- What is CBD and How Does It Work for Pain?
- Types of Pain Addressed by CBD
- Medical Research and Clinical Trials on CBD for Pain
- Legal and Regulatory Considerations for CBD Use
- CBD in Pain Management Practices
- Associated Medical Conditions and CBD Treatment
- Future Directions in CBD Research and Pain Management
- Conclusion
- People Also Ask:
- Frequently Asked Questions on CBD and Pain

In recent years, CBD has emerged as a potential game-changer in the world of pain management. As chronic pain affects millions of Americans, many are turning to this natural compound derived from the cannabis plant for relief. This comprehensive guide explores the relationship between CBD and pain, diving into the science, a≥plications, and considerations for those seeking alternative pain management solutions.
What is CBD and How Does It Work for Pain?
Cannabidiol, commonly known as CBD, is a non-psychoactive compound found in cannabis plants. Unlike its cousin THC, CBD doesn’t produce a “high” but has gained attention for its potential therapeutic properties, particularly in pain management.
Definition and Origin of CBD
CBD is one of over 100 cannabinoids found in the Cannabis sativa plant. It’s typically extracted from hemp, a variety of cannabis with low THC content. CBD interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system, which plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes, including pain sensation.
The Endocannabinoid System and Pain Perception
The endocannabinoid system consists of receptors throughout the body that respond to cannabinoids, both those produced naturally by the body (endocannabinoids) and those from external sources like CBD. This system helps regulate pain, mood, appetite, and other functions. CBD is thought to modulate pain by influencing endocannabinoid receptor activity, reducing inflammation, and interacting with neurotransmitters.
CBD vs. THC: Key Differences in Pain Management

While both CBD and THC have potential pain-relieving properties, their mechanisms and effects differ:
- CBD is non-psychoactive and doesn’t produce a “high”
- THC is psychoactive and can alter perception and mood
- CBD may have fewer side effects compared to THC
- Some studies suggest CBD may be more effective for certain types of pain, while THC may be better for others
Types of Pain Addressed by CBD
CBD has shown promise in addressing various types of pain, from chronic conditions to acute injuries. Additionally, CBD’s potential in managing cancer pain, especially when traditional opioid therapies are inadequate, has been noted.
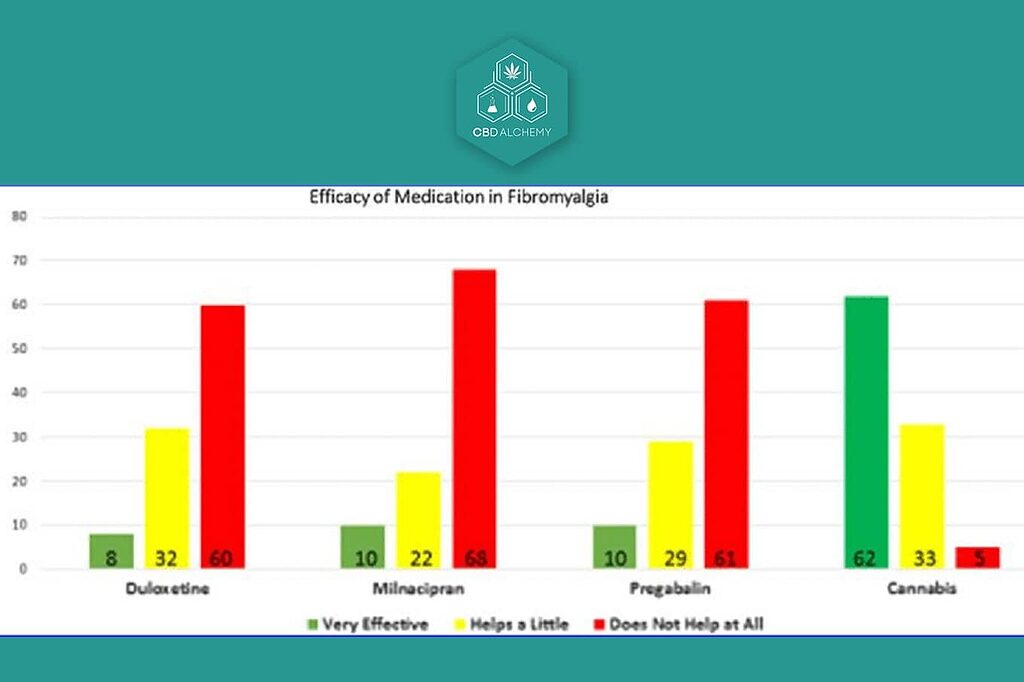
Chronic Pain Conditions and CBD Efficacy

Chronic pain management, defined as pain lasting more than 12 weeks, affects an estimated 50 million U.S. adults. Studies have suggested that CBD may be effective in managing chronic pain conditions such as:
- Fibromyalgia
- Osteoarthritis
- Lower back pain
- Migraines
A 2018 review published in the Journal of Pain Research found that CBD was effective in overall pain management without adverse side effects.
