- Understanding CBD and Its Interaction with the Brain
- CBD vs. THC: Key Differences
- The Legal Landscape of CBD
- The Endocannabinoid System Explained
- How CBD Interacts with the Brain
- Neuroprotective Properties of CBD
- CBD’s Role in Neurogenesis and Brain Plasticity
- CBD’s Impact on Anxiety and Depression
- CBD and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- CBD’s Role in Autism Spectrum Disorders
- Modulation of Brain Activity and Connectivity
- CBD and Epilepsy
- CBD’s Potential in Neurodegenerative Diseases
- CBD and Psychotic Symptoms
- Current Therapeutic Applications and Future Research
- Safety Profile and Side Effects of CBD
- Practical Aspects of CBD Use
- Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
- Frequently Asked Questions About CBD and Brain Function
- Expert Insights on CBD’s Potential
- Resources for Further Information
Understanding CBD and Its Interaction with the Brain

What is Cannabidiol (CBD)?
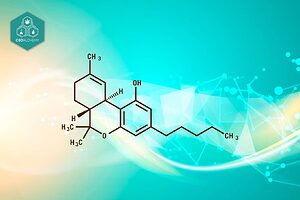
Cannabidiol, commonly known as CBD, is a naturally occurring compound found in the Cannabis sativa plant. It belongs to a class of molecules called cannabinoids, which interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system. Unlike its more famous counterpart, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), CBD does not produce psychoactive effects or the “high” associated with cannabis use. Some of the typical CBD-rich products sold are CBD oils, CBD flowers, CBD hashish and CBD cosmetics.
Origins and Extraction of CBD
CBD is primarily derived from hemp, a variety of Cannabis sativa that contains high levels of CBD and low levels of THC (typically less than 0.3%).
The extraction process involves several methods, including CO2 extraction, ethanol extraction, and oil infusion. CO2 extraction is considered the gold standard due to its efficiency and ability to produce pure, high-quality CBD without residual solvents.
The use of cannabis for medicinal purposes dates back thousands of years, with evidence of its use in ancient civilizations such as China and Egypt. However, it wasn’t until 1940 that CBD was first isolated and identified by American chemist Roger Adams. This discovery paved the way for further research into the potential therapeutic applications of cannabinoids.
Chemical Structure and Properties
CBD has a molecular formula of C21H30O2 and a molecular weight of 314.4 g/mol.
Its chemical structure consists of 21 carbon atoms, 30 hydrogen atoms, and two oxygen atoms.
This arrangement gives CBD unique properties that allow it to interact with various receptors in the body, particularly in the brain and nervous system.
One of the key characteristics of CBD is its lipophilicity, meaning it has an affinity for fats.
This property allows CBD to cross the blood-brain barrier effectively, enabling it to exert its effects on the central nervous system and influence blood flow in various brain regions.
Additionally, CBD is known for its antioxidant properties, which contribute to its potential neuroprotective effects.
CBD vs. THC: Key Differences

While CBD and THC are both cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant, they have distinct properties and effects on the human body:
- Psychoactivity: THC is responsible for the intoxicating effects of cannabis, while CBD is non-psychoactive.
- Receptor binding: THC primarily binds to CB1 receptors in the brain, leading to its psychoactive effects. CBD, on the other hand, has a low affinity for CB1 and CB2 receptors and modulates their activity indirectly.
- Legal status: CBD derived from hemp (containing less than 0.3% THC) is legal at the federal level in the United States, while THC remains a controlled substance.
- Medical applications: Both compounds have potential therapeutic uses, but their applications differ. THC is often used for pain relief and appetite stimulation, while CBD is being studied for its anti-inflammatory, anxiolytic, and neuroprotective properties.
- Side effects: THC can cause side effects such as anxiety, paranoia, and impaired memory. CBD generally has a more favorable side effect profile, with mild effects like fatigue or changes in appetite being most common.
Understanding these differences is crucial for both researchers and consumers, as it informs the potential applications and risks associated with each compound.
The Legal Landscape of CBD
The legal status of CBD has evolved rapidly in recent years, with significant variations across different jurisdictions. This complex legal landscape has implications for research, medical use, and consumer access to CBD products.
Federal Regulations in the United States
At the federal level in the United States, the legal status of CBD is primarily determined by its source and THC content. The 2018 Farm Bill legalized hemp and hemp-derived products, including CBD, as long as they contain no more than 0.3% THC on a dry weight basis. This legislation removed hemp-derived CBD from the Controlled Substances Act, effectively legalizing its production and sale under certain conditions.However, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) maintains regulatory authority over CBD products.
As of 2023, the FDA has approved only one CBD-based drug, Epidiolex, for the treatment of certain forms of epilepsy. The agency has expressed concerns about the marketing of CBD products with unproven medical claims and potential safety issues.
The FDA’s stance has created a complex regulatory environment where CBD is legal to produce and sell, but cannot be marketed as a dietary supplement or added to food products without FDA approval. This has led to a proliferation of CBD products in a legal gray area, with enforcement actions primarily focused on egregious health claims rather than the sale of CBD itself.
State-by-State Variations in CBD Laws
While federal law provides a baseline for CBD regulation, individual states have implemented their own laws and regulations, creating a patchwork of legal frameworks across the country. Some states have fully embraced CBD, allowing its sale and use with minimal restrictions, while others have imposed more stringent regulations or even maintained prohibition.For example:
- California allows the sale of CBD in foods and beverages, contrary to FDA guidelines.
- Texas permits the sale of CBD products but requires retailers to register with the state.
- Idaho only allows CBD products with zero THC content, more restrictive than the federal 0.3% limit.
These variations can create confusion for consumers and challenges for businesses operating across state lines. It’s crucial for individuals and companies to be aware of the specific regulations in their state and any states where they conduct business.
International Perspectives on CBD Legality
Globally, the legal status of CBD varies widely. Some countries have embraced CBD as a wellness product or medicine, while others maintain strict prohibitions.
In the European Union, for example, CBD is not considered a narcotic, and many member states allow its sale as a food supplement. The United Kingdom has established a regulatory framework for CBD as a novel food, requiring safety assessments before products can be sold.
