- Key Takeaways
- What is Cannabigerolic Acid (CBGA)?
- The Biosynthesis of CBGA: A Biosynthetic Precursor
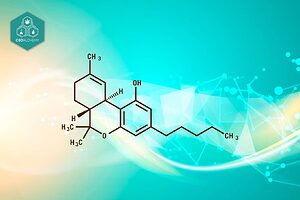
- The CBGA Molecule
- Potential Health Benefits of CBGA
- Industrial Applications of Cannabigerolic Acid
- CBGA vs. Other Cannabinoids
- How to Use CBGA Products
- Research and Studies on CBGA
- Legal Status of CBGA
- Summary
- Frequently Asked Questions
Cannabigerolic acid, commonly referred to as CBGA, is a pivotal compound in the cannabis plant. Often hailed as the ‘mother of all cannabinoids,’ it serves as the foundation from which significant cannabinoids such as THC and CBD are synthesized. This piece delves into the characteristics that distinguish CBGA, its potential therapeutic advantages, and how it stands apart from other cannabinoids within the plant. Both CBGA and CBG offer unique therapeutic benefits, making them significant in the treatment of various conditions.
Key Takeaways
- Cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) is a crucial precursor for the synthesis of major cannabinoids and plays a significant role in the overall cannabinoid content of the cannabis plant.
- CBGA has demonstrated potential health benefits, including anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties, with promising applications for cardiovascular health and metabolic disorders.
- The legal status of CBGA is supported by the 2018 Farm Bill, permitting its production and sale, although consumers should verify local regulations regarding its use.
- Despite its potential, minimal research has been conducted on CBGA to date.
What is Cannabigerolic Acid (CBGA)?
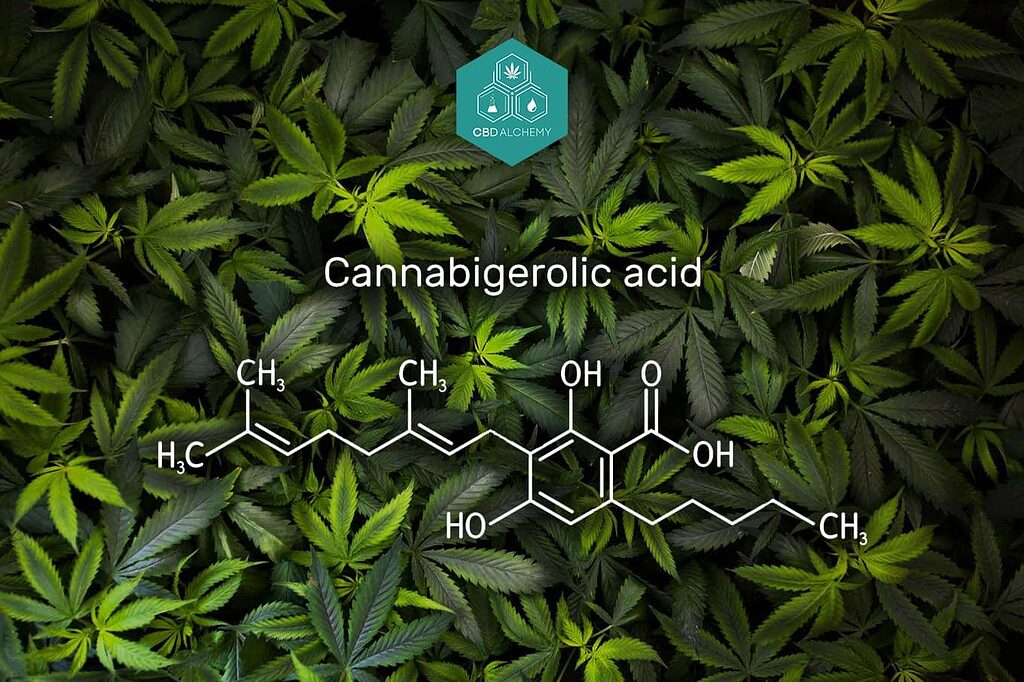
The cannabis plant produces a cannabinoid known as cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), which, despite being less prominent than others, is crucial for the generation of key cannabinoids. Cannabigerolic acid has been dubbed the “mother” because it serves as a biosynthetic precursor to essential compounds like tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA), cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), and cannabichromenic acid (CBCA) along with other acidic cannabinoids. Without CBGA’s presence, these important cannabinoids would not be formed.
