-relieving qualities also make it an indispensable treatment choice for those suffering from chronic conditions that bring about substantial discomfort.
THC’s role extends to the management of cancer-related symptoms. By controlling vomiting and nausea linked with oncological therapies, it becomes a pivotal element in medical cannabis treatments designed to aid patients facing such distressing effects.
Highlighting its considerable therapeutic potential, THC stands out as a key medicinal agent, serving essential functions in alleviating pain, stimulating hunger, and managing chemotherapy-induced nausea. THC has also shown promise in improving sleep quality and reducing nightmares in individuals with post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Combined Use: The Entourage Effect
Utilizing CBD and THC together, a phenomenon often called the entourage effect, may amplify the efficacy of treatment for certain health issues. The collaborative effect between these cannabinoids contributes to an enhanced spectrum of medical benefits, especially in treating conditions such as chronic pain or epilepsy.
The presence of CBD has been shown to counteract some undesirable effects associated with THC use, like anxiety and paranoia. This harmonization allows patients to experience the therapeutic qualities of THC while minimizing its potential adverse reactions.
For optimal medicinal impact, it’s essential to determine the correct proportion of THC and CBD. The endocannabinoid system is integral in managing various physiological processes. Identifying an effective ratio can markedly improve therapeutic effectiveness.
Medical Marijuana and CBD vs THC
Medical marijuana refers to the use of cannabis or its constituents, such as THC and CBD, for therapeutic purposes under the guidance of healthcare professionals. The use of medical marijuana is often regulated by local laws and requires a recommendation or prescription from a healthcare professional. Both THC and CBD have shown promise in alleviating symptoms associated with various medical conditions. THC is particularly effective in reducing pain, stimulating appetite, and controlling nausea, making it beneficial for patients undergoing chemotherapy. CBD, on the other hand, is known for its anti-inflammatory, anti-anxiety, and anti-seizure properties, making it a versatile option for treating conditions like chronic pain, epilepsy, and anxiety disorders. The combined use of both THC and CBD can enhance their therapeutic effects, providing a comprehensive approach to symptom management.
Legality and Regulation
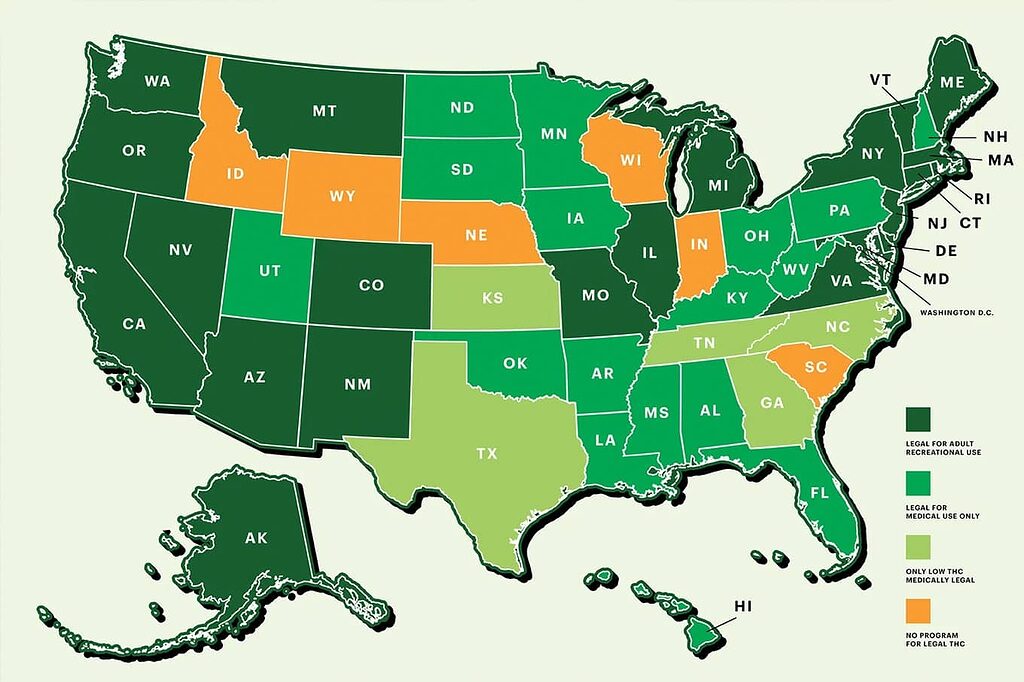
Navigating the intricate legalities of CBD and THC can be perplexing, with notable differences from one region to another. The acknowledged medicinal benefits of medical marijuana contrast sharply with the varying laws that govern the availability and consumption of these substances.
