Marijuana has significant effects on the mind and body, including the marijuana effects that can be observed. In this article, we will detail its immediate and long-term impacts, including mental effects, physical effects, and potential health risks.
Key Points
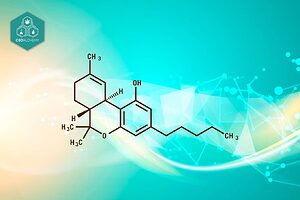
- Marijuana contains more than 100 cannabinoids, with THC being the main psychoactive compound, while CBD acts as a regulator of THC’s effects.
- Marijuana use can cause short-term effects such as euphoria, altered perception and increased appetite, but it also carries risks such as cognitive impairment and long-term mental health problems.
- There are multiple ways to consume marijuana, each with different effects and risks, including smoking, vaping, and consuming edibles, which underscores the importance of choosing informed and responsible methods.
Main components of cannabis

Marijuana is a mixture of dried parts of the marijuana plant, known scientifically as Cannabis sativa, and contains a variety of chemicals that affect the brain. Among the more than 100 cannabinoids present in the plant, the two most studied are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD).
THC is the main psychoactive cannabinoid in cannabis and is responsible for the mental effects experienced when consuming marijuana. This compound causes mental alterations by stimulating areas of the brain containing specific receptors, producing feelings of euphoria and disinhibition.
On the other hand, CBD is not psychoactive and has been found to regulate THC potency and metabolism, which can mitigate some of the more intense effects of THC.
Over the past few decades, there has been a steady increase in the amount of THC in marijuana, which has led to a change in the experience of consumers and the effects they feel. This evolution in the composition of marijuana makes it even more important to understand how these compounds interact with our bodies and what implications they have for our health.
Short-term effects of marijuana use

Marijuana use causes a wide variety of physical and mental effects that can be felt almost immediately when smoked or, later, when ingested. These effects can include:
- an increase in heart rate
- an increase in blood pressure
- alterations in perception
- changes in mood
Common short-term effects include euphoria, relaxation, altered perception and motor coordination, and increased appetite. Each of these effects has different implications for the user, and we will explore each in detail in the following subsections.
Euphoria and relaxation
THC, the main psychoactive compound in marijuana, causes euphoria through overstimulation of areas of the brain containing specific receptors. This overstimulation can lead to disinhibition and unbridled joy, which are some of the immediate effects most sought after by users.
However, this feeling of euphoria and relaxation can vary significantly between individuals and depends on factors such as dosage and tolerance. While some experience a profound sense of calm and well-being, others may feel anxious or paranoid, especially if they consume high doses.
Altered Perception and Motor Coordination
Marijuana can distort the perception of time, making it seem slower, which can be disconcerting to some users. It also negatively affects motor coordination, making movement more difficult and increasing the risk of accidents, especially when driving.
These effects on perception and coordination can be particularly dangerous if combined with other substances, such as alcohol. The combination of marijuana and alcohol can significantly increase the risk of accidents and injuries.
Increased appetite and other physiological effects
One of the most well-known effects of marijuana is increased appetite, often referred to as ‘munchies’. This phenomenon occurs because cannabis use tends to stimulate the appetite of users, making them feel hungrier, which highlights the effects of marijuana.
In addition to increased appetite, marijuana use can cause other physiological effects such as dry mouth, reddening of the eyes and an increase in heart rate. These effects can be uncomfortable, but are generally not dangerous.
Long-term effects of marijuana use

Prolonged marijuana use can have a number of long-term effects on health and well-being. These effects can range from respiratory problems to cognitive impairment and mental disorders. It is important to understand these risks in order to make informed decisions about marijuana use.
Among the most concerning long-term effects are the impact on memory and attention, as well as the link to mental disorders. Below, we will explore each of these effects in detail to better understand how marijuana can affect our long-term health.
Impact on memory and attention
Chronic cannabis use can cause significant problems with memory and learning. The effects of cannabis on memory include deficits in short-term memory and working memory, which can affect planning and inhibitory control.
In adolescents, marijuana use can reduce thinking ability, memory and cognitive functions, affecting their attention. In addition, drug use can have similar effects.
Even in adults, those who stopped using marijuana did not fully recover the mental capacity they had lost, affecting their academic and professional performance.
Relationship with mental disorders
Cannabis is also being investigated for use in the treatment of disorders such as anxiety and inflammatory problems. However, prolonged marijuana use may lead to an increased incidence of emotional disorders such as anxiety and depression.
Research indicates that marijuana may be useful in the treatment of multiple sclerosis and Crohn’s disease. However, it is crucial to consider that prolonged use can lead to deterioration in mental health, including problems such as depression and anxiety.
Risks and complications of marijuana use