In contrast, some countries, particularly in Asia and Africa, maintain strict cannabis prohibition laws that include CBD.
Japan, for instance, allows CBD products but prohibits any detectable amount of THC.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has recognized CBD’s potential therapeutic value and recommended that it not be scheduled as a controlled substance internationally.
This stance has influenced some countries to reconsider their approach to CBD regulation.
As research continues to unveil the potential benefits of CBD and CBDA, it’s likely that the legal landscape will continue to evolve both domestically and internationally.
This ongoing change presents both opportunities and challenges for researchers, healthcare providers, and consumers interested in CBD’s effects on brain function.
The Endocannabinoid System Explained
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex cell-signaling system that plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis in the body. Discovered in the early 1990s, the ECS has been found to regulate various physiological processes, including mood, appetite, sleep, and immune function. Understanding the ECS is essential for comprehending how CBD interacts with the brain and body.
Components of the Endocannabinoid System
The ECS consists of three main components:
- Endocannabinoids: These are naturally occurring cannabinoids produced by the body. The two primary endocannabinoids are anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG).
- Cannabinoid receptors: These are found throughout the body and are the binding sites for both endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids like CBD and THC. The two main types are CB1 and CB2 receptors.
- Enzymes: These are responsible for synthesizing and breaking down endocannabinoids. The main enzymes are fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), which breaks down AEA, and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL), which breaks down 2-AG.
Endogenous Cannabinoids and Their Functions
Endocannabinoids are lipid-based neurotransmitters that are synthesized on-demand in response to various stimuli. They act as retrograde messengers, meaning they travel backwards across synapses to modulate neurotransmitter release.Anandamide (AEA), often referred to as the “bliss molecule,” is involved in regulating mood, appetite, and pain perception. It has been found to play a role in the runner’s high phenomenon and is associated with feelings of well-being.2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) is more abundant in the brain than AEA and is involved in various physiological processes, including immune function, neuroprotection, and synaptic plasticity.These endocannabinoids help maintain balance in the body by fine-tuning the activity of other neurotransmitter systems. They can either enhance or inhibit the release of neurotransmitters, depending on the specific physiological needs of the moment.
CB1 and CB2 Receptors in the Brain and Body
Cannabinoid receptors are G protein-coupled receptors that are activated by endocannabinoids, phytocannabinoids, and synthetic cannabinoids. The two main types of cannabinoid receptors are CB1 and CB2, each with distinct distributions and functions in the body.CB1 Receptors:
- Primarily found in the central nervous system, particularly in the brain
- Highly concentrated in areas responsible for memory, emotion, pain perception, and motor control
- Also present in peripheral tissues, including the gastrointestinal tract and reproductive organs
- Activation of CB1 receptors is associated with the psychoactive effects of THC
CB2 Receptors:
- Predominantly found in the peripheral nervous system and immune cells
- Present in lower concentrations in the brain, particularly in microglia (the brain’s immune cells)
- Involved in modulating immune function and inflammation
- Activation of CB2 receptors is not associated with psychoactive effects
The distribution of these receptors throughout the body explains the wide-ranging effects of cannabinoids on various physiological processes. It’s important to note that while THC directly activates these receptors, CBD has a more complex interaction with the ECS, which leads to its unique effects on brain function.
How CBD Interacts with the Brain
CBD’s interaction with the brain is multifaceted and involves various mechanisms beyond the direct activation of cannabinoid receptors. Changes in cerebral blood flow are assessed using neuroimaging techniques like SPECT and fMRI, and these measurements correlate with cognitive tasks or the therapeutic potential of CBD in conditions affecting memory and emotion. This complexity contributes to CBD’s wide range of potential therapeutic effects and its distinct profile compared to other cannabinoids.
CBD’s Influence on Neurotransmitters
CBD exerts its effects on brain function partly through its interaction with various neurotransmitter systems. Studies investigating the acute effects of CBD on brain function in healthy volunteers compare brain activity and connectivity during resting states and cognitive tasks, highlighting the significance of their findings in understanding the therapeutic potential of CBD:
- Serotonin: CBD has been shown to modulate the activity of serotonin receptors, particularly the 5-HT1A receptor. This interaction may contribute to CBD’s anxiolytic and antidepressant-like effects.
- GABA: CBD may enhance the signaling of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. This action could contribute to CBD’s calming effects and potential anti-anxiety properties.
- Glutamate: Some studies suggest that CBD may modulate glutamate signaling, which could have implications for its neuroprotective and anti-seizure effects.
- Dopamine: While CBD doesn’t directly bind to dopamine receptors, it may indirectly influence dopaminergic signaling, which could have implications for motivation and reward-related behaviors.
Impact on Brain Receptors and Neurons
CBD interacts with various receptors in the human brain, often in ways that are distinct from traditional cannabinoids:
- CB1 and CB2 receptors: Unlike THC, CBD has a low affinity for these cannabinoid receptors. However, it may act as an allosteric modulator, influencing how these receptors respond to other cannabinoids.
- TRPV1 receptors: CBD activates transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) receptors, which are involved in pain perception and inflammation.
- GPR55 receptors: CBD has been shown to antagonize GPR55, a G protein-coupled receptor that may be involved in regulating bone density and blood pressure.
- PPARγ receptors: CBD can activate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ), which may contribute to its anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects.
These diverse interactions contribute to CBD’s complex effects on neuronal function and signaling.
Modulation of Synaptic Plasticity
CBD has been shown to influence synaptic plasticity, the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time in response to increased or decreased activity. This process is crucial for learning, memory, and overall brain function. CBD attenuates activity in the left medial prefrontal cortex during the processing of salient versus non-salient stimuli, which has implications for emotional regulation and cognitive tasks.
- Neurogenesis: Some studies suggest that CBD may promote neurogenesis, particularly in the hippocampus, a region critical for memory formation.
- Long-term potentiation (LTP): CBD has been shown to enhance LTP in some brain regions, which could have implications for learning and memory processes.