The passage of the 2018 Farm Bill in the United States marked a significant milestone by sanctioning industrial hemp cultivation, thereby permitting commerce in hemp-derived CBD products as long as they maintain a THC concentration below 0.3%. Nevertheless, complications arise because FDA designates CBD as a pharmaceutical drug, which complicates its potential sale marketed as a dietary supplement—posing predicaments for both consumers and producers within this realm.
On another front, under U.S. regulations, THC remains listed as a Schedule I controlled substance due to presumed high abuse risk along with lack of recognized therapeutic use—a designation that starkly constrains any lawful application especially related to recreational endeavors. Grasping these complexities is crucial for those contemplating engagement with cannabis-related items.
Legal Status of CBD
The legality of CBD hinges on its level of THC, with the 2018 Farm Bill in the United States allowing hemp-derived CBD products to be legal if they contain 0.3% or less THC. Yet, despite this threshold, the FDA still classifies CBD as a drug and not a dietary supplement.
In an indicator of growing recognition for its therapeutic promise, by 2024 hemp-derived medical cannabis has been sanctioned in 47 states within the U.S.
CBD is legally permitted throughout the EU when derived from Cannabis sativa L. plants containing no more than 0.2% THC. This status was solidified by the Court of Justice of the European Union’s pivotal 2020 ruling, which definitively established that CBD is not a narcotic substance and affirmed the free movement of legal CBD products between member states.
For both consumers and manufacturers, navigating this space is vital – it ensures adherence to various state medical cannabis laws while optimizing access to cbd products’ therapeutic potential.
International Legal Framework for THC Control
The global regulation of THC operates within a complex system of international treaties and conventions that shape national policies worldwide.
Core International Treaties
The international control of THC is primarily governed by three United Nations conventions:
- The 1961 Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs
- The 1971 Convention on Psychotropic Substances
- The 1988 Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs
UN Classification
Cannabis and THC maintain distinct classifications under international law. Cannabis is controlled under the 1961 Convention, while THC specifically falls under the 1971 Convention’s purview. Following a landmark 2020 decision, cannabis was removed from Schedule IV of the 1961 Convention, acknowledging its potential therapeutic benefits.
Across Europe, approaches to THC regulation vary significantly:
- Malta has established the EU’s most progressive framework, allowing personal possession
- Germany is advancing toward regulated legalization
- The Netherlands maintains its established tolerance policy
- Several countries, including Hungary and Sweden, maintain strict prohibitions
Regulatory Bodies
- The Commission on Narcotic Drugs (CND) guides global policy
- The International Narcotics Control Board (INCB) monitors treaty implementation
- The World Health Organization (WHO) provides scientific assessment and scheduling recommendations
Side Effects and Risks of THC and CBD

CBD and THC, while known for their therapeutic properties, also come with potential side effects and dangers. These substances can interfere with other medications a person might be taking as well as various physiological processes in the body, sometimes resulting in unfavorable reactions.
Most individuals tolerate CBD quite well. It can cause some mild adverse effects including dry mouth, diarrhea, reduced appetite, drowsiness, and fatigue. Despite this acceptable safety profile in many users’ experience, more comprehensive research is imperative to understand fully what implications long-term usage of CBD may have on adolescents.