Regular marijuana use is not without risks and complications. From dependence to drug interactions, it is essential to be well-informed about these dangers to minimize potential harm.
Some of the most significant risks include dependence and withdrawal, the possibility of overdose and adverse reactions, and drug interactions. We will explore each of these issues in the following subsections to provide a comprehensive overview of the risks associated with marijuana use.
Dependence and withdrawal
Dependence symptoms include irritability, aggressiveness, and sleep problems that improve with cannabis use. Withdrawal symptoms after quitting marijuana usually last between one to two weeks, being worse during the first few days.
Cannabis use is associated with an increased risk of developing mental disorders, especially in genetically predisposed individuals. Factors that increase the likelihood of marijuana dependence include daily use and beginning use in adolescence.
Overdose and adverse reactions
Symptoms of marijuana overdose can include anxiety, panic, and hallucinations. Although there are no reported deaths exclusively from marijuana overdose, these symptoms can result in emergency room visits.
The use of marijuana concentrates, which are more potent, can increase the risk of adverse effects, including tachycardia and other health problems. Despite its low toxicity, excessive marijuana use, especially through edibles, can lead to panic situations and spillover use.
Interaction of CBD and Cannabis with Medications
The use of cannabis and its derivatives, such as CBD, can interact significantly with various medications, which requires special attention and medical monitoring. These interactions occur mainly through two mechanisms:
- Alteration of liver metabolism: Cannabinoids, especially delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), can influence the activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes in the liver. This can alter the speed at which the body processes certain drugs, potentially altering their blood levels and, consequently, their efficacy and side effect profile.
- Pharmacodynamic effects: cannabinoids can interact directly with the mechanisms of action of other drugs, potentiating or antagonizing their effects.
Specific examples of interactions:
- Anticoagulants: Concomitant use of cannabis and anticoagulants such as warfarin may increase the risk of bleeding. This is because cannabinoids may influence clotting factors and potentiate the anticoagulant effect.
- Antidepressants and anxiolytics: CBD may increase serum levels of certain antidepressants and anxiolytics, enhancing their effects and possible side effects.
- Antiepileptics: It has been observed that CBD may interact with antiepileptic drugs such as clobazam, increasing their blood levels.
It is critical that patients inform their physicians about the use of cannabis or CBD, especially if they are taking other medications. Health professionals can adjust dosages or recommend alternatives to minimize the risks of potentially dangerous drug interactions.
Potential therapeutic uses of marijuana