Valued for its transformative abilities, CBGA can evolve into various other compounds through an enzymatic process that occurs within the cannabis plant itself. Upon encountering certain enzymes in the plant, CBGA can convert into several major cannabinoids such as CBG, CBD, and THC — illustrating why this compound is so fundamental to enriching the cannabinoid content within cannabis flowers. CBGA research highlights its foundational role in the development of cannabinoids and its potential to disrupt the hemp industry.
As interest in understanding more about what makes up cannabis intensifies amongst researchers around the world, the unique role played by CPBA during this process is increasingly coming under spotlight. Highlighting how significant CPBA research really could be when delving deeper into what shapes both development and production of different cannabinoid profiles across strains/plants alike.
With this burgeoning awareness comes new avenues for scientific exploration and consumer product innovation centered on cannabigerolica Acid – opening doors wide open toward harnessingpotnetial therapeutic advantages held within one of the most intriguing elements comprising Cannabis sativa L.
The Biosynthesis of CBGA: A Biosynthetic Precursor
Within the cannabis plant, the generation of cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) involves a sophisticated biochemical process. The starting materials, olivetolic acid and geranyl pyrophosphate, are transformed through enzymatic reactions led by specialized enzymes. A notable step in this pathway is when olivetolic acid receives a prenyl group—a reaction facilitated by an aromatic prenyltransferase enzyme.
The biosynthesis pathway for cannabinoids prominently features olivetolic acid cyclase—essential for creating olivetolic acid, which acts as a building block for cannabinoid production. Following that critical stage, geranyldiphosphate:olivetolate-geranyltransferase (GOT) facilitates CBGA formation while another important compound required in the synthesis of CBGA —geranyl pyrophosphate— is produced via geranyl pyrophosphate synthase action. This complex series of processes underscores how intricate and refined cannabinoid synthesis within the cannabis plant truly is.
In female cannabis flowers’ glandular trichomes—which function akin to miniature chemical laboratories—the creation of cannabinoids like CBGA unfolds as part of natural protective measures called phytoprotectants. It’s here where these valuable compounds, including various other cannabinoids, are synthesized. Thereby establishing glandular trichomes’ pivotal role in contributing to the overall cannabinoid profile present within natural products derived from cannabis plants. Producing CBGA specifically proves fundamental given its precursor status influencing eventual cannabinoid content levels throughout different strains and specimens of this botanical species. The mechanisms involved in converting CBGA into THCA are critical for its pharmaceutical and research uses.
The CBGA Molecule
The CBGA molecule is a naturally occurring compound found in the cannabis plant, playing a pivotal role in the biosynthesis of other cannabinoids. As the acidic form of cannabigerol (CBG), CBGA is considered a biosynthetic precursor, meaning it is the foundational compound from which other cannabinoids are synthesized. This unique chemical structure sets it apart from other cannabinoids, making it a subject of significant interest in both scientific and industrial circles.
Research on the CBGA molecule is ongoing, with scientists delving into its potential therapeutic benefits and industrial applications. The molecule’s unique properties make it a promising candidate for the treatment of various diseases and disorders. For instance, its role in inhibiting certain enzymes and receptors in the body could pave the way for new treatments for metabolic disorders and inflammatory conditions.
The CBGA molecule’s potential extends beyond therapeutic uses. Its unique chemical structure and properties make it an ideal candidate for various industrial applications, including the production of pharmaceuticals and research chemicals. As research continues, the full scope of the CBGA molecule’s potential is gradually being unveiled, promising exciting developments in both medicine and industry.
Potential Health Benefits of CBGA

Emerging studies indicate that cannabigerolic acid, commonly referred to as CBGA, is being recognized for its array of potential health advantages such as anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and neuroprotective effects. Current research points towards the efficacy of CBGA in addressing kidney inflammation and injury, along with controlling inflammatory bowel diseases and inhibiting polyp proliferation. CBGA appears to have unique effects, such as potentially stimulating properties and significant therapeutic benefits.
Given these benefits, cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) is increasingly considered a valuable prospect for diverse medicinal uses where it seems to exert substantial influence.
Cardiovascular Health
CBGA shows promise in alleviating cardiovascular disease, particularly in diabetic patients. One of the key mechanisms behind this benefit is CBGA’s ability to inhibit aldose reductase, an enzyme that contributes to complications related to cardiovascular health. Inhibiting this enzyme with CBGA may reduce cardiovascular complications linked to diabetes, suggesting potential pharmaceutical applications for this cannabinoid.
