- What is CBD (Cannabidiol)?
- The Endocannabinoid System & How CBD Works
- CBD vs. THC: Key Differences Explained
- Types of CBD Products
- Potential Benefits of CBD: What Research Shows
- CBD Safety, Side Effects & Drug Interactions
- CBD Dosage Guidelines
- Legality & Regulation of CBD
- How to Choose Quality CBD Products
- Frequently Asked Questions About CBD
- Conclusion
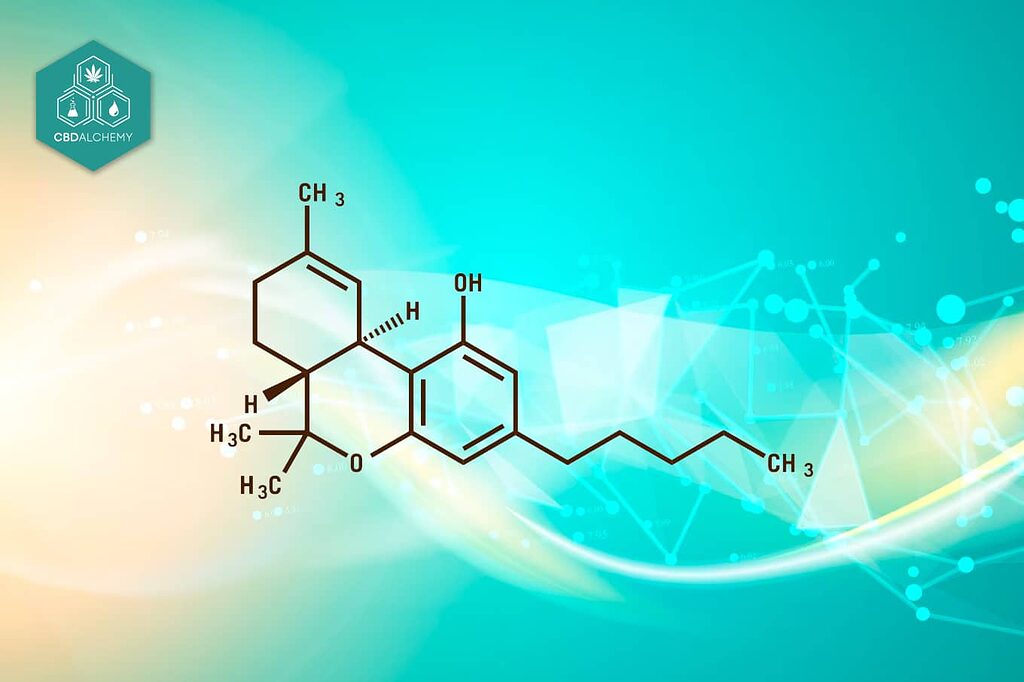
In recent years, few natural compounds have captured public interest quite like cannabidiol, commonly known as CBD. This non-intoxicating extract from the cannabis plant has transformed from a little-known molecule to a mainstream wellness ingredient found in everything from oils and capsules to skincare products and beverages. As an active ingredient in various medicinal products, CBD has gained regulatory approvals for conditions like muscle spasticity in multiple sclerosis and epilepsy, highlighting its therapeutic potential without psychoactive effects. But what exactly is CBD, how does it work in the human body, and what does science actually tell us about its potential benefits?
This comprehensive guide cuts through marketing claims and misinformation to provide evidence-based answers about CBD. Whether you’re considering trying CBD for the first time or looking to deepen your understanding of this fascinating compound, this article offers the scientific context, practical information, and safety considerations you need to make informed decisions.
What is CBD (Cannabidiol)?