Neuropathic Pain and CBD Treatment
Chronic neuropathic pain, caused by damage to the nervous system, can be particularly challenging to treat. CBD has shown potential in managing chronic neuropathic pain by:
- Reducing inflammation in neural tissues
- Modulating pain signaling pathways
- Providing antioxidant effects that may protect nerve cells
A 2020 study in the journal Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology reported that CBD could significantly reduce neuropathic pain in patients with multiple sclerosis.
Arthritis Pain Management with CBD
Arthritis, affecting over 54 million Americans, is another area where CBD shows promise. The Arthritis Foundation has acknowledged the potential of CBD in managing arthritis pain and has called for more research in this area. CBD may help with arthritis pain by:
- Reducing inflammation in joints
- Decreasing pain sensitivity
- Improving sleep quality, which can indirectly affect pain perception
Medical Research and Clinical Trials on CBD for Pain
The scientific community has been increasingly interested in CBD’s potential for pain management, leading to a growing body of research.
Overview of Current Scientific Studies
Recent years have seen a surge in CBD studies, with many focusing on its pain-relieving properties. Key areas of research include:
- CBD’s effect on chronic pain conditions
- Comparison of CBD efficacy to traditional pain medications
- Long-term safety and efficacy of CBD use
- The role of medical cannabis in pain management research1
Efficacy and Safety Findings
While research is still ongoing, several studies have reported positive findings:
- A 2019 study in the journal Pain found that CBD could help alleviate pain and improve quality of life in patients with neuropathic pain.
- A 2020 review in Frontiers in Pharmacology concluded that CBD has potential as an analgesic and anti-inflammatory agent.
Regarding safety, a comprehensive review by the World Health Organization found that CBD is generally well-tolerated with a good safety profile. Additionally, medical marijuana faces regulatory challenges but shows potential therapeutic benefits for chronic pain management.
Limitations and Future Research Needs
Despite promising results, more research is needed to fully understand CBD’s role in pain management. Current limitations include:
- Small sample sizes in many studies
- Lack of long-term data on CBD use
- Variability in CBD products and dosages used in studies
Future research should focus on larger, long-term clinical trials and standardization of CBD formulations for medical use.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations for CBD Use
The legal landscape for CBD in the United States is complex and evolving.