Contrastingly, THC presents considerably greater risks, particularly when used by adolescents over an extended period. Persistent utilization of THC has been linked to disruptions in brain development, which could potentially foster addictive behaviors and engender mental health concerns such as anxiety disorders, cognitive dysfunction, or even psychosis.
Adverse Effects of CBD
CBD is often well received, but some individuals may encounter minor digestive issues such as a dry mouth or diarrhea. Additional typical side effects include alterations in appetite and feelings of tiredness. While these adverse reactions are usually brief and not severe, it remains crucial to be vigilant for any symptoms that could stem from sustained use.
The comprehensive repercussions of long-term CBD usage remain elusive, necessitating Investigation into its enduring safety profile. This need for clarity becomes even more significant regarding teenagers since the consequences of continuous CBD exposure during vital growth periods have yet to be fully understood.
Before embarking on a regimen involving CBD treatment, it’s imperative to seek guidance from medical professionals with an aim to ensure its safe and efficacious application while paying close attention to possible drug interactions.
Risks Associated with THC
The use of THC carries substantial hazards, especially for young individuals and those with pre-existing mental health conditions. Prolonged consumption can hinder the maturation of the brain, which may result in cognitive deficiencies, memory issues, and a heightened likelihood of developing anxiety disorders or psychosis.
Young people are particularly susceptible to THC’s detrimental impacts. Research indicates that early use can precipitate drug addiction as well as persistent mental health challenges. The continuous intake of high doses of THC is linked to neurotoxicity and neuroinflammation, thereby elevating the danger associated with addiction and cognitive dysfunction.
It’s imperative for potential users to comprehend these dangers when considering using THC either medicinally or recreationally. Engaging in discussions with medical professionals and strictly adhering to legal protocols can aid in reducing these risks and promote responsible utilization.
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
Understanding the body’s interaction with CBD and THC requires an in-depth look at their pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. This includes examining how they are absorbed, distributed throughout the body, metabolized, and eventually excreted—a process which determines both their potential therapeutic effects and safety profiles.
In terms of metabolism, CBD is chiefly broken down by liver enzymes belonging to the cytochrome P450 system into hydroxylated forms. These metabolites are then predominantly eliminated through defecation. The metabolic pathway for THC mirrors this somewhat. It is processed into 11-OH-THC by the enzyme CYP2C9 within that same P450 system with assistance from fatty acid binding proteins (FABP).
How cannabinoids like CBD and THC are administered—whether smoked or vaporized (inhalation), ingested orally, or applied topically—has a substantial impact on bioavailability as well as their resultant health benefits. Gaining insight into these mechanisms plays a vital role in enhancing the medicinal applications of both substances.
Absorption and Metabolism of CBD
The efficacy of CBD absorption, or bioavailability, is greatly affected by the chosen method of intake. Inhalation provides a notably higher bioavailability that ranges from 11% to 45%, compared to oral ingestion which has a lower efficiency at around only 6%. The substantial reduction in orally consumed CBD’s effectiveness can be attributed to its processing via first-pass metabolism within the liver, diminishing the amount that actually enters into systemic circulation.
In terms of metabolic processing, CBD is transformed into hydroxylated compounds once it passes through the liver. This process primarily involves cytochrome P450 enzymes. Following this conversion, these metabolites are predominantly disposed of through fecal elimination. The onset and duration of CBD’s effects can be influenced by various modes of delivery such as vaping products, edible items or tincture oils.
Selecting an optimal administration route for CBD plays an integral role in realizing desired therapeutic benefits. To identify which method aligns best with specific health requirements, individuals should seek advice from medical experts.
THC Pharmacokinetics
The process of THC pharmacokinetics encompasses the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination of the compound. The act of smoking THC is a widely used method for consuming cannabis due to its quick effect delivery, with peak blood levels typically achieved within minutes following inhalation. This expeditious effect onset contributes to its popularity among those using cannabis for both therapeutic purposes and recreational enjoyment.