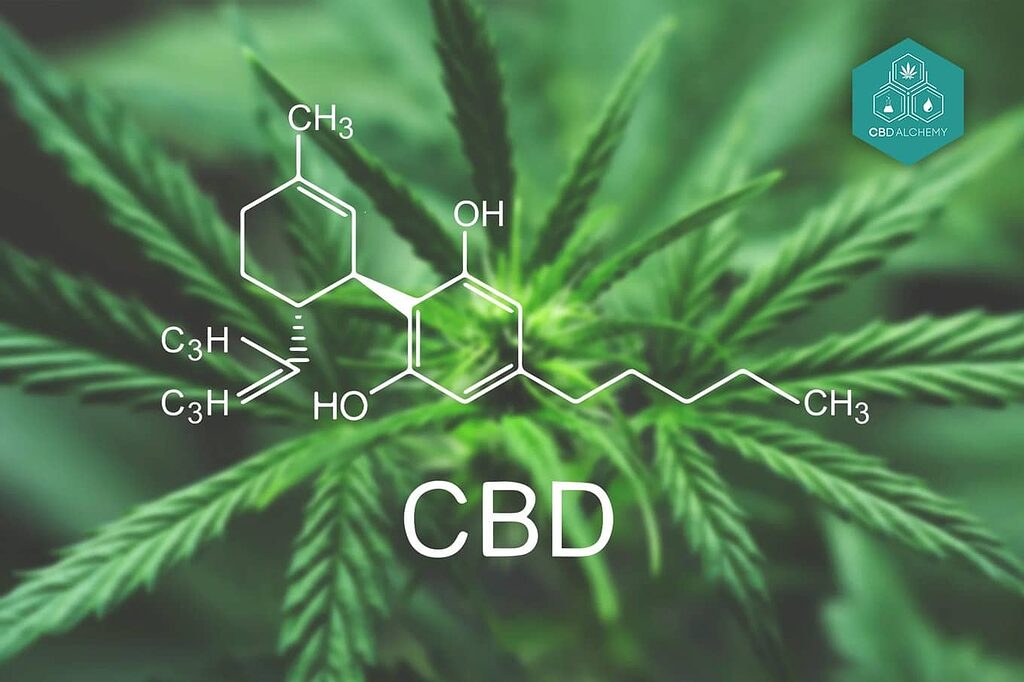
Cannabidiol (CBD) is one of over 100 naturally occurring compounds called cannabinoids found in the Cannabis sativa plant. Unlike its more famous cousin tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), CBD does not produce psychoactive effects—in other words, it won’t get you “high.” This crucial distinction has allowed CBD to emerge as a widely accepted wellness supplement even as cannabis regulations continue to evolve.
Cannabidiol oil (CBD oil) is a popular natural remedy for various ailments, emphasizing its health benefits.
The Cannabis sativa plant has been cultivated for thousands of years for its fiber, seeds, oil, and medicinal properties. Within this species, we find two primary varieties: marijuana and hemp. While both contain CBD, hemp is specifically bred to contain minimal THC (legally defined as less than 0.3% in the United States) while often producing higher concentrations of CBD.
Chemically, CBD is a 21-carbon molecule that interacts with specific receptors throughout the body. It was first isolated from cannabis in 1940, but researchers didn’t begin to understand its mechanisms and potential effects until decades later. The discovery of the endocannabinoid system in the early 1990s marked a breakthrough in understanding how cannabinoids, including CBD, interact with the human body.
Today, most commercially available CBD is derived from industrial hemp plants, which are legally grown under specific regulations established by the 2018 Farm Bill. This legislation distinguished hemp (cannabis with less than 0.3% THC) from marijuana, removing hemp-derived products from Schedule I controlled substance classification at the federal level.
The Endocannabinoid System & How CBD Works
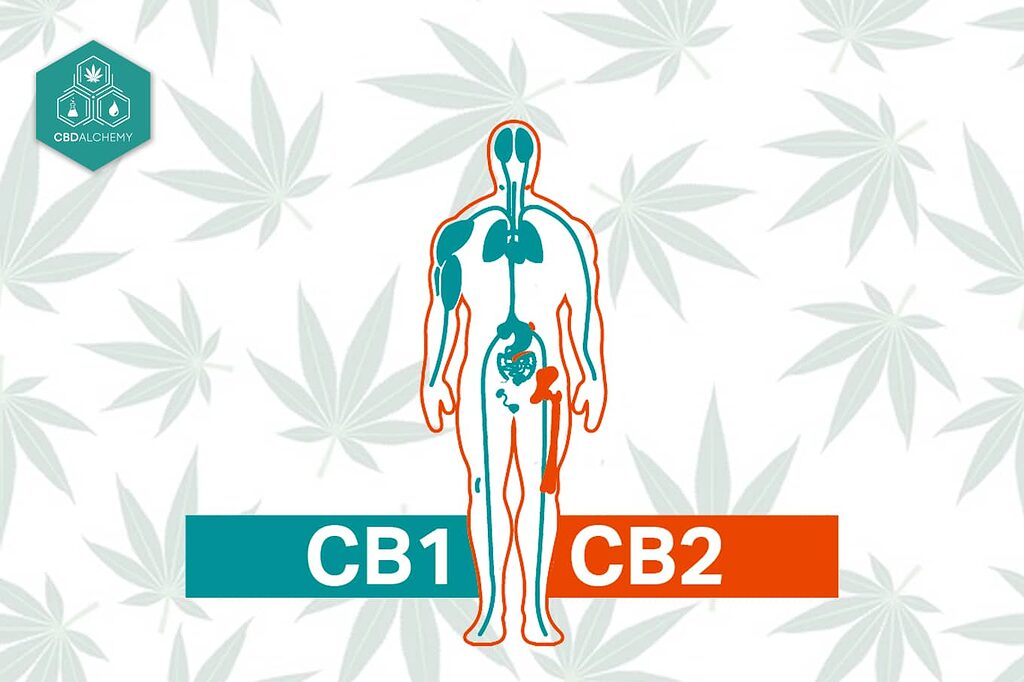
To understand how CBD works, we must first explore the remarkable biological network it primarily interacts with: the endocannabinoid system (ECS).