CBD Legality in the United States
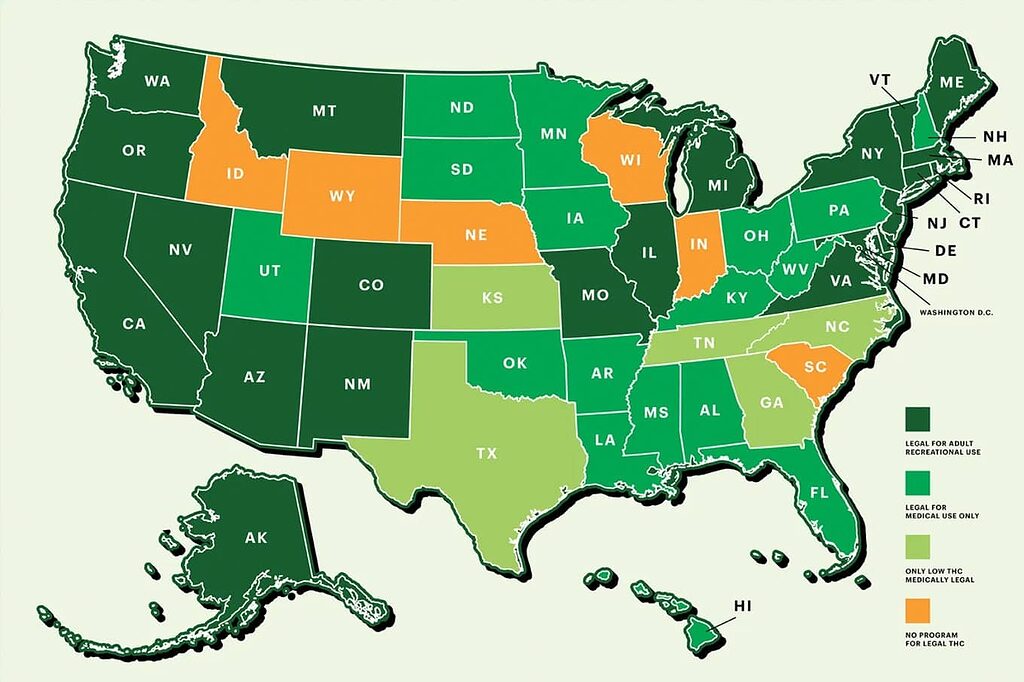
At the federal level, CBD derived from hemp (containing less than 0.3% THC) was legalized under the 2018 Farm Bill. However, CBD derived from marijuana remains federally illegal.
FDA Guidelines on CBD Products
The FDA has approved one CBD-based drug, Epidiolex, for certain types of epilepsy. However, the FDA has not approved CBD for pain management and maintains that it’s illegal to market CBD as a dietary supplement or add it to food products.
State vs. Federal Regulations
While hemp-derived CBD is federally legal, state laws vary:
- Some states have fully legalized CBD
- Others have restrictions on CBD use
- A few states still prohibit CBD entirely
Consumers should check their local laws before purchasing or using CBD products.
CBD in Pain Management Practices
Incorporating CBD into pain management requires understanding different product types and usage methods. CBD oil, in particular, has shown potential health benefits in reducing inflammation, alleviating pain, and treating symptoms related to conditions like arthritis and multiple sclerosis.
Forms of CBD for Pain Relief
CBD is available in various forms, each with its own advantages:
- CBD Oils and Tinctures
- Fast-acting when taken sublingually
- Easy to adjust dosage
- Topical CBD Products
- Creams, lotions, and balms for localized pain relief
- May be effective for arthritis and muscle pain
- CBD Edibles
- Convenient and discreet
- Longer-lasting effects but slower onset
- CBD Capsules
- Precise dosing
- Easy to incorporate into daily routines
Dosage Recommendations and Administration
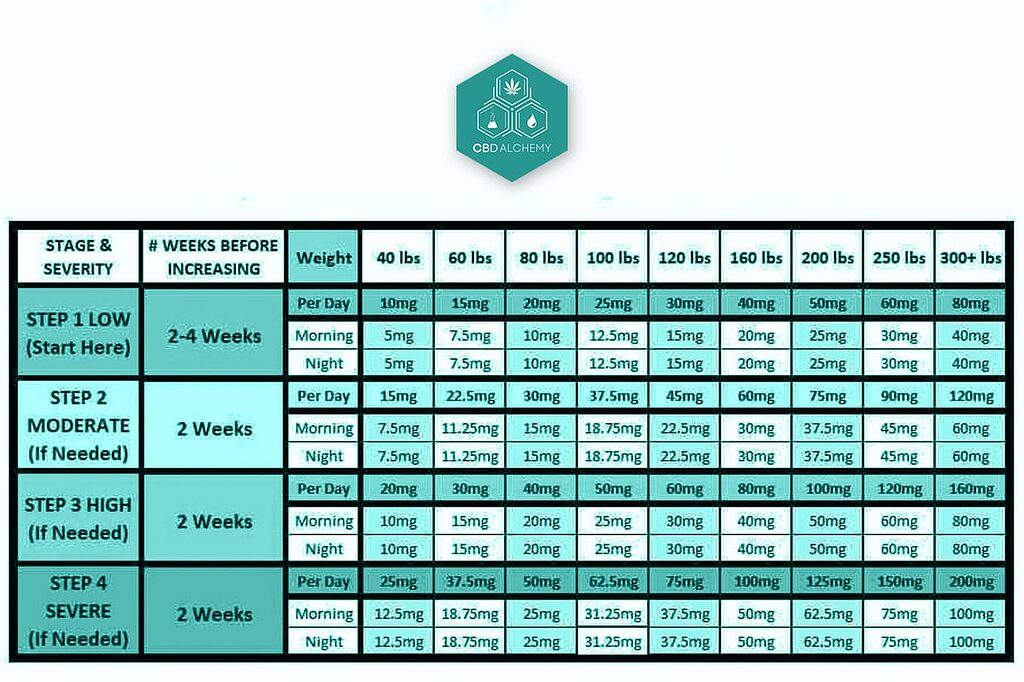
CBD dosage can vary widely depending on factors such as:
- Individual body chemistry
- The severity of pain
- The concentration of CBD in the product
General recommendations suggest starting with a low dose (5-10 mg) and gradually increasing until the desired effect is achieved. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before starting CBD, especially for those on other medications.
Potential Side Effects and Drug Interactions
While CBD is generally well-tolerated, some potential side effects include:
- Fatigue
- Changes in appetite
- Diarrhea
- Dry mouth
CBD can interact with certain medications, particularly those metabolized by the liver. It’s essential to discuss CBD use with a healthcare provider, especially if taking other medications.
Associated Medical Conditions and CBD Treatment
Beyond general pain management, CBD has shown potential to treat pain associated with specific medical conditions.