- Neuroprotection: CBD’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties may help protect neurons from damage and degeneration, potentially preserving synaptic function.
By modulating synaptic plasticity, CBD may have long-term effects on brain function and structure, which could contribute to its potential therapeutic applications in various neurological and psychiatric conditions. In conclusion, CBD’s interaction with the brain is complex and multifaceted, involving various neurotransmitter systems, receptors, and cellular processes. This complexity underlies CBD’s diverse effects on brain function and its potential as a therapeutic agent for a wide range of conditions. As research in this field continues to advance, our understanding of how CBD influences brain function at the molecular and cellular levels will likely expand, potentially leading to new therapeutic applications and insights into brain health.
Neuroprotective Benefits and Mental Health Applications
Neuroprotective Properties of CBD
Cannabidiol (CBD) has emerged as a promising neuroprotective agent, with research indicating its potential to safeguard neurons from various forms of damage and degeneration. This section explores the multifaceted neuroprotective properties of CBD, focusing on its anti-inflammatory effects, antioxidant properties, and role in neurogenesis and brain plasticity.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects in the Brain

Neuroinflammation is a common feature in many neurological disorders and can contribute to neuronal damage and cognitive decline. CBD has demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory properties in the brain, which may contribute to its neuroprotective effects:
- Microglial Modulation: CBD has been shown to regulate the activation of microglia, the brain’s primary immune cells. By modulating microglial activity, CBD can help reduce excessive inflammation in the central nervous system.
- Cytokine Regulation: Studies have indicated that CBD can decrease the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines while promoting the release of anti-inflammatory mediators. This balanced approach helps mitigate neuroinflammation without completely suppressing the immune response.
- NF-κB Pathway Inhibition: CBD has been found to inhibit the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway, a key regulator of inflammatory responses in the brain. This inhibition can lead to reduced expression of inflammatory genes and decreased neuroinflammation.
- Blood-Brain Barrier Protection: Research suggests that CBD may help maintain the integrity of the blood-brain barrier, reducing the infiltration of inflammatory cells and molecules into the brain tissue.
These anti-inflammatory effects of CBD contribute to its potential as a therapeutic agent for various neurological conditions, including neurodegenerative diseases and neuroinflammatory disorders.
Antioxidant Properties and Neuronal Health
Oxidative stress plays a significant role in neuronal damage and is implicated in the pathogenesis of many neurological disorders. CBD’s potent antioxidant properties offer protection against oxidative damage:
- Free Radical Scavenging: CBD acts as a powerful antioxidant, capable of neutralizing harmful free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ROS) that can damage neurons.
- Nrf2 Activation: CBD has been shown to activate the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway, which regulates the expression of antioxidant genes. This activation enhances the brain’s natural antioxidant defenses.
- Metal Ion Chelation: Studies have demonstrated CBD’s ability to chelate transition metal ions, which can contribute to the formation of reactive oxygen species. By reducing the concentration of these ions, CBD may help prevent oxidative damage to neurons.
- Mitochondrial Function: CBD has been found to improve mitochondrial function and reduce oxidative stress in neurons, potentially preserving cellular energy production and viability.
The antioxidant properties of CBD contribute to its neuroprotective effects by reducing oxidative damage to neurons, preserving cellular function, and potentially slowing the progression of neurodegenerative diseases.
CBD’s Role in Neurogenesis and Brain Plasticity
Emerging research suggests that CBD may play a role in promoting neurogenesis and enhancing brain plasticity, which are crucial processes for maintaining cognitive function and adapting to new experiences:
- Hippocampal Neurogenesis: Studies have shown that CBD can promote the growth of new neurons in the hippocampus, a brain region critical for memory formation and cognitive function.
- BDNF Expression: CBD has been found to increase the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that supports the survival of existing neurons and encourages the growth and differentiation of new neurons and synapses.
- Synaptic Plasticity: Research indicates that CBD may enhance synaptic plasticity, the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time. This process is fundamental to learning, memory, and overall cognitive function.
- Neuroprotection in Chronic Stress: CBD has demonstrated neuroprotective effects in models of chronic stress, potentially mitigating stress-induced reductions in neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity.
By promoting neurogenesis and enhancing brain plasticity, CBD may offer potential therapeutic benefits for conditions characterized by impaired neural regeneration or reduced cognitive flexibility.
CBD’s Impact on Anxiety and Depression
The potential of CBD as a treatment for anxiety and depression has garnered significant attention in recent years. This section explores the mechanisms by which CBD may alleviate symptoms of these common mental health disorders and compares its efficacy to traditional medications.
Mechanisms of Action in Anxiety Disorders
CBD has shown promise in reducing anxiety through various mechanisms:
- Serotonin Receptor Modulation: CBD acts as a partial agonist of the 5-HT1A serotonin receptor, which is implicated in anxiety and mood regulation. This interaction may contribute to CBD’s anxiolytic effects.
- GABA Enhancement: CBD may enhance the signaling of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. Increased GABA activity can lead to reduced anxiety and a calming effect.
- Endocannabinoid System Modulation: CBD influences the endocannabinoid system, which plays a role in regulating stress and anxiety responses. By enhancing endocannabinoid signaling, CBD may help reduce anxiety.
- Neuroplasticity: CBD’s effects on neuroplasticity and neurogenesis in regions like the hippocampus may contribute to its anxiolytic properties, particularly in stress-induced anxiety models.
Studies have demonstrated CBD’s potential efficacy in various anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, and panic disorder. For example, CBD has been shown to reduce anxiety in simulated public speaking tests at doses ranging from 300 mg to 600 mg.
Potential for Treating Major Depressive Disorder
While research on CBD’s antidepressant effects is still in its early stages, several studies suggest its potential in treating depression:
- Serotonin Modulation: CBD’s interaction with serotonin receptors may contribute to its antidepressant-like effects, as serotonin plays a crucial role in mood regulation.
- Neuroplasticity Enhancement: CBD’s ability to promote neurogenesis and enhance synaptic plasticity may contribute to its antidepressant effects, as impaired neuroplasticity is associated with depression.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Given the growing evidence linking inflammation to depression, CBD’s anti-inflammatory properties may contribute to its potential antidepressant effects.