Understanding the Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex cell-signaling system identified in the early 1990s by researchers exploring THC’s effects. Remarkably, this vital physiological system exists and is active in your body even if you don’t use cannabis.
The ECS consists of three primary components:
- Endocannabinoids: Naturally produced cannabinoid-like molecules that act as chemical messengers in the body.
- Receptors: Primarily CB1 (concentrated in the central nervous system) and CB2 (predominantly found in the peripheral nervous system and immune cells).
- Enzymes: Responsible for breaking down endocannabinoids once they’ve served their purpose.
The ECS plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis—the body’s internal balance—across numerous physiological functions including:
- Mood regulation
- Sleep-wake cycles
- Appetite and digestion
- Pain perception
- Immune system response
- Reproductive function
- Memory formation
- Stress response
This widespread influence explains why cannabinoids like CBD may affect so many different aspects of human physiology.
How CBD Interacts With Your Body
Unlike THC, which binds directly and strongly to cannabinoid receptors (particularly CB1), CBD interacts with the endocannabinoid system in more subtle and complex ways:
- Indirect receptor interaction: Rather than binding directly to cannabinoid receptors, CBD acts as a modulator, influencing how other compounds interact with these receptors.
- Enzyme inhibition: CBD inhibits the enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), which breaks down anandamide—an endocannabinoid often called the “bliss molecule.” By slowing anandamide’s breakdown, CBD may enhance and prolong its effects.
- Beyond the ECS: CBD also interacts with several non-cannabinoid receptors and ion channels, including:
- Serotonin receptors (5-HT1A), which influence anxiety and mood.
- Vanilloid receptors (TRPV1), involved in pain perception and inflammation. CBD’s interaction with these receptors can help reduce inflammation and alleviate joint pain.
- Nuclear receptors (PPARs), which play roles in energy homeostasis and inflammation.
This diverse interaction profile explains why CBD may influence so many physiological processes without producing intoxication or significant side effects—a characteristic that has contributed significantly to its popularity as a wellness supplement.
CBD’s complex mechanisms of action remain an active area of research, with new discoveries regularly adding to our understanding of this versatile compound.