CBGA’s inhibition of aldose reductase is particularly relevant for diabetic cardiovascular health. This action can reduce complications faced by diabetic patients, positioning CBGA as a valuable compound for further research and therapeutic use in managing diabetes-related cardiovascular issues.
Metabolic Disorders
Research indicates that CBGA acts as a dual agonist for PPAR and PPAR, receptors that play a crucial role in lipid metabolism and fat storage. Activating these receptors, CBGA may enhance lipid metabolism and reduce fat buildup, offering potential benefits for managing metabolic conditions. This dual agonist action highlights the biochemical effects of CBGA and its potential role in treating metabolic disorders.
CBGA’s effect on metabolism is evident in its capacity to manage metabolic disorders through biochemical actions. Activating PPAR receptors, CBGA could be a valuable tool in addressing metabolic issues, marking it as a significant area for future research and therapeutic applications.
Industrial Applications of Cannabigerolic Acid
Cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) is not only a cornerstone in the biosynthesis of other cannabinoids but also holds significant promise for various industrial applications. One of the primary uses of CBGA is in the production of pharmaceuticals and research chemicals. As a starting material, CBGA is essential for synthesizing other cannabinoids such as tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) and cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), which are crucial for developing a wide range of therapeutic products.
The acidic form of CBGA makes it particularly suitable for the production of conjugate acids, which have various industrial applications. These conjugate acids are used in the formulation of natural products, including cosmetics and food additives, where they contribute to the product’s stability and efficacy.
Moreover, the potential of CBGA in industrial applications is continually being explored. Researchers are investigating its use in creating more efficient and sustainable production processes for cannabinoids and other natural products. The versatility of CBGA, combined with its foundational role in cannabinoid biosynthesis, makes it a valuable asset in the industrial sector.
As the understanding of CBGA’s properties and potential applications grows, it is likely to become an increasingly important component in various fields, from pharmaceuticals to consumer goods. This ongoing research and development promise to unlock new uses and benefits of CBGA, further solidifying its place in both the scientific and industrial landscapes.
CBGA vs. Other Cannabinoids

Cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) is a distinctive cannabinoid found in cannabis plants, acting as the precursor to other key cannabinoids. It differs from THC and CBD, which are famous for their psychoactive and calming effects respectively. CBGA does not induce intoxication, but rather delivers slightly stimulating effects. This positions CBGA apart within the world of cannabinoids, providing an alternate array of potential benefits and applications.
Consistency marks the process of cannabinoid biosynthesis across different species of cannabis plants, with CBGA playing a pivotal role. In hemp varieties, it is transformed into CBD whereas marijuana variations convert it first into THCA before becoming THC. These conversion processes illustrate the specific biochemical routes contingent on plant type that highlight the significance and influence of CBGAs presence on shaping the overall profile of cannabinoids within cannabis plants.
CBGA vs. CBG
Through the process of decarboxylation, where a carboxyl group is eliminated at around 110°C, CBGA converts into CBG. This change leads to notable distinctions in chemical structure and characteristics between the two cannabinoids, granting each their own set of effects and advantages.
Although both substances belong to the cannabinoid family, CBGA and CBG are not synonymous. Their distinct properties render them useful for varied therapeutic purposes due to their individual benefits.
CBGA vs. CBD
The chemical structures and impacts of CBGA and CBD are distinctly different. CBGA exists as a carboxylic acid, whereas CBD takes the form of a stabilized cannabinoid, pointing to inherent chemical variances. While CBGA might exert stimulating effects on users, CBD is typically characterized by its calming influence.
These contrasting characteristics underscore the individual attributes of each cannabinoid and hint at their possible applications within diverse therapeutic settings.
How to Use CBGA Products

There are a range of CBGA products on the market, including options such as tinctures and capsules to suit various preferences for ingestion. It’s advisable for newcomers to initiate their regimen with 5mg doses of CBGA twice per day and progressively escalate up to a maximum dose of 40mg if needed. Commonly, dosing guidelines recommend starting with an intake between 10-20mg daily of CBGA, which should be adjusted according to personal tolerance levels and the effects one wishes to achieve.
Tinctures provide a particularly efficient method for consuming CBGA since they allow quick absorption directly into the bloodstream. The impact that CBGA has can greatly differ depending on how it is used. Hence it is crucial for individuals to select an administration route that aligns well with their specific needs and comfort.