Upon entering the body’s system, THC undergoes metabolic transformation in the liver into 11-OH-THC via enzyme CYP2C9 activity while leveraging fatty acid binding proteins (FABP). Subsequently, these metabolites are expelled from the body via urine and fecal matter. Compared to inhalation, ingesting THC orally induces effects more gradually with maximum concentrations apparent between one and three hours post-consumption.
Gaining insight into how THC operates pharmaceutically is crucial when looking at enhancing its medicinal benefits while reducing any adverse reactions that may arise. Seeking advice from medical professionals can be beneficial in choosing an apt route of administration as well as appropriate dosing considerations.
Practical Considerations for Use
When contemplating the utilization of CBD and THC, recognizing the key factors in selecting appropriate products and guaranteeing their safe use is crucial. The pharmacokinetics, which include how these substances are absorbed and ultimately made available to the body, differ based on how they’re administered.
The preference for inhalation methods has been highlighted by a 150% increase in market share for THC extracts within Washington State from 2014 to 2016. This points towards an increased consumer inclination towards this form of consumption. Various cannabis product types including edibles, tinctures, and concentrates offer users differing timescales for onset of effects as well as varying durations.
For optimal safety and efficacy when using cannabis products, it’s essential to seek advice from medical professionals regarding possible drug interactions.
Choosing the Right Cannabis Products
Navigating the selection of an appropriate cannabis product requires careful examination of factors like the THC/CBD balance, your preferred method of intake, and seeking advice from medical experts. The spectrum of THC products encompasses a variety including but not limited to dried blossoms, oils, edible forms, and concentrated extracts. Each with distinct timelines for onset and duration.
CBD is a THC-free substance. Alchemy presents an extensive assortment of CBD offerings such as blooms, oil variants, resinous hashishes, beauty care items, and full-spectrum CBD oils available in different strengths. Determining the ideal choice hinges on personal health goals and tastes along with consideration for any specific medical issues that are being addressed.
To ensure therapeutic objectives are met when utilizing various cannabis derivatives, it’s crucial to comprehend their unique properties and impacts. Engaging with healthcare providers can aid in pinpointing which options will be most beneficial tailored to individual needs.
Drug Interactions and Safety
It’s crucial to engage with healthcare providers before initiating the use of cannabis products, particularly if you’re concurrently administering other medications. This is due to the possibility that CBD may interfere with CYP450 enzymes, which could influence how different drugs are metabolized, especially blood thinners such as warfarin. Alterations in drug metabolism might lead to the need for adjusting dosages.
Accurate labeling on CBD products also raises issues since some items have been found to contain lower levels of CBD than what’s stated. To guarantee both safety and effectiveness when using these products, it’s important to be cognizant of potential drug interactions and adhere strictly to suggested dosages.
By grasping these safety considerations and seeking advice from healthcare experts, one can minimize hazards associated with cannabis product usage while ensuring their safe consumption.
Latest Research Developments

Ongoing investigations into CBD and THC are revealing their possible healing properties and uses. Research has indicated encouraging outcomes in terms of enhancing immune function, quality of sleep, and overall health indicators, drawing increasing attention to the medicinal possibilities offered by these cannabinoids.
CBD’s potential advantages include amelioration of sleep quality, which may be exceptionally beneficial for people suffering from sleeping disorders. There is evidence suggesting that CBD can have a positive effect on immune system functionality, thereby adding to its allure as a therapeutic agent.
To completely comprehend the impact of CBD and THC and verify their effectiveness for various medical purposes, additional research along with clinical studies is crucial. Studies underway persistently probe the capabilities inherent in these cannabinoids with prospects for innovative treatments and therapeutic interventions.