CBD vs. THC: Key Differences Explained
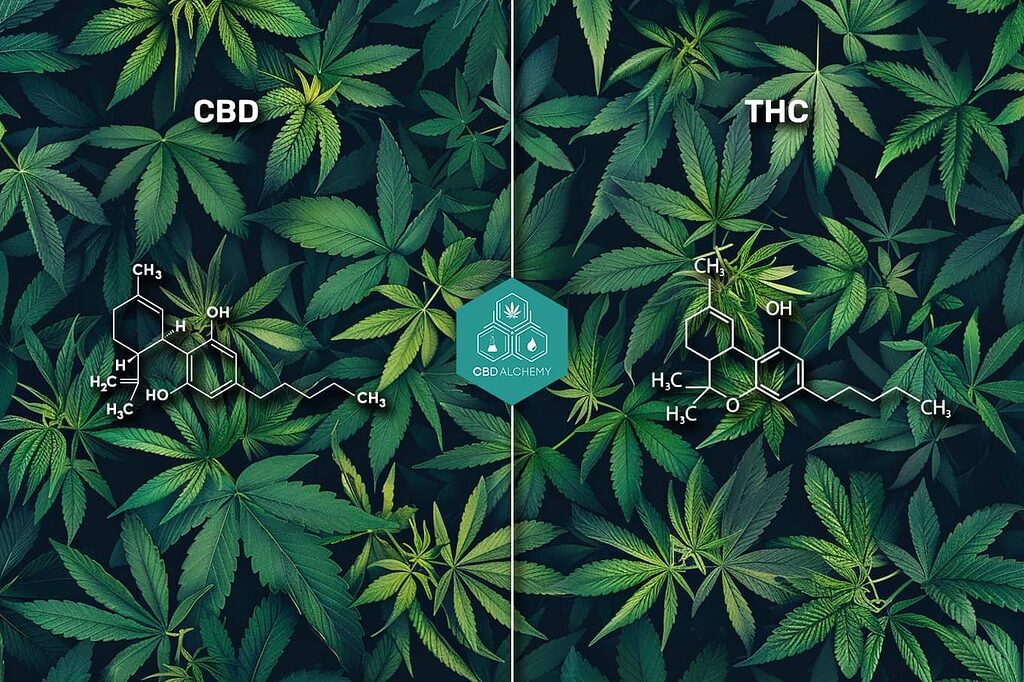
While CBD and THC are both cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant, they have distinctly different effects on the body and different legal statuses. Understanding these differences is crucial for consumers navigating the cannabis product landscape.
| Characteristic | CBD | THC |
| Psychoactivity | Non-intoxicating | Produces “high” or euphoria |
| Receptor binding | Indirect interaction with CB1/CB2 | Strong direct binding to CB1 receptors |
| Legal status | Federally legal if derived from hemp with <0.3% THC | Federally illegal (Schedule I); legal in some states |
| Medical applications | Research ongoing; FDA-approved for specific seizure disorders | State-approved for various conditions including pain, nausea, glaucoma |
| Side effects | Generally well-tolerated with minimal side effects | Can include anxiety, paranoia, cognitive impairment |
| Drug testing | Typically doesn’t trigger positive results (full-spectrum may) | Triggers positive cannabis results |
The molecular structures of CBD and THC are remarkably similar—both share the exact same molecular formula (C₂₁H₃₀O₂)—but with a crucial difference in how their atoms are arranged. This slight variation dramatically changes how each molecule interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid receptors, resulting in their distinct effects.
CBD and THC can also influence each other’s effects when consumed together, a phenomenon known as the “entourage effect.” For example, CBD may moderate some of THC’s psychoactive effects while potentially enhancing certain therapeutic properties. This interaction highlights the complex relationship between cannabinoids and explains why some medical cannabis formulations contain specific ratios of both compounds.
The legal distinction between these compounds primarily hinges on their source and concentration. Hemp-derived CBD with less than 0.3% THC is federally legal under the 2018 Farm Bill, while THC remains a Schedule I controlled substance at the federal level, despite state-level legalization for medical or recreational use in many parts of the country.
Types of CBD Products
The CBD market offers a variety of product types that differ in their cannabinoid composition, delivery methods, and potential effects. Understanding these differences helps consumers select products aligned with their specific preferences and wellness goals.
Full-Spectrum CBD
Full-spectrum CBD contains all the naturally occurring compounds found in the hemp plant, including:
- CBD (the primary cannabinoid)
- Minor cannabinoids (CBG, CBN, CBC, etc.)
- Trace amounts of THC (always below the legal limit of 0.3%)
- Terpenes (aromatic compounds that may have their own effects)
- Flavonoids and other plant nutrients
The primary advantage of full-spectrum products is the “entourage effect”—the theory that cannabinoids and terpenes work synergistically, enhancing each other’s beneficial effects. Research suggests that full-spectrum extracts may provide more pronounced effects at lower doses compared to isolated CBD.
However, full-spectrum products have a distinctive earthy taste that some find unpleasant, and the trace amounts of THC, while not enough to cause intoxication, could potentially trigger a positive result on extremely sensitive drug tests with heavy, regular use.
Broad-Spectrum CBD
Broad-spectrum CBD offers a middle ground between full-spectrum and isolate products. These formulations contain multiple cannabinoids and terpenes but with THC specifically removed through additional processing steps.