CBD for Fibromyalgia and Multiple Sclerosis
Fibromyalgia and multiple sclerosis are chronic conditions often accompanied by persistent pain. Some studies suggest that CBD may help manage pain in these conditions:
- A 2019 study in the Journal of Clinical Medicine found that CBD improved pain and sleep quality in fibromyalgia patients.
- Research published in Frontiers in Neurology in 2018 indicated that CBD could reduce fatigue, pain, and spasticity in multiple sclerosis patients.
Epilepsy and Seizure Disorders
The FDA-approved CBD drug Epidiolex has shown effectiveness in reducing seizures in certain forms of epilepsy. This success has led to increased interest in CBD’s potential for other neurological disorders.
Anxiety and Depression in Chronic Pain Patients
Chronic pain often coexists with anxiety and depression. CBD’s potential anxiolytic and antidepressant properties may offer additional benefits for pain patients:
- A 2019 study in the Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy found that CBD exhibited anxiolytic-like effects in several studies.
- Research published in CNS & Neurological Disorders – Drug Targets in 2014 suggested CBD’s potential as an antidepressant.
Future Directions in CBD Research and Pain Management
The field of CBD research is rapidly evolving, with exciting developments on the horizon.
Emerging Trends in CBD Studies
Current research trends include:
- Investigating the entourage effect of full-spectrum CBD products
- Exploring CBD’s potential in reducing opioid use for pain management
- Studying the long-term effects of CBD use
Potential for Personalized CBD Treatments
As our understanding of CBD grows, there’s potential for developing personalized treatment plans based on:
- Individual genetic profiles
- Specific pain conditions
- Interaction with other medications
Integrating CBD into Comprehensive Pain Management Plans
Future pain management strategies may increasingly incorporate CBD as part of a holistic approach, combining it with:
- Traditional pain medications
- Physical therapy
- Lifestyle modifications
- Other alternative therapies
Conclusion
CBD represents a promising frontier in pain management, offering potential relief for millions suffering from chronic pain conditions. While research is still ongoing, early studies and anecdotal evidence suggest that CBD may be a valuable tool in the pain management toolkit. As with any treatment, it’s crucial to approach CBD use thoughtfully, consulting with healthcare professionals and staying informed about the latest research and regulations.