For enhanced efficacy when taking both types of cannabinoids, it’s suggested that users maintain at least a four-hour interval between consuming CBD or CBDA products alongside those containing CBGA.
Research and Studies on CBGA

Present studies on CBGA are revealing its potential for therapeutic use and expanding knowledge about its impact. Research has indicated that CBGA can eliminate cells of colon cancer and prevent the growth of polyps, highlighting its possible application in treating cancer.
Research specifically into CBGA is at a nascent phase, with the primary focus being on how it transforms into THCA instead of exploring its intrinsic effects. Despite its potential, minimal research has been conducted on CBGA to date.
Recent Findings
Recent research has underscored the therapeutic promise of CBGA, particularly its capability as a medication sourced from plants. A noteworthy benefit of using CBGA compared to synthetic alternatives is that it typically results in fewer harsh side effects. The efficacy of CBGA in suppressing aldose reductase activity is strongly correlated with dosage amount, suggesting it could play a role in controlling diseases such as diabetes.
Evidence demonstrates that CBGA can block the TRPM7 ion channel, which contributes to its kidney-protective properties. These discoveries offer significant contributions to our understanding of how CBGA functions pharmaceutically and imply potential uses for it concerning renal health and disorders related to metabolism.
Future Directions
Expected future studies on CBGA will delve into its medicinal capabilities for a range of health issues, given its status as a precursor to other cannabinoids. Current research is focused on elucidating how CBGA interacts with TRPM7 and the potential impact this has for managing ailments such as kidney disease and cancer.
As these inquiries move forward, there will probably be an increased emphasis on establishing uniform dosage guidelines and safety evaluations for cannabinoids including CBGA when used medicinally. The progression of this research will illuminate the possible advantages of using CBGA, leading to novel treatment options and cannabinoid-based products.
Legal Status of CBGA
The 2018 Farm Bill has had a significant impact on the legality of CBGA by stating that hemp and its derivatives, including cannabinoids like CBGA, are legal for production, sale, and consumption. This federal law differentiates between cannabis plants with low THC levels—considered as hemp—and those with high THC content in terms of their legal status.
At the federal level, substances derived from hemp such as CBGA are not classified as controlled substances. Local laws can differ so it’s important for buyers to confirm their state regulations before acquiring products containing CBGA. Products containing this cannabinoid are legally permissible to be marketed provided they originate from plants of hemp which contain under 0.3% Delta-9 THC.
Summary
In summary, cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) is a foundational cannabinoid that plays a crucial role in the biosynthesis of major cannabinoids like THC, CBD, and CBC. Its potential health benefits, including anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and neuroprotective properties, make it a promising candidate for various therapeutic applications. As research into CBGA continues, its unique properties and potential uses are becoming increasingly clear.
For those interested in exploring CBGA, there are various products available, including tinctures and capsules, with specific dosage recommendations to ensure optimal effectiveness. With the legal landscape supporting the use of hemp-derived cannabinoids, CBGA products are accessible to consumers, offering a new avenue for exploring the benefits of this fascinating cannabinoid.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of CBGA in the cannabis plant?
CBGA serves as a vital biosynthetic precursor for major cannabinoids such as THC, CBD, and CBC, thereby significantly contributing to cannabinoid production in the cannabis plant.
How does CBGA differ from CBD?
CBGA mainly serves as a compound that stimulates, in contrast to CBD, which is known for its soothing effects.
This essential distinction between their characteristics underscores the unique functions they perform within cannabinoid interactions.
What are some potential health benefits of CBGA?
CBGA could deliver considerable health advantages such as reducing inflammation, combating microbes, and protecting nerve cells. This compound might be beneficial in managing inflammatory kidney diseases, conditions affecting the gut like inflammatory bowel diseases, and disorders related to metabolism.
How should I start using CBGA products?
Initiate the use of CBGA products with a minimal dose, which is recommended to be 5mg administered twice a day. Over time, incrementally elevate this dosage up to a ceiling of 40mg if necessary, although usual initial daily dosages commonly fall between 10mg and 20mg.
By adopting such measured increments in dosage, you can ensure that your body acclimates smoothly to the introduction of CBGA products.
Is CBGA legal to use?
It is essential to confirm with local laws for adherence, yet CBGA can be legally utilized provided that it comes from hemp which holds a Delta-9 THC content of less than 0.3%, in accordance with the 2018 Farm Bill.