This format aims to provide many of the benefits of the entourage effect while eliminating concerns about THC exposure. Broad-spectrum options are particularly valuable for:
- People subject to drug testing
- Those with THC sensitivity
- Individuals who prefer avoiding THC for personal reasons
- Consumers seeking more complete plant benefits than isolate offers
The production of high-quality broad-spectrum CBD requires sophisticated extraction and purification techniques, which often makes these products more expensive than CBD isolate but typically less costly than premium full-spectrum options.
CBD Isolate
CBD isolate is the purest form of cannabidiol, containing 99%+ CBD with all other plant compounds removed. This crystalline powder or oil contains no other cannabinoids, terpenes, or plant matter.
Isolate products offer several distinct advantages:
- No risk of THC exposure
- No hemp taste or smell (important for those sensitive to cannabis flavors)
- Precise dosing control
- Versatility in formulation (easily dissolved in various carriers)
- Often less expensive per milligram of CBD
However, without the entourage effect, some users report needing higher doses of isolate to achieve effects comparable to full-spectrum products. Isolate is ideal for consumers who want the potential benefits of CBD without any other cannabis compounds, or for those creating custom formulations by adding CBD to foods, beverages, or skincare products.
Common CBD Product Forms
CBD is available in numerous delivery formats, each offering different onset times, durations, and applications:
- Oils and Tinctures
- Taken sublingually (under the tongue) for faster absorption
- Typically packaged with droppers for precise dosing
- Effects generally begin within 15-30 minutes and last 4-6 hours
- Bioavailability of approximately 20-35% when used sublingually
- Capsules and Edibles
- Convenient, pre-measured doses
- No taste concerns
- Slower onset (45-90 minutes) due to digestion
- Longer-lasting effects (6-8 hours)
- Lower bioavailability (approximately 10-20%) due to first-pass metabolism
- Topicals (Creams, Balms, Lotions)
- Applied directly to skin for localized effects
- Does not enter bloodstream significantly
- Ideal for specific areas
- Effects typically develop within 15-45 minutes and last 4-6 hours
- Varying CBD concentrations (typically 1-10mg/mL)
- Vape Products
- Fastest onset (1-5 minutes) as CBD enters bloodstream through lungs
- Highest bioavailability (approximately 30-50%)
- Shorter duration (2-4 hours)
- Respiratory considerations compared to other methods
- Flowers (Hemp Buds)
- Traditional format for whole-plant benefits
- Can be vaporized, smoked, or used in food preparation
- Rich in natural terpenes and cannabinoids
- Variable CBD content depending on strain (typically 10-20%)
When selecting a CBD product form, consider your specific wellness goals, lifestyle factors, and personal preferences regarding onset time, duration, convenience, and consumption method.
Potential Benefits of CBD: What Research Shows
As interest in CBD has surged, so has scientific research examining its potential benefits. However, it’s essential to distinguish between preliminary research, strong clinical evidence, and FDA-approved medical applications. This section examines the current state of evidence regarding CBD’s potential effects.
Important disclaimer: CBD is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease except for the specific conditions for which FDA-approved drugs containing CBD exist. The following information summarizes current research but should not be interpreted as medical claims. Always consult a healthcare professional.
FDA-Approved Uses
The strongest evidence for CBD’s therapeutic potential comes from research on certain forms of epilepsy. In 2018, the FDA approved Epidiolex, a purified CBD oral solution, for the treatment of seizures associated with:
- Lennox-Gastaut syndrome
- Dravet syndrome
- Tuberous sclerosis complex
Epidiolex is a prescription drug containing highly purified CBD.
These approvals followed rigorous clinical trials demonstrating that CBD significantly reduced seizure frequency compared to placebo in these rare, severe forms of epilepsy. It’s important to note that Epidiolex is a prescription pharmaceutical containing highly purified CBD in specific dosages (typically 5-20 mg/kg/day), which differs from over-the-counter CBD wellness products.
This FDA approval represents a significant milestone, establishing CBD’s therapeutic potential through the conventional pharmaceutical approval process for specific conditions.
Areas With Strong Research Evidence
Beyond FDA-approved applications, several areas have accumulated substantial research evidence, though not yet sufficient for medical claims or FDA approval:
- Anxiety Reduction: Multiple small-scale human studies have observed anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing) effects following CBD administration. Studies found CBD reduced anxiety in social anxiety disorder during public speaking tests, and reviews conclude CBD may have anxiolytic effects, though larger trials are needed. Neuroimaging suggests changes in blood flow to anxiety-related brain regions.