- Stress Response Modulation: CBD may help regulate the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which is often dysregulated in depression.
A recent exploratory cohort study (n = 90) investigating the use of CBD for self-treatment of depression symptoms found that participants reported improvements in mood, sleep, and appetite. However, more rigorous clinical trials are needed to establish CBD’s efficacy in treating major depressive disorder.
Comparative Efficacy with Traditional Medications
While direct comparisons between CBD and traditional antidepressant or anxiolytic medications are limited, some studies and anecdotal evidence suggest potential advantages of CBD:
- Rapid Onset: Some studies indicate that CBD may have a more rapid onset of action compared to traditional antidepressants, which often take several weeks to show effects.
- Side Effect Profile: CBD generally has a more favorable side effect profile compared to many traditional psychiatric medications, with common side effects being mild and well-tolerated.
- Non-Addictive: Unlike some anxiolytic medications (e.g., benzodiazepines), CBD is not associated with a risk of dependence or addiction.
- Broad Spectrum Effects: CBD’s multi-target effects may provide benefits across various symptoms associated with anxiety and depression, potentially offering a more holistic approach to treatment.
However, it’s important to note that while CBD shows promise, it should not be considered a replacement for established treatments without proper medical supervision. More research is needed to fully understand CBD’s efficacy compared to traditional medications and to establish optimal dosing and treatment protocols.
CBD and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a complex psychiatric condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Recent research has explored the potential of CBD in managing PTSD symptoms, with promising results in several key areas.
Effects on Fear Extinction and Memory Reconsolidation
CBD has shown potential in modulating fear-related memories, which are central to PTSD:
- Fear Extinction Enhancement: Studies suggest that CBD may enhance the extinction of fear memories, a process crucial for overcoming trauma-related fears. This effect is thought to be mediated through CBD’s interaction with the endocannabinoid system and its influence on brain regions involved in fear processing, such as the amygdala.
- Memory Reconsolidation Disruption: CBD may interfere with the reconsolidation of traumatic memories, potentially reducing their emotional impact. This process involves briefly reactivating a memory and then modifying it, which could help in reducing the intensity of traumatic recollections.
- Contextual Fear Processing: Research indicates that CBD may help in the processing of contextual fear, which is often impaired in PTSD. This could aid in distinguishing between safe and threatening contexts, a crucial aspect of PTSD recovery.
Reduction of Hyperarousal Symptoms
Hyperarousal is a key symptom cluster in PTSD, characterized by heightened anxiety, irritability, and hypervigilance. CBD may help in managing these symptoms:
- Anxiety Reduction: As discussed earlier, CBD has anxiolytic properties that could help in reducing the overall anxiety levels associated with PTSD.
- Sleep Improvement: CBD has been shown to potentially improve sleep quality, which is often disrupted in individuals with PTSD. Better sleep can contribute to reduced hyperarousal and improved daytime functioning.
- Stress Response Modulation: CBD’s influence on the endocannabinoid system may help in regulating the stress response, potentially reducing the exaggerated startle response and hypervigilance characteristic of PTSD.
Potential as an Adjunct Therapy for PTSD
While more research is needed, CBD shows promise as a potential adjunct therapy for PTSD:
- Complementary to Psychotherapy: CBD could potentially enhance the effects of evidence-based psychotherapies for PTSD, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), by facilitating fear extinction and memory processing.
- Symptom Management: CBD may help in managing various PTSD symptoms, including anxiety, sleep disturbances, and hyperarousal, potentially improving overall treatment outcomes.
- Reduced Side Effects: Compared to some traditional PTSD medications, CBD may offer a more favorable side effect profile, potentially improving treatment adherence and quality of life.
- Neuroplasticity Enhancement: CBD’s potential to promote neuroplasticity could support the brain changes necessary for recovery from PTSD.
While these findings are promising, it’s important to note that research on CBD for PTSD is still in its early stages. Larger, well-controlled clinical trials are needed to establish CBD’s efficacy, optimal dosing, and long-term safety in PTSD treatment.
CBD’s Role in Autism Spectrum Disorders
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition characterized by challenges in social communication and interaction, as well as restricted and repetitive behaviors. Recent research has explored the potential of CBD in managing various symptoms associated with ASD.
Impact on Social Behavior and Communication
While research is still in its early stages, some studies suggest that CBD may have potential benefits for social behavior and communication in individuals with ASD:
- Anxiety Reduction: CBD’s anxiolytic properties may help reduce social anxiety, potentially facilitating improved social interactions for individuals with ASD.
- Improved Social Responsiveness: Some preliminary studies have reported improvements in social responsiveness scales following CBD treatment in children with ASD, although more research is needed to confirm these findings.
- Communication Enhancement: Anecdotal reports and small-scale studies have suggested potential improvements in communication skills in some individuals with ASD following CBD treatment, possibly due to reduced anxiety and improved overall functioning.
Reduction of Repetitive Behaviors
Repetitive behaviors are a core symptom of ASD, and some research suggests that CBD may help in reducing their frequency and intensity:
- Stereotypic Behaviors: Preliminary studies have reported reductions in stereotypic behaviors (repetitive, purposeless actions) in some individuals with ASD following CBD treatment.
- Self-Injurious Behaviors: There have been reports of decreased self-injurious behaviors in individuals with ASD treated with CBD, although more research is needed to confirm these effects.
- Behavioral Flexibility: CBD’s potential to enhance neuroplasticity may contribute to increased behavioral flexibility, potentially reducing rigid or repetitive behavior patterns.
Challenges and Opportunities in ASD Research
While the potential of CBD in ASD treatment is promising, several challenges and opportunities exist in this field of research:
- Heterogeneity of ASD: The diverse nature of ASD presents challenges in studying CBD’s effects, as responses may vary widely among individuals. Future research should focus on identifying subgroups that may benefit most from CBD treatment.
- Dosing and Administration: Determining optimal dosing regimens and methods of administration for individuals with ASD, particularly children, remains a challenge. More research is needed to establish safe and effective protocols.