Scientific References
Academic studies serve as the cornerstone for understanding both the impacts and possible uses of CBD and THC. These investigations indicate that these cannabinoids interact with the endocannabinoid system, which has an influence on a range of physiological processes.
Through different molecular pathways, cannabidiol (CBD) has demonstrated an array of therapeutic benefits by influencing inflammation, pain sensation, and oxidative stress. The modulation of CB1 and CB2 receptors is integral to these effects. Such receptors are critical in managing pain perception and inflammatory responses.
On the other hand, Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) predominantly targets CB1 receptors located in the brain. This interaction accounts for its psychoactive outcomes while also offering therapeutic promise for conditions like chronic discomfort and nausea. Grasping these molecular interactions is vital in enhancing how we leverage CBD and THC therapeutically.
Molecular Mechanisms
THC and CBD interact with the body’s cannabinoid receptors, CB1 and CB2, which are found throughout the brain and various tissues. THC has a high affinity for CB1 receptors located in areas of the brain governing memory, coordination, and emotions—this association triggers THC’s psychoactive effects.
Conversely, CBD primarily targets CB2 receptors situated within the immune system. These play a significant role in managing inflammation and pain. Consequently, this mechanism underscores CBD’s capability to potentially alleviate ailments such as chronic pain through its therapeutic properties.
Both THC and CBD also have an impact on several other receptor types like serotonin and TRP channels. This suggests that their influence goes beyond interacting solely with cannabinoid receptors. Such multifaceted interactions are part of what contributes to their extensive array of possible medicinal benefits.
Clinical Applications
Research in clinical settings has revealed that cannabinoids are effective for treating a range of health issues. Notably, CBD is promising in the reduction of anxiety symptoms and the management of some neurological conditions. It stands out as an alternative treatment option with its ability to mitigate nausea and vomiting induced by chemotherapy when standard treatments do not suffice.
In cases involving chronic pain, patient testimonials frequently reflect substantial relief following cannabinoid use, which subsequently decreases their dependence on opioid medications. Short-term application of cannabinoids has been proven to lessen spasticity-related symptoms among individuals diagnosed with multiple sclerosis.
Investigations into cannabinoids have shown they could potentially stimulate appetite in patients grappling with HIV/AIDS-induced anorexia, presenting a significant therapeutic avenue. The breadth of these clinical uses emphasizes the potential value CBD and THC hold across diverse medical scenarios.
Safety & Clinical Trials
The safety considerations of CBD and THC play a vital role in their medical applications. Adverse reactions linked to CBD are usually minor, often involving digestive discomfort and tiredness as the most frequent complaints. It is observed that both THC and CBD can lead to unwanted effects. Certain reports suggest that CBD may alleviate some of the detrimental psychiatric impacts associated with THC.
Studies focusing on individuals experiencing persistent cancer-related pain have demonstrated that a synergistic mix of both THC and CBD provides more substantial pain relief than the use of just THC alone without an increase in adverse side effects. These results endorse the advantage of combining these cannabinoids to bolster therapeutic efficacy.
To truly comprehend the safety profiles along with the therapeutic potential possessed by both THC and CBD, continuing investigations coupled with additional clinical trials remain crucial. The insights gleaned from such studies will aid in refining dosing guidelines while pinpointing any possible hazards, thereby facilitating secure yet efficacious medicinal application.
Therapeutic Applications
Compounds such as CBD and THC have been recognized for their potential in managing a spectrum of medical issues, ranging from cancer to neurodegenerative and inflammatory diseases. The combination drug Nabiximols, which includes both THC and CBD, has shown efficacy in reducing pain and muscle stiffness, particularly associated with multiple sclerosis.
Two other drugs that the FDA has approved — Dronabinol and nabilone — are effective against nausea caused by chemotherapy treatments. They also help stimulate appetite in patients suffering from AIDS-related anorexia. Research is currently exploring how CBD might play a role in lessening oxidative stress and neural inflammation observed in Alzheimer’s disease cases.