- Sleep Support: Research shows mixed but promising results. CBD may affect sleep by reducing anxiety and influencing circadian rhythms. One study showed improved sleep scores in many participants. Effects might be biphasic (low doses = alertness, high doses = relaxation). More research is ongoing.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: Laboratory and animal studies consistently demonstrate anti-inflammatory effects. CBD appears to inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines and modulate immune cells. Human studies on skin/bowel inflammation show preliminary positive results, but more clinical trials are needed. These anti-inflammatory effects also contribute to CBD’s potential for pain relief, particularly in managing chronic pain and cancer-related symptoms.
Emerging Research Areas
Several other potential applications for CBD have emerging but preliminary evidence:
- Neuroprotective Properties: Preclinical research suggests CBD may reduce oxidative stress and neuroinflammation and influence neuroplasticity. Research on neurodegenerative conditions is ongoing but early.
- Mood Regulation: Early research suggests CBD may interact with serotonin receptors. Animal studies are promising, but human research is limited. Observational studies report mood benefits, needing validation.
- Pain Management: Preclinical studies show analgesic/anti-inflammatory properties. Human studies show mixed results for specific pain types. Interaction with pain processing systems is under investigation.
It’s important to note that research into CBD’s effects continues to evolve rapidly. The coming years will likely provide more definitive answers as larger, well-designed clinical trials are completed.
CBD Safety, Side Effects & Drug Interactions
While CBD is generally well-tolerated by most consumers, responsible use requires awareness of potential side effects, drug interactions, and appropriate precautions.
Common Side Effects
Clinical studies and consumer reports have identified several potential side effects of CBD, though these are typically mild and transient:
- Drowsiness and Fatigue: Reported by 10-15% of users, especially at higher doses.
- Dry Mouth: Temporary reduction in saliva (10-20% of users). Manage with hydration.
- Changes in Appetite: Mild increases or decreases reported.
- Gastrointestinal Discomfort: Nausea or loose stools (5-10% of users), often when starting or with high doses.
- Lightheadedness: Potential temporary drops in blood pressure, especially at higher doses.
- Liver Injury: High doses of CBD, particularly in prescription forms like Epidiolex, have been associated with signs of liver injury.
Most side effects are dose-dependent and often diminish with continued use.
Drug Interactions
One of the most significant safety considerations with CBD involves its potential interactions with other medications:
- Cytochrome P450 Interactions: CBD can inhibit liver enzymes (CYP450) responsible for metabolizing ~60% of prescribed drugs. This can slow the breakdown of other medications, increasing their levels and effects (similar to grapefruit juice). The extent varies by dose, individual metabolism, and specific medications.
- Medications with Potential Interactions: Include (but not limited to):
- Blood Thinners (e.g., Warfarin)
- Antiepileptic Drugs (e.g., Clobazam, Valproate)
- Immunosuppressants (e.g., Cyclosporine)
- Antidepressants (SSRIs, SNRIs, etc.)
- Certain Heart Medications
- Statins
- Minimizing Interaction Risks:
- Consult Healthcare Provider: ALWAYS discuss CBD use with your doctor, especially if taking prescriptions or certain medications. This is crucial to avoid adverse effects and ensure proper dosing.
- Timing Separation: Take CBD 2-4 hours apart from other medications to minimize interaction risks with other drugs.
- Start Low and Monitor: Begin with low CBD doses and watch for unusual effects.
Special Populations
Certain groups should exercise additional caution:
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Avoid CBD due to lack of safety data and potential transfer to fetus/infant.
- Liver Conditions: Consult doctor; may need lower doses due to altered metabolism.
- Children and Adolescents: Avoid outside of medical supervision due to unknown long-term effects on development.
These considerations highlight the importance of treating CBD responsibly.
CBD and Pregnancy
Cannabidiol (CBD) is a chemical found in the cannabis plant, and its effects on pregnancy are not yet fully understood. While some studies suggest that CBD may have potential health benefits, such as reducing anxiety and chronic pain, its use during pregnancy is not recommended due to the lack of scientific evidence on its safety. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved CBD for use in pregnant women, and its use may pose potential risks to the developing fetus. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should consult with their healthcare provider before using any CBD products, including CBD oil and dietary supplements. More research is needed to determine the safety and efficacy of CBD use during pregnancy, and until then, it is best to err on the side of caution and avoid its use.