- Long-term Effects: Studies investigating the long-term effects of CBD use in individuals with ASD are crucial, particularly given the potential for lifelong treatment.
- Mechanism of Action: Further research is needed to elucidate the precise mechanisms by which CBD may influence ASD symptoms, which could lead to more targeted and effective treatments.
- Combination Therapies: Exploring the potential of CBD as an adjunct to established behavioral and educational interventions for ASD could yield valuable insights into comprehensive treatment approaches.
- Biomarker Identification: Identifying biomarkers that predict responsiveness to CBD treatment could help in personalizing therapy for individuals with ASD.
While the research on CBD’s role in ASD is still emerging, it represents an exciting area of investigation with the potential to improve the lives of individuals with ASD and their families. However, it’s crucial to approach this topic with caution and to emphasize the need for more rigorous, large-scale clinical trials to establish the safety and efficacy of CBD in ASD treatment.
CBD shows promising potential in various aspects of neuroprotection and mental health, including anxiety, depression, PTSD, and ASD. Its multi-faceted mechanisms of action, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, coupled with its ability to modulate neurotransmitter systems and enhance neuroplasticity, make it an intriguing subject for further research.
However, while the preliminary findings are encouraging, more comprehensive clinical studies are needed to fully understand CBD’s therapeutic potential, optimal dosing regimens, and long-term safety profile in these applications. As research progresses, CBD may emerge as a valuable tool in the treatment of various neurological and psychiatric conditions, potentially offering new hope for individuals struggling with these challenging disorders.
Modulation of Brain Activity and Connectivity
Recent neuroimaging studies have provided valuable insights into how cannabidiol (CBD) influences brain function and connectivity. Studies employing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques, such as functional MRI (fMRI), have assessed changes in cerebral blood flow and neural connectivity in response to CBD. These findings are crucial for understanding the neurobiological basis of CBD’s therapeutic effects and its potential applications in various neurological and psychiatric conditions.
CBD’s Impact on Resting State Brain Function
Resting state functional connectivity (RSFC) studies have revealed that CBD can significantly alter brain activity patterns even when the brain is not engaged in specific tasks. Studies using advanced imaging techniques like Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) and functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) have measured regional cerebral blood flow and assessed brain activity in various states or during cognitive tasks:
- Default Mode Network (DMN): CBD has been shown to modulate activity within the DMN, a network associated with self-referential thinking and mind-wandering. Some studies suggest that CBD may normalize DMN connectivity in conditions where it is disrupted, such as in anxiety disorders.
- Salience Network: Research indicates that CBD can influence the salience network, which is involved in detecting and filtering salient stimuli. This modulation may contribute to CBD’s effects on attention and cognitive processing.
- Limbic System Connectivity: CBD has been found to alter functional connectivity between limbic structures, such as the amygdala and the prefrontal cortex. This may underlie CBD’s anxiolytic and emotion-regulating effects.
- Hippocampal Connectivity: Prolonged CBD exposure has been shown to affect the resting-state functional connectivity of the hippocampus, a region crucial for memory formation and emotional processing.
These alterations in resting state brain function may contribute to CBD’s therapeutic effects across various neurological and psychiatric conditions.
Enhancement of Cognitive Functions
While research on CBD’s cognitive effects is still emerging, some studies suggest potential benefits:
- Attention and Executive Function: CBD may enhance attentional control and executive functioning, possibly through its modulation of prefrontal cortex activity.
- Memory: Some studies indicate that CBD might have memory-enhancing effects, particularly in conditions where memory is impaired. This could be related to CBD’s influence on hippocampal function and neurogenesis.
- Processing Speed: There is preliminary evidence suggesting that CBD might improve processing speed in certain cognitive tasks, although more research is needed to confirm these effects.
It’s important to note that the cognitive effects of CBD may vary depending on the dose, the individual’s baseline cognitive function, and the presence of any underlying neurological or psychiatric conditions.
Influence on Emotional Processing Networks
CBD has been shown to modulate brain regions and networks involved in emotional processing:
- Amygdala Reactivity: Studies have demonstrated that CBD can reduce amygdala activation in response to emotional stimuli, which may contribute to its anxiolytic effects.
- Prefrontal-Limbic Connectivity: CBD has been found to alter the functional connectivity between the prefrontal cortex and limbic regions, potentially enhancing emotional regulation.
- Negative Bias Reduction: Some research suggests that CBD may reduce negative bias in emotional processing, which could have implications for mood disorders.
These effects on emotional processing networks provide a neurobiological basis for CBD’s potential therapeutic applications in anxiety disorders, depression, and PTSD.
CBD and Epilepsy
Epilepsy is one of the neurological conditions where CBD has shown the most promising results, leading to FDA-approved treatments. Various studies indicate that CBD has shown potential benefits in reducing seizure frequency and influencing electrical activity in the brains of patients suffering from treatment-resistant epilepsy.
Mechanisms of Anticonvulsant Effects
CBD exhibits anticonvulsant properties through various mechanisms:
- Ion Channel Modulation: CBD interacts with several ion channels implicated in epilepsy, including voltage-gated sodium channels and T-type calcium channels. This modulation can reduce neuronal excitability and seizure susceptibility.
- GABA Enhancement: CBD may enhance GABAergic transmission, the primary inhibitory system in the brain, which can help suppress excessive neuronal firing.
- Adenosine Signaling: CBD has been shown to inhibit the uptake of adenosine, an endogenous anticonvulsant, potentially contributing to its seizure-suppressing effects.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: The anti-inflammatory properties of CBD may contribute to its anticonvulsant effects, as inflammation is increasingly recognized as a factor in epileptogenesis.
Clinical Trials and FDA-Approved Treatments
The efficacy of CBD in treating epilepsy has been demonstrated in several clinical trials:
- Dravet Syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome: CBD has shown significant efficacy in reducing seizure frequency in these severe forms of childhood-onset epilepsy.
- Epidiolex Approval: In 2018, the FDA approved Epidiolex, a purified CBD oral solution, for the treatment of seizures associated with Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome in patients two years of age and older.