As the field of CBD research continues to evolve, we can expect more refined understanding of its mechanisms, optimal dosages, and specific applications for various pain conditions. For those considering CBD for pain management, it’s essential to approach it as part of a comprehensive treatment plan, always under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
The future of CBD in pain management looks promising, but it’s important to maintain a balanced perspective.
People Also Ask:
Is CBD effective for chronic pain?
CBD has shown promise in managing chronic pain, with studies indicating potential benefits for conditions like arthritis, fibromyalgia, and neuropathic pain. However, more research is needed to fully establish its efficacy.
How long does it take for CBD to work for pain?
The onset of CBD’s effects can vary depending on the method of administration. Sublingual oils may take effect within 15-45 minutes, while edibles can take 1-2 hours. Topical applications may provide relief within 15-20 minutes.
What are the side effects of using CBD for pain?
Common side effects of CBD include fatigue, changes in appetite, diarrhea, and dry mouth. These are generally mild, but it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting CBD, especially if you’re taking other medications.
Can CBD interact with other pain medications?
Yes, CBD can interact with certain medications, particularly those metabolized by the liver’s cytochrome P450 enzyme system. It’s crucial to discuss CBD use with your doctor if you’re taking any other medications.
Is CBD legal for pain management in all states?
While hemp-derived CBD (containing less than 0.3% THC) is federally legal in the US, state laws vary. Some states have fully legalized CBD, others have restrictions, and a few still prohibit it. Always check local laws before purchasing or using CBD products.
Frequently Asked Questions on CBD and Pain
1. What is CBD and how does it help with pain?
CBD, or cannabidiol, is a non-psychoactive compound found in cannabis plants, particularly hemp. It interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system, which plays a role in regulating pain perception. CBD may help alleviate pain by influencing endocannabinoid receptor activity, reducing inflammation, and modulating neurotransmitter release, thus providing pain relief without the “high” associated with THC.
2. Is CBD oil effective for pain relief?
Yes, CBD oil has shown promise in providing pain relief for various conditions. Studies suggest that CBD oil can be effective in managing chronic pain, neuropathic pain, and arthritis pain by reducing inflammation and interacting with neurotransmitters involved in pain signaling. However, individual responses may vary, and more research is needed to fully understand its efficacy.
3. Can CBD help with chronic pain management?
CBD may be beneficial for chronic pain management. Research indicates that CBD can reduce chronic pain by impacting endocannabinoid receptor activity and decreasing inflammation. Conditions like fibromyalgia, lower back pain, and chronic neuropathic pain have been areas where CBD showed potential benefits in clinical studies.
4. How does CBD compare to traditional pain medications?
CBD offers a natural alternative to traditional pain medications like opioids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Unlike opioids, CBD is not addictive and has a favorable safety profile. While traditional medications target pain symptoms, CBD may address underlying inflammation and modulate pain perception. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional before replacing any prescribed medications with CBD.
5. Are there clinical trials supporting the use of CBD for pain?
Yes, several clinical trials and systematic reviews have investigated CBD’s effectiveness for pain relief. Studies published in reputable journals have found that CBD can significantly reduce pain and improve quality of life in patients with conditions like multiple sclerosis and neuropathic pain. However, more large-scale clinical trials are needed to establish standardized dosing and long-term safety.
6. Is CBD legal for pain management in all states?
The legality of CBD varies by state in the U.S. Federally, hemp-derived CBD products containing less than 0.3% THC are legal under the 2018 Farm Bill. However, some states have stricter regulations, and others have fully legalized or restricted CBD use. It’s essential to check your state’s laws and regulations before purchasing or using CBD products.
7. What are the potential side effects of using CBD for pain?
CBD is generally well-tolerated, but some users may experience side effects such as fatigue, dry mouth, diarrhea, changes in appetite, or drowsiness. CBD can also interact with certain medications, so it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before starting CBD, especially if you’re taking other drugs.