Recently, some governments have begun to recognize cannabis as an option for symptomatic treatment of various medical conditions. More than half of the states in the U.S. have legalized marijuana for medical purposes.
The use of medical cannabis has shown positive results in the management of chronic pain, especially in cases of neuropathic and oncologic pain. Below, we will explore some of the most promising therapeutic uses of marijuana.
Chronic pain relief
Cannabis can decrease pain transmission by activating CB1 receptors in the central nervous system. Products with a balanced combination of THC and CBD are often more effective in treating chronic pain.
The use of vaporized cannabis has been shown to be more effective in relieving pain when combined with opioids in some studies. Marijuana can be effective in treating different types of chronic pain, including neuropathy.
Reducing nausea in chemotherapy
Cannabinoids may help mitigate nausea and vomiting in cancer patients receiving chemotherapy. These compounds can act as serotonin receptor antagonists, thus helping to control nausea in chemotherapy patients.
THC-containing drugs are used to control nausea in cancer patients receiving chemotherapy. Dronabinol and nabilone, both Cannabis derivatives, have been approved to treat nausea and vomiting that do not respond to other antiemetic treatments.
Other medical uses
Cannabidiol (CBD) has been investigated for its potential benefits in the treatment of severe childhood epilepsy. In addition, recent studies suggest that CBD may have applications in the treatment of disorders such as obesity and certain addictions.
Marijuana may interfere with the metabolism of certain medications, altering their effects. Although more research is needed, these potential medical uses of cannabis are promising and may offer valuable therapeutic alternatives in the future.
Marijuana use in different forms
Marijuana consumption can be accomplished in a variety of ways, each with its own effects and degrees of intensity. Here are the most common methods:
- Smoking it
- Vaporizing
- Consuming it in the form of edibles
- Using concentrates
Each method has its peculiarities, and it’s crucial to understand them in order to choose the form that best suits individual people’s needs and preferences.
Below, we will explore two of the most common forms of marijuana consumption: smoking and vaping, and the use of edibles and concentrates. These categories vary not only in the effects they produce, but also in the risks and benefits associated with each.
Smoking and vaping
Smoking marijuana is perhaps the most traditional form of consumption, but not necessarily the healthiest. Inhaling marijuana smoke can have negative effects on the lung and respiratory system, similar to those of smoking. On the other hand, the use of vaporizers, which extract the active ingredients and allow inhaling vapor instead of smoke, is considered a less harmful option for the respiratory system.
Although vaping is perceived as a healthier alternative, it also presents its own risks. THC, when inhaled through vaporizers, has been associated with health problems related to vaping, although these effects are less severe compared to smoking.
Vaping allows active compounds to be inhaled without the harmful effects of combustion, offering a healthier option for users.
Edibles and concentrates
Consuming marijuana in the form of edibles and concentrates is another popular way to enjoy its effects. Edibles, such as cannabis-infused treats and edibles, can take longer to produce effects compared to smoking or vaping, which can lead some users to consume more than necessary. This can result in more intense and prolonged intoxication.
Marijuana concentrates, on the other hand, are resins with high THC content extracted from the plant. These products may offer a more potent and fast-acting experience, but they also carry a higher risk of adverse effects due to their high concentration of cannabinoids.
Summary
Throughout this article, we have explored the various effects marijuana can have on health and well-being. From euphoria and relaxation to long-term risks and potential therapeutic applications, it is clear that marijuana use is a complex and multifaceted topic. Knowing the main components of cannabis, such as THC and CBD, and their effects on the body is critical to making informed decisions about its use.
As the legalization and medical use of marijuana continues to expand, it is crucial to continue to research and understand its effects in order to maximize its benefits and minimize its risks. Whether you are interested for recreational or therapeutic reasons, marijuana has the potential to significantly impact your life. Stay informed and make conscious decisions for your health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions about Cannabis and its Constituents
What are the main short-term effects of marijuana use?
Short-term effects include euphoria, relaxation, altered perception of time and space, increased appetite, dry mouth and eye redness. It can also affect motor coordination and concentration.
What are the long-term risks of regular marijuana use?
Prolonged use can lead to memory problems, cognitive impairment, increased risk of mental disorders such as anxiety and depression, and possible dependence. In adolescents, it can affect brain development and academic performance.
How does marijuana affect mental health?
Marijuana can increase the risk of developing mental disorders, especially in people who are genetically predisposed. It can cause anxiety, paranoia and, in some cases, psychotic episodes. Frequent use has been associated with an increased risk of depression.
Is there a difference between the effects of THC and CBD?
Yes, THC is the main psychoactive component responsible for the euphoric effects, while CBD is non-psychoactive and is associated with therapeutic effects such as anxiety reduction and anti-inflammatory properties.
Can marijuana have medicinal uses?
Yes, marijuana has potential medicinal uses, including relief of chronic pain, reduction of nausea in chemotherapy patients, and treatment of certain types of epilepsy. However, its medical use should be supervised by health care professionals.
References
Volkow, N. D., Baler, R. D., Compton, W. M., & Weiss, S. R. (2014). Adverse health effects of marijuana use. New England Journal of Medicine, 370(23), 2219-2227.
Crean, R. D., Crane, N. A., & Mason, B. J. (2011). An evidence-based review of acute and long-term effects of cannabis use on executive cognitive functions. Journal of addiction medicine, 5(1), 1.
Meier, M. H., Caspi, A., Ambler, A., Harrington, H., Houts, R., Keefe, R. S., … & Moffitt, T. E. (2012). Persistent cannabis users show neuropsychological decline from childhood to midlife. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 109(40), E2657-E2664.
Silins, E., Horwood, L. J., Patton, G. C., Fergusson, D. M., Olsson, C. A., Hutchinson, D. M., … & Mattick, R. P. (2014). Young adult sequelae of adolescent cannabis use: an integrative analysis. The Lancet Psychiatry, 1(4), 286-293.
Moore, T. H., Zammit, S., Lingford-Hughes, A., Barnes, T. R., Jones, P. B., Burke, M., & Lewis, G. (2007). Cannabis use and risk of psychotic or affective mental health outcomes: a systematic review. The Lancet, 370(9584), 319-328.
Lev-Ran, S., Roerecke, M., Le Foll, B., George, T. P., McKenzie, K., & Rehm, J. (2014). The association between cannabis use and depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Psychological medicine, 44(4), 797-810.
Pertwee, R. G. (2008). The diverse CB1 and CB2 receptor pharmacology of three plant cannabinoids: Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabivarin. British journal of pharmacology, 153(2), 199-215.
Blessing, E. M., Steenkamp, M. M., Manzanares, J., & Marmar, C. R. (2015). Cannabidiol as a potential treatment for anxiety disorders. Neurotherapeutics, 12(4), 825-836.
Whiting, P. F., Wolff, R. F., Deshpande, S., Di Nisio, M., Duffy, S., Hernandez, A. V., … & Kleijnen, J. (2015). Cannabinoids for medical use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Jama, 313(24), 2456-2473.
Abrams, D. I. (2018). The therapeutic effects of Cannabis and cannabinoids: An update from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine report. European journal of internal medicine, 49, 7-11.