In individuals with Parkinson’s disease, cannabinoid-based treatments have yielded positive outcomes by improving motor functions while diminishing dyskinesia symptoms related to therapy sessions. These findings underscore the significant therapeutic capabilities of cannabinoids like CBD and THC across diverse health conditions.
Summary
To summarize, the two primary compounds of interest in the cannabis plant, CBD and THC, provide distinct yet synergistic health benefits. CBD is prized for its lack of psychoactive properties and a broad spectrum of potential medical uses while THC is known for inducing psychoactive effects that can be therapeutically beneficial—offering pain relief and helping to stimulate appetite.
It’s essential to grasp how CBD and THC differ regarding their effect on the central nervous system, their therapeutic capabilities, as well as where they stand legally. This knowledge aids in educated decision-making about utilizing these cannabinoids. Their combined usage leads to what’s referred to as ‘the entourage effect,’ which may amplify healing outcomes by offering a wider array of advantages.
Ongoing research into cannabinoids paves the way towards groundbreaking treatments exploiting these intriguing molecules’ complete capacities. For those seeking wellness improvements through either medical or recreational avenues, both CBD and THC present optimistic opportunities for enhancing overall quality of life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cannabis plant is a complex species that contains over 100 different compounds known as cannabinoids. THC and CBD are the two most well-known cannabinoids, with THC being the primary psychoactive compound and CBD being a non-psychoactive compound with potential therapeutic applications. Understanding the differences between THC and CBD is crucial for making informed decisions about the use of medical cannabis. By consulting with healthcare professionals and following state medical cannabis laws, individuals can safely and effectively use medical cannabis to alleviate symptoms associated with various medical conditions. The ongoing research into cannabinoids continues to uncover new therapeutic potentials, paving the way for innovative treatments and improved quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the legal status of CBD in the United States?
The legal status of CBD in the United States is complex; while the 2018 Farm Bill legalized industrial hemp, the FDA classifies CBD as a pharmaceutical drug, prohibiting its sale as a dietary supplement.
Therefore, caution is advised when considering the use of CBD products.
Do patients benefit from CBD-only laws?
Patients do not significantly benefit from CBD-only laws, as they require access to a wider range of whole plant cannabis remedies for optimal treatment.
What types of CBD products does CBD Alchemy offer?
CBD stands for CBD. Alchemy offers a diverse selection of products, including CBD flowers, oils, and cosmetics.
It’s an excellent choice for those seeking various CBD options.
What are some benefits of using CBD?
The employment of CBD has been shown to offer considerable advantages, including alleviating pain, diminishing anxiety levels, and enhancing the quality of sleep.
Such benefits underscore its potential utility as an essential supplement for wellness.
How do CBD and THC work together?
Through a phenomenon known as the entourage effect, CBD and THC enhance each other’s therapeutic benefits by working together synergistically.
This partnership potentially results in better treatment outcomes for a range of health conditions.
Scientific References
Molecular Mechanisms
Stella N. “THC and CBD: Similarities and differences between siblings.” Neuropsychopharmacology (2023) – Comprehensive molecular analysis of THC and CBD interactions with the endocannabinoid system – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9898277/
Clinical Applications
Boggs DL, et al. “CBD and THC: Do They Complement Each Other Like Yin and Yang?” Pharmacotherapy (2020) – Analysis of synergistic effects between CBD and THC in clinical settings. <a href="https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33080058/">https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33080058/https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33080058/
Safety & Clinical Trials
Freeman AM, et al. “Evidence for THC versus CBD in cannabinoids.” Canadian Family Physician (2019)
Systematic review of clinical trials comparing THC and CBD efficacy. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6042662/
Therapeutic Applications
Chesney E, et al. “Cannabidiol Drugs Clinical Trial Outcomes and Adverse Effects.” Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research (2020)
Comprehensive review of CBD clinical trials and safety profiles.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7053164/