8. Can CBD be used for neuropathic pain?
CBD has shown potential in managing neuropathic pain, which is caused by nerve damage. Studies suggest that CBD may alleviate neuropathic pain by reducing inflammation and modulating pain signaling pathways. Patients with conditions like multiple sclerosis and diabetes-induced neuropathy may find relief with CBD use.
9. How does CBD help with arthritis pain?
CBD may help reduce arthritis pain by targeting inflammation in the joints and affecting pain receptors. Topical CBD products like creams and balms can be applied directly to affected areas for localized relief. Some studies have found that CBD use led to significant improvements in pain and physical function among arthritis patients.
10. Should I consult a health professional before using CBD for pain?
Yes, it’s highly recommended to consult a healthcare professional before starting CBD for pain management. A doctor can provide personalized advice, consider potential drug interactions, and help determine an appropriate dosage based on your specific condition and overall health.
11. Is there a difference between CBD oil and other CBD products for pain relief?
Different CBD products offer various methods of administration and absorption rates:
- CBD Oils and Tinctures: Taken sublingually for faster absorption.
- Topical CBD Products: Applied directly to the skin for localized pain relief.
- CBD Edibles and Capsules: Ingested orally, providing longer-lasting effects but slower onset.
The choice depends on personal preference, the type of pain, and desired onset time.
12. How does CBD interact with the body’s pain receptors?
CBD interacts indirectly with CB1 and CB2 receptors in the endocannabinoid system. Instead of binding directly, it influences these receptors to modulate pain signals and reduce inflammation. This interaction can alter pain perception and provide relief without psychoactive effects.
13. Can CBD help with cancer-related pain?
Some studies suggest that CBD may help alleviate pain associated with cancer and cancer treatments. CBD’s anti-inflammatory properties and ability to modulate pain signals can contribute to pain reduction. However, it’s essential to consult with an oncologist before incorporating CBD into cancer pain management.
14. What does the World Health Organization say about CBD?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has stated that CBD is generally well-tolerated with a good safety profile. They also noted that CBD exhibits no effects indicative of any abuse or dependence potential and that there is no evidence of public health-related problems associated with pure CBD use.
15. Are there any long-term effects of using CBD for pain management?
Long-term effects of CBD use are still under investigation. Current research indicates that CBD is safe for long-term use in adults. However, more extensive studies are needed to fully understand any potential long-term risks or benefits. Regular consultation with a healthcare provider is advisable when using CBD over an extended period.
16. How does CBD affect inflammation and neuropathic pain?
CBD has anti-inflammatory properties that can reduce inflammation contributing to pain. In neuropathic pain, CBD may inhibit inflammatory responses in neural tissues and modulate pain signaling pathways, potentially providing relief from nerve-related pain.
17. Is more research needed on CBD and pain management?
Yes, while current studies are promising, more comprehensive research is needed. Future studies should focus on standardized dosing, long-term safety, efficacy across different populations, and comparisons with existing pain management therapies to fully establish CBD’s role in pain management.
18. Can CBD help with sleep disorders related to chronic pain?
CBD may improve sleep quality by addressing factors that cause sleep disturbances, such as pain and anxiety. By reducing pain levels and promoting relaxation, CBD can help individuals with chronic pain achieve better sleep. Some studies have reported improvements in sleep patterns among CBD users.
19. What are the legal risks associated with using CBD products?
While hemp-derived CBD products are federally legal if they contain less than 0.3% THC, legal risks arise due to varying state laws. Using CBD products with higher THC levels can lead to legal issues. Additionally, some employers may have policies against cannabis products, potentially affecting drug testing results.
20. How do state medical marijuana laws affect CBD use?
State medical marijuana laws can impact the availability and legality of CBD products, especially those derived from marijuana plants with higher THC content. In states with medical marijuana programs, patients may have access to a wider range of CBD products. Conversely, in states with stricter laws, access may be limited to hemp-derived CBD products only.