- Tuberous Sclerosis Complex: In 2020, the FDA expanded the approval of Epidiolex to include the treatment of seizures associated with tuberous sclerosis complex.
These approvals represent a significant milestone in the medical use of CBD and have paved the way for further research into its potential applications in other forms of epilepsy.
Potential for Drug-Resistant Epilepsies
CBD shows promise in treating drug-resistant epilepsies, which are characterized by seizures that do not respond adequately to conventional antiepileptic drugs:
- Add-on Therapy: Studies have shown that CBD, when used as an add-on therapy to existing antiepileptic drugs, can significantly reduce seizure frequency in patients with drug-resistant epilepsy.
- Synergistic Effects: CBD may have synergistic effects with certain antiepileptic drugs, potentially enhancing their efficacy while allowing for lower doses and reduced side effects.
- Novel Mechanisms: CBD’s unique mechanisms of action may provide a new avenue for treating seizures that are resistant to conventional antiepileptic drugs.
While these findings are promising, more research is needed to fully understand the long-term efficacy and safety of CBD in drug-resistant epilepsies, as well as to optimize dosing and treatment protocols.
CBD’s Potential in Neurodegenerative Diseases
Neurodegenerative diseases represent a significant health burden, and current treatments are often limited in their efficacy. CBD’s neuroprotective properties have sparked interest in its potential applications in these conditions.
Neuroprotective Effects in Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is characterized by progressive cognitive decline, amyloid-β plaques, and neurofibrillary tangles. CBD shows promise in addressing several aspects of AD pathology:
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: CBD’s anti-inflammatory properties may help reduce neuroinflammation, a key factor in AD progression.
- Antioxidant Properties: As a potent antioxidant, CBD may protect neurons from oxidative stress, which is elevated in AD.
- Amyloid-β Reduction: Some studies suggest that CBD may help reduce amyloid-β production and aggregation, potentially slowing disease progression.
- Neurogenesis Promotion: CBD’s potential to promote neurogenesis in the hippocampus could help counteract the neuronal loss seen in AD.
While these preclinical findings are promising, more clinical research is needed to establish CBD’s efficacy in treating AD in humans.
CBD and Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is characterized by motor symptoms such as tremor, rigidity, and bradykinesia, as well as non-motor symptoms including anxiety, depression, and sleep disturbances. CBD has shown potential in addressing various aspects of PD:
- Motor Symptom Improvement: Some studies suggest that CBD may help improve motor symptoms in PD, possibly through its effects on the basal ganglia and its anti-inflammatory properties.
- Non-motor Symptom Management: CBD has shown promise in managing non-motor symptoms of PD. A recent study reported that some participants with PD who were taking CBD/THC experienced improved pain levels, sleep, and reductions in anxiety.
- Neuroprotection: CBD’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties may offer neuroprotection, potentially slowing the progression of dopaminergic neuron loss in PD.
- Quality of Life Enhancement: By addressing both motor and non-motor symptoms, CBD may help improve overall quality of life for individuals with PD.
While these findings are encouraging, larger, well-controlled clinical trials are needed to establish the efficacy and safety of CBD in PD treatment.
Potential Applications in Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease characterized by demyelination and neurodegeneration. CBD’s properties make it a promising candidate for MS treatment:
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: CBD’s ability to modulate the immune system and reduce inflammation may help in managing the autoimmune aspects of MS.
- Neuroprotection: The neuroprotective properties of CBD could potentially slow the progression of neurodegeneration in MS.
- Symptom Management: CBD may help manage various MS symptoms, including pain, spasticity, and sleep disturbances.
- Remyelination Potential: Some preclinical studies suggest that CBD might promote remyelination, although more research is needed to confirm this effect in humans.
While a CBD/THC combination (Sativex) is approved in some countries for MS-related spasticity, more research is needed to fully understand the potential of CBD alone in MS treatment.
CBD and Psychotic Symptoms
The potential antipsychotic properties of CBD have garnered significant interest in recent years, particularly given the limitations and side effects associated with traditional antipsychotic medications.
Antipsychotic Properties of CBD
Several mechanisms have been proposed for CBD’s potential antipsychotic effects:
- Dopamine Modulation: Unlike THC, which can increase dopamine release and potentially exacerbate psychotic symptoms, CBD may have a stabilizing effect on the dopaminergic system.
- Endocannabinoid System Regulation: CBD’s interaction with the endocannabinoid system may help regulate neurotransmitter systems implicated in psychosis.
- NMDA Receptor Modulation: CBD may influence NMDA receptors, which are involved in glutamatergic signaling and have been implicated in schizophrenia.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Given the growing evidence linking neuroinflammation to psychosis, CBD’s anti-inflammatory properties may contribute to its antipsychotic effects.
Comparison with Traditional Antipsychotics
While research is still ongoing, CBD shows some potential advantages compared to traditional antipsychotics:
- Side Effect Profile: CBD generally has a more favorable side effect profile compared to many antipsychotic medications, which can cause significant metabolic, cardiovascular, and neurological side effects.
- Cognitive Function: Unlike some antipsychotics that may impair cognitive function, CBD has shown potential cognitive-enhancing effects in some studies.
- Addiction Potential: CBD is not associated with addiction or dependence, unlike some antipsychotic medications that can lead to physical dependence.
- Broader Symptom Coverage: CBD may address a wider range of symptoms associated with psychotic disorders, including anxiety and depression, which are often comorbid with psychosis.
However, it’s important to note that while these comparisons are promising, more extensive clinical trials are needed to fully establish CBD’s efficacy and safety profile in treating psychosis.
Potential for Early Intervention in Psychosis
One of the most exciting areas of research is the potential use of CBD in the early stages of psychosis or in individuals at high risk of developing psychotic disorders:
- Neuroprotection: CBD’s neuroprotective properties may help prevent or slow the neurological changes associated with the development of psychosis.
- Symptom Attenuation: Early intervention with CBD might help attenuate prodromal symptoms, potentially preventing or delaying the onset of full-blown psychosis.