CBD and Children
The use of CBD in children is a topic of ongoing debate, and its safety and efficacy have not been extensively studied. While some parents may consider using CBD to treat certain health issues, such as epilepsy and anxiety, its use in children is not recommended due to the lack of scientific evidence on its safety and potential long-term effects. The FDA has approved a prescription cannabidiol product, Epidiolex, for the treatment of certain rare forms of epilepsy in children, but its use should only be done under the guidance of a healthcare provider. CBD products, including CBD oil and dietary supplements, may contain contaminants and have unproven claims, and their use in children may pose potential risks, such as adverse effects and interactions with other medications. More research is needed to determine the safety and efficacy of CBD use in children, and parents should consult with their healthcare provider before considering its use.
CBD Dosage Guidelines
Finding the right CBD dose is highly individual. There’s no one-size-fits-all answer.
Factors Affecting Optimal Dosage
- Body Weight and Composition: Higher weight may need higher doses; fat solubility affects metabolism.
- Endocannabinoid System Tone: Individual variations influence response.
- Metabolism and Genetics: Variations in liver enzymes (CYP450) affect processing speed and duration.
- Consumption Method: Affects bioavailability (sublingual/inhaled > oral).
- Product Formulation: Full-spectrum may be effective at lower doses than isolate (entourage effect). Advanced delivery systems (liposomes) can also alter needs.
- Wellness Goals: Different effects may require different doses.
Start Low and Go Slow Approach
Most experts recommend:
- Start with a minimal dose: 5-10mg CBD (sublingual/oral) once daily.
- Maintain for 3 days: Allow time for effects to develop.
- Journal effects: Track targeted parameters and overall well-being.
- Incrementally increase: If needed, increase by 5-10mg every 3 days.
- Continue until optimal: Find the minimum effective dose.
- Reassess periodically: Adjust as needed over time.
General Dosage Frameworks
(Starting points, individual optimization is key):
- Mild effects: 10-25mg per day
- Moderate effects: 25-50mg per day
- Strong effects: 50-100mg per day
- Very strong effects: 100-200mg+ per day
(Assumes sublingual/oral use for average adult weight). Microdosing (2-5mg multiple times daily) is another approach. Remember potential biphasic effects (different effects at low vs. high doses).
It is important to consult healthcare professionals to determine the best treatment options and appropriate dosing.
Legality & Regulation of CBD
The legal landscape for CBD in the United States is complex.
The 2018 Farm Bill and Federal Status
- Legalized hemp (cannabis < 0.3% THC) and its derivatives (like CBD) federally.
- While it is legal to sell hemp and hemp-derived products, not all CBD items are allowed to be marketed as food or dietary supplements.
- Removed hemp from the Controlled Substances Act.
- Maintained FDA authority over CBD products.
FDA Regulation Status
- FDA has approved only one CBD drug (Epidiolex).
- Has not approved CBD as a dietary supplement or food additive.
- Currently considers it illegal to market CBD added to food or labeled as a supplement.
- Focuses enforcement on companies making illegal health claims.
- Working on clearer regulatory frameworks, but the process is ongoing.
State-Level Variations
- State laws vary significantly regarding CBD legality and regulation (testing, labeling).
- Products legal in one state may not be legal in another.
Legal Considerations for Consumers
- THC Content: Must be <0.3% THC for federal legality. Verify with testing.
- Cross-State Travel: Research destination state laws.
- Drug Testing: Trace THC in full-spectrum products could trigger positive results. Use caution if tested.
- International Travel: Avoid; CBD legality varies widely globally.
Stay informed about evolving federal and state regulations.
How to Choose Quality CBD Products
Variability in the market makes choosing quality products essential.
Source and Cultivation
- Hemp Source Origin: Look for US-grown hemp (CO, OR, KY have strong programs).
- Organic Certification: USDA organic ensures no synthetic pesticides/fertilizers.
- Sustainable Practices: Signal commitment to quality (regenerative ag, water conservation).
Pure CBD does not lead to public health related problems, as supported by a World Health Organization report that highlights its safety profile and lack of abuse potential.
Extraction Methods
- CO₂ Extraction: Gold standard; solvent-free, clean extract. More expensive.
- Ethanol Extraction: Can yield high quality if done properly with full solvent purging. More affordable.
- Methods to Avoid: Hydrocarbon (butane/propane) due to safety/residue risks; harmful solvents (hexane).