- Cognitive Preservation: By potentially preserving cognitive function, CBD could help maintain functional capacity in individuals at risk of psychosis.
- Stress Reduction: Given the role of stress in psychosis onset, CBD’s anxiolytic properties may be particularly beneficial in early intervention strategies.
While these potential applications are promising, it’s crucial to emphasize that more research, particularly long-term clinical trials, is needed to fully understand the efficacy and safety of CBD in early psychosis intervention.
CBD’s effects on brain activity and its potential applications in neurological disorders represent a rapidly evolving field of research. From its impact on brain connectivity and cognitive function to its promising results in epilepsy treatment and potential in neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders, CBD continues to reveal new therapeutic possibilities.
However, while the preliminary findings are encouraging, it’s important to approach these potential applications with cautious optimism. More comprehensive, large-scale clinical trials are needed to fully establish the efficacy, optimal dosing, and long-term safety of CBD across various neurological and psychiatric conditions. As research progresses, CBD may emerge as a valuable tool in the treatment of a wide range of brain-related disorders, potentially offering new hope for patients and clinicians alike.
Future Directions, Safety, and Practical Considerations
Current Therapeutic Applications and Future Research
As the field of CBD research continues to evolve, new therapeutic applications are being explored, and existing ones are being refined. This section examines the current state of CBD research and its future directions.
Ongoing Clinical Trials
The landscape of CBD clinical trials is rapidly expanding, reflecting the growing interest in its therapeutic potential:
- Neurological Disorders: Numerous trials are investigating CBD’s efficacy in conditions such as epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, and Parkinson’s disease. For instance, a recent study explored the effects of CBD on anxiety and tremor in Parkinson’s disease patients.
- Psychiatric Conditions: Clinical trials are underway to assess CBD’s potential in treating anxiety disorders, depression, and PTSD. Harvard Health reports that studies and clinical trials are exploring the common claim that CBD can reduce anxiety.
- Pain Management: Several trials are examining CBD’s analgesic properties in various types of pain, including neuropathic pain and chronic pain conditions.
- Sleep Disorders: Research is ongoing to evaluate CBD’s effects on sleep quality and disorders like insomnia.
- Addiction: Clinical trials are investigating CBD’s potential in treating substance use disorders, including opioid addiction.
These trials are crucial for establishing the efficacy and safety of CBD across various conditions and will help inform future treatment guidelines.
Emerging Areas of CBD Research
Several promising areas of CBD research are emerging:
- Neuroprotection: Studies are exploring CBD’s potential neuroprotective effects in conditions like traumatic brain injury and stroke.
- Autism Spectrum Disorders: Research is ongoing to evaluate CBD’s effects on symptoms associated with autism spectrum disorders.
- Cardiovascular Health: Preliminary studies suggest potential benefits of CBD in cardiovascular health, prompting further investigation.
- Metabolic Disorders: Some research is exploring CBD’s potential effects on metabolism and its possible role in managing conditions like diabetes.
- Cancer-Related Symptoms: While not a cancer treatment itself, CBD is being studied for its potential to alleviate cancer-related symptoms and treatment side effects.
Challenges in CBD Research Methodology
Despite the growing interest in CBD research, several challenges persist:
- Standardization: The lack of standardization in CBD products used in research can make it difficult to compare results across studies.
- Dosing Protocols: Establishing optimal dosing protocols for different conditions remains a challenge, as effective doses can vary widely.
- Long-Term Effects: More longitudinal studies are needed to understand the long-term effects of CBD use.
- Placebo Effect: Given the high public interest in CBD, controlling for placebo effects in clinical trials can be challenging.
- Regulatory Hurdles: The complex legal status of cannabis and its derivatives can create obstacles for researchers seeking to conduct large-scale clinical trials.
Addressing these challenges will be crucial for advancing CBD research and translating findings into clinical applications.
Safety Profile and Side Effects of CBD
Understanding the safety profile and potential side effects of CBD is essential for its responsible use in therapeutic contexts.
Common Side Effects and Their Mechanisms
While CBD is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects in some individuals:
- Fatigue and Drowsiness: CBD may cause drowsiness, particularly at higher doses. This effect may be due to its interaction with adenosine receptors.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Some users report diarrhea or changes in appetite. These effects may be related to CBD’s interaction with the endocannabinoid system in the gut.
- Dry Mouth: CBD can reduce saliva production, possibly due to its interaction with cannabinoid receptors in the salivary glands.
- Changes in Liver Enzymes: CBD may affect liver enzyme levels, particularly in individuals taking high doses or those with pre-existing liver conditions.
- Mood Changes: While CBD is often used to improve mood, some individuals may experience irritability or other mood changes.
It’s important to note that these side effects are generally mild and often resolve with continued use or dose adjustment.
Drug Interactions and Contraindications
CBD can interact with various medications, primarily due to its effect on liver enzymes:
- Cytochrome P450 Enzymes: CBD inhibits certain cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are responsible for metabolizing many medications. This can lead to higher blood levels of these medications, potentially increasing their effects and side effects.
- Blood Thinners: CBD may increase the effects of blood thinners like warfarin, necessitating close monitoring of coagulation parameters.
- Antiepileptic Drugs: CBD can interact with some antiepileptic drugs, potentially affecting their blood levels. This interaction is particularly relevant given CBD’s use in epilepsy treatment.
- Sedatives: CBD may enhance the effects of sedative medications, potentially increasing drowsiness and sedation.
Individuals taking any medications should consult with a healthcare provider before using CBD to avoid potential interactions.
Long-Term Safety Considerations
While short-term use of CBD appears to be generally safe, long-term safety data is still limited:
- Cumulative Effects: More research is needed to understand any potential cumulative effects of long-term CBD use.
- Developmental Effects: The long-term effects of CBD use during pregnancy or adolescence are not yet fully understood and require further study.
- Tolerance and Dependence: While CBD is not associated with addiction, more research is needed to understand if tolerance develops with long-term use.
- Impact on Endocannabinoid System: The long-term effects of CBD on the body’s endocannabinoid system are not yet fully elucidated.
Ongoing research and post-market surveillance will be crucial for establishing the long-term safety profile of CBD.
Practical Aspects of CBD Use
As CBD becomes more widely available, understanding the practical aspects of its use is essential for both consumers and healthcare providers.
Determining Appropriate Dosage
Determining the right CBD dosage can be challenging due to several factors:
- Individual Variability: Factors such as body weight, metabolism, and the condition being treated can all affect the optimal CBD dose.
- Condition-Specific Dosing: Different conditions may require different CBD doses. For example, doses used in epilepsy treatment are often higher than those used for anxiety.
- Start Low and Go Slow: A common approach is to start with a low dose and gradually increase it until the desired effect is achieved.
- Consultation with Healthcare Providers: Given the potential for drug interactions and individual variability, consulting with a healthcare provider is recommended for determining appropriate CBD dosage.
Methods of Administration and Bioavailability
CBD can be administered through various methods, each with different bioavailability:
- Oral Ingestion: CBD oils, capsules, and edibles are common oral forms. However, oral CBD has relatively low bioavailability (estimated at 6-19%) due to first-pass metabolism in the liver.
- Sublingual Administration: Holding CBD oil under the tongue allows for absorption through the oral mucosa, potentially increasing bioavailability compared to oral ingestion.
- Inhalation: Vaporizing CBD provides rapid onset and higher bioavailability but may have respiratory risks.
- Topical Application: CBD creams and lotions are used for localized effects but have limited systemic absorption.
- Transdermal Patches: These provide steady, long-lasting CBD delivery but are less common.
Recent research is exploring strategies to improve CBD bioavailability, including the use of nanoemulsions and other advanced delivery systems.
Selecting High-Quality CBD Products
With the proliferation of CBD products, selecting high-quality options is crucial:
- Third-Party Testing: Look for products that have been tested by independent laboratories for potency and purity.
- Certificate of Analysis (COA): A COA provides detailed information about the product’s cannabinoid content and the presence of any contaminants.
- Source of CBD: Consider products made from organically grown hemp to minimize exposure to pesticides and other contaminants.
- Extraction Method: CO2 extraction is generally considered the cleanest method for extracting CBD from hemp.
- Full-Spectrum vs. Isolate: Full-spectrum products contain other cannabinoids and terpenes, which may provide additional benefits through the “entourage effect.”
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
The rapidly evolving landscape of CBD use and research raises important ethical and regulatory considerations.
Ethical Implications of CBD Research and Use
Several ethical considerations surround CBD research and use:
- Informed Consent: Ensuring that research participants and consumers are fully informed about the potential risks and benefits of CBD use.
- Equity in Access: Addressing disparities in access to CBD-based treatments, particularly for FDA-approved medications like Epidiolex.
- Use in Vulnerable Populations: Careful consideration of CBD use in pregnant women, children, and individuals with certain medical conditions.
- Balancing Benefits and Risks: Weighing the potential benefits of CBD against known and unknown risks, particularly in conditions where conventional treatments are limited.
Regulatory Challenges and Future Directions
The regulatory landscape for CBD is complex and evolving:
- FDA Oversight: The FDA is working to develop a regulatory framework for CBD products, balancing consumer access with safety concerns.
- Quality Control: Implementing standardized quality control measures for CBD products to ensure consistency and safety.
- Labeling Requirements: Developing clear labeling requirements to help consumers make informed choices.
- International Harmonization: Working towards harmonized regulations across countries to facilitate research and trade.
Public Health and Policy Implications
The widespread use of CBD has significant public health and policy implications:
- Education: Developing public education initiatives to inform consumers about the potential benefits and risks of CBD use.
- Healthcare Integration: Integrating CBD into mainstream healthcare, including training for healthcare providers.
- Research Funding: Allocating resources for comprehensive CBD research to address knowledge gaps.
- Workplace Policies: Developing policies regarding CBD use in the workplace, particularly in safety-sensitive positions.
- Driving Laws: Addressing the potential impact of CBD use on driving and developing appropriate policies.
Frequently Asked Questions About CBD and Brain Function
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Does CBD get you high?
No, CBD does not produce the intoxicating effects associated with THC. It is non-psychoactive and does not impair cognitive function when used as directed.
Is CBD addictive?
Current evidence suggests that CBD is not addictive and does not produce dependence. In fact, some studies are exploring its potential in treating substance use disorders.
Does CBD work immediately?
The onset of CBD’s effects can vary depending on the method of administration and the individual. While some people may feel effects quickly, others may require several days or weeks of consistent use to notice benefits.
Expert Insights on CBD’s Potential
Experts in the field of cannabinoid research generally agree that CBD shows promise for various conditions, but more research is needed:
- Dr. Yasmin Hurd, Director of the Addiction Institute at Mount Sinai, notes that CBD shows potential in treating anxiety and addiction but emphasizes the need for more clinical trials.
- Dr. Ethan Russo, a neurologist and cannabis researcher, highlights CBD’s potential in treating epilepsy and its possible neuroprotective effects.
- Dr. Raphael Mechoulam, known as the “father of cannabis research,” has emphasized the need for more studies on CBD’s mechanisms of action and potential therapeutic applications.
Resources for Further Information
For those seeking more information about CBD and its effects on brain function, the following resources may be helpful:
- The National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH) provides evidence-based information on CBD research.
- Project CBD offers a comprehensive database of scientific studies on CBD and other cannabinoids.
- The International Association for Cannabinoid Medicines (IACM) provides updates on clinical studies and research findings related to medical cannabis and cannabinoids.
- ClinicalTrials.gov lists ongoing clinical trials involving CBD, allowing interested individuals to stay updated on current research.
In conclusion, while CBD shows significant promise in various therapeutic applications, particularly in neurological and psychiatric conditions, much remains to be learned about its long-term effects, optimal dosing, and full range of potential applications.
As research progresses and regulatory frameworks evolve, it’s crucial for consumers, healthcare providers, and policymakers to stay informed about the latest developments in CBD science and policy.
The future of CBD research and use holds exciting possibilities, but it must be approached with scientific rigor, ethical consideration, and a commitment to public health and safety.