Third-Party Testing
The most crucial quality indicator:
- Certificate of Analysis (CoA): From independent, accredited lab. Should be easily accessible (QR code, website).
- Comprehensive Testing Scope: Verify CBD/THC potency AND test for contaminants (pesticides, heavy metals, solvents, microbes, mycotoxins).
- Batch-Specific Testing: Results should match the specific product batch and be recent.
Product Transparency
- Clear Labeling: State total CBD (mg), CBD per serving, CBD type (full/broad/isolate), ingredients, batch number, usage guidelines, QR code for labs.
- Manufacturing Standards: Look for GMP or ISO certifications.
- Realistic Claims: Avoid companies making exaggerated “cure” claims.
Red Flags to Watch For
- Unrealistic Pricing: Too cheap often means compromised quality.
- No Batch Testing / Limited Testing: May hide potency/contamination issues.
- Misleading Labeling: Focusing on “hemp extract” weight instead of actual CBD mg.
- Limited Company Information: Lack of transparency about location, contact info.
Investing in quality ensures safety and potentially better efficacy.
Frequently Asked Questions About CBD
Will CBD make me feel high? No, properly produced CBD products (<0.3% THC) will not cause intoxication. CBD is non-psychoactive. Some users report relaxation or calm, but it’s distinct from a THC high.
Will CBD show up on a drug test? Standard tests look for THC. Full-spectrum CBD contains trace THC which could accumulate and cause a positive result with heavy use. Isolate and broad-spectrum (THC-free) are lower risk, but cross-contamination is possible with poor manufacturing. Use caution if subject to testing.
How long do CBD effects last? Typically 4-8 hours, but varies by method: Inhalation (2-4 hrs), Sublingual (4-6 hrs), Oral (6-8+ hrs), Topical (4-6 hrs, localized). Duration depends on dose, metabolism, etc.
Can I take CBD with medications? Consult your doctor first. CBD can interact with many medications (blood thinners, seizure meds, antidepressants, etc.) via liver enzymes (CYP450). Take CBD 2-4 hours apart from other meds and start with low doses if approved by your doctor.
What’s the difference between hemp oil and CBD oil? Hemp seed oil is from seeds, has no significant CBD, used for nutrition (omega fats). CBD oil is from flowers/leaves/stalks, rich in CBD, used for wellness effects. Check labels carefully for actual CBD content (mg).
Is CBD safe for pets? Consult your veterinarian. Animals metabolize CBD differently. Use pet-specific formulas (no xylitol), dose by weight, verify THC content (THC is more toxic to dogs). Limited research exists.
How should I store CBD products? Store cool (60-70°F), dark, dry, and airtight. Proper storage maintains potency for 1-2 years typically. Check expiration dates.
Is CBD addictive? Current evidence indicates CBD is not addictive and has low abuse potential (WHO). It doesn’t appear to cause tolerance or withdrawal.
What does CBD feel like? Effects are often subtle. Common reports include calm, reduced physical tension, mood maintenance, focus improvement. Some notice little initially; benefits may be recognized over time. ~15-20% report minimal acute effects.
Conclusion
CBD represents a fascinating intersection of ancient plant wisdom and modern science. As research continues to evolve, our understanding of this versatile compound and its interactions with the human body grows increasingly sophisticated. While CBD is not a panacea, evidence suggests it offers promising wellness potential for many individuals when used thoughtfully and with appropriate expectations.
Key takeaways from this comprehensive guide include:
- CBD is not THC: Cannabidiol offers potential wellness benefits without intoxication.
- Quality matters tremendously: Effectiveness and safety depend on source, extraction, and testing.
- Personalization is essential: Dosing and effects vary individually.
- Research is evolving: Evidence varies; approach claims critically.
- Safety considerations exist: Interactions and suitability require attention; consult doctors.
If you’re considering trying CBD, approach it with informed curiosity. Start with high-quality products from reputable manufacturers like CBD Alchemy, begin with low doses, and pay attention to how your unique body responds. Consult healthcare providers when appropriate.
The future of CBD looks promising as regulatory frameworks mature, research advances, and product innovation continues. By staying informed and approaching CBD with balanced expectations, consumers can make decisions that best support their individual wellness journeys.
Note: This article is intended for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with qualified healthcare providers regarding any wellness supplement, including CBD.






