What is THC and how does it affect your body? THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the main psychoactive component of marijuana, responsible for the ‘high’. In this article, you will learn what THC is, how it acts in the body and its effects, both positive and negative. THC is a resin produced by the trichomes of the marijuana plant.
Key Points
- THC is the most important psychoactive cannabinoid and its concentration varies between strains of cannabis, influencing the consumer’s experience. THC is found primarily in the buds of the marijuana plant.
- THC use can cause both pleasurable and adverse effects, including anxiety, respiratory problems, and short- and long-term cognitive impairment.
- Despite its risks, THC has significant therapeutic benefits, such as chronic pain relief and mood enhancement, although its use must be carefully controlled.
What is THC?
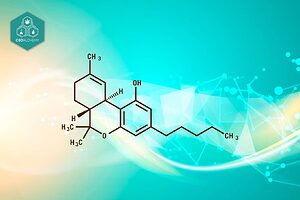
The Δ-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the most important and abundant psychoactive cannabinoid in cannabis strains classified as psychoactive. This component is produced in the trichomes of the cannabis sativa plant as a defense mechanism. The concentration of THC can vary significantly between cannabis strains, reaching more than 25% in some, which influences the preparation and effects of cannabis.
THC is the main psychoactive component of marijuana, and is responsible for the “high” effects felt by users. This variability in THC concentration means that each strain of marijuana can offer a unique experience, from mild relaxation to intense euphoria. In addition, THC is a substance that accumulates in the body’s fatty tissue.
How THC acts in the body
To understand how THC affects the body, we must first understand the endocannabinoid system, which plays a crucial role in functions related to behavior, learning, gratification, food intake, pain and emotions. When we consume cannabis, the endocannabinoid system is activated externally and artificially, altering many of these functions.
CB1 and CB2 receptors are fundamental in this process, as they transmit information related to the central nervous system:
- pleasure
- memory
- reasoning
- coordination of movements
By binding to these receptors, THC influences thoughts, memories and the notion of time, and can provoke laughter, distorting the perception of the environment.
This interaction can result in a range of effects, from euphoria and relaxation to anxiety and paranoia, depending on the dose and the individual susceptibility of the user. The way THC affects the body and mind is complex and multifaceted, making each cannabis experience unique. Unlike alcohol, THC has no minimum allowable limit for driving in many countries.
Short-term effects of THC

The short-term effects of THC are varied and can be both pleasurable and disturbing. Here are some of the most common effects that users experience:
- Increased sensory perception, intensifying visual, auditory and taste experiences.
- Feeling of relaxation and drowsiness.
- Distorted perception of time, which can be both pleasurable and disorienting.
These effects can vary from person to person and depend on the dose and form of consumption.
Although many seek THC for its ability to induce euphoria, at high doses it can lead to episodes of intense anxiety. The ability to react and concentrate is significantly diminished, which can be dangerous in situations requiring attention and coordination, such as driving. Other immediate physical effects include dry mouth, reddening of the eyes, and an increased heart rate.
How THC is consumed also influences the speed and duration of these effects. For example, smoking THC can cause a significant increase in heart rate immediately after consumption, while eating foods containing THC results in slower but prolonged absorption.
Adverse effects of THC

Despite the pleasurable effects that many associate with THC, there are also adverse effects that can affect physical and mental health. Uncontrolled marijuana use can trigger significant problems, including psychosis and anxiety, as well as physical health problems. The adverse effects can be diverse and affect different body systems, from cardiovascular to respiratory to cognitive.
It is important to be aware of these risks and consider how THC use can impact long-term health. The following subsections will specifically detail the cardiovascular, respiratory and cognitive effects of THC.
Cardiovascular effects
One of the most common cardiovascular effects after consuming THC is an increased heart rate. This effect can last up to three hours after consumption, which can be problematic for people with pre-existing heart conditions. Prolonged cannabis use has been associated with an increased likelihood of developing cardiovascular problems, including tachycardia and an increased risk of heart attack.
This increased heart rate and associated risk underscores the importance of using THC with caution, especially among those who already have cardiovascular problems. Constant stimulation of the cardiovascular system can lead to long-term complications.
Respiratory effects
Chronic THC use is associated with obstruction of airflow in the lungs, which can lead to serious respiratory problems. Frequent marijuana smoking can result in a persistent cough and other respiratory problems. In addition, prolonged use can increase the risk of developing lung disease and certain types of cancer.
These adverse effects on the respiratory system are of particular concern for regular marijuana smokers. Opting for alternative consumption methods, such as vaporizer leaves, can help mitigate some of these risks.
Cognitive effects
THC use is associated with various cognitive impairments, including memory loss and decreased verbal fluency. These impairments can make learning difficult and negatively affect the ability to concentrate. In addition, verbal fluency is compromised, which can impact effective communication.
The impact on memory and attention is especially significant during adolescence, when the brain is still developing. Young users should be particularly cautious with THC use because of these long-term negative effects.
Long-term effects of THC
Long-term use of THC can have lasting effects on memory and brain development. Repeatedly activating the cannabinoid system with THC can impair memory and recall of recent events. In addition, there is an increased risk of developing schizophrenia and episodes of psychosis in some individuals.
Marijuana use during adolescence can have a negative impact on brain development, affecting critical cognitive functions. These long-term effects underscore the importance of carefully considering THC use, especially among youth.
Therapeutic benefits of THC
Despite its adverse effects, THC also offers significant therapeutic benefits. One of the most prominent advantages is its ability to trigger the release of dopamine in the brain, improving mood and thinking. This makes it useful in the treatment of chronic pain, including neuropathic pain.
THC is commonly used to control nausea and vomiting in patients receiving chemotherapy. In addition, it can stimulate appetite, being especially beneficial for people suffering from weight loss due to illnesses such as HIV/AIDS. Some studies have also shown that THC can help alleviate symptoms in conditions such as multiple sclerosis and inflammatory bowel disease.
These therapeutic benefits make THC a valuable option in the treatment of various medical conditions, although its use should be carefully monitored to avoid adverse effects.
Differences between THC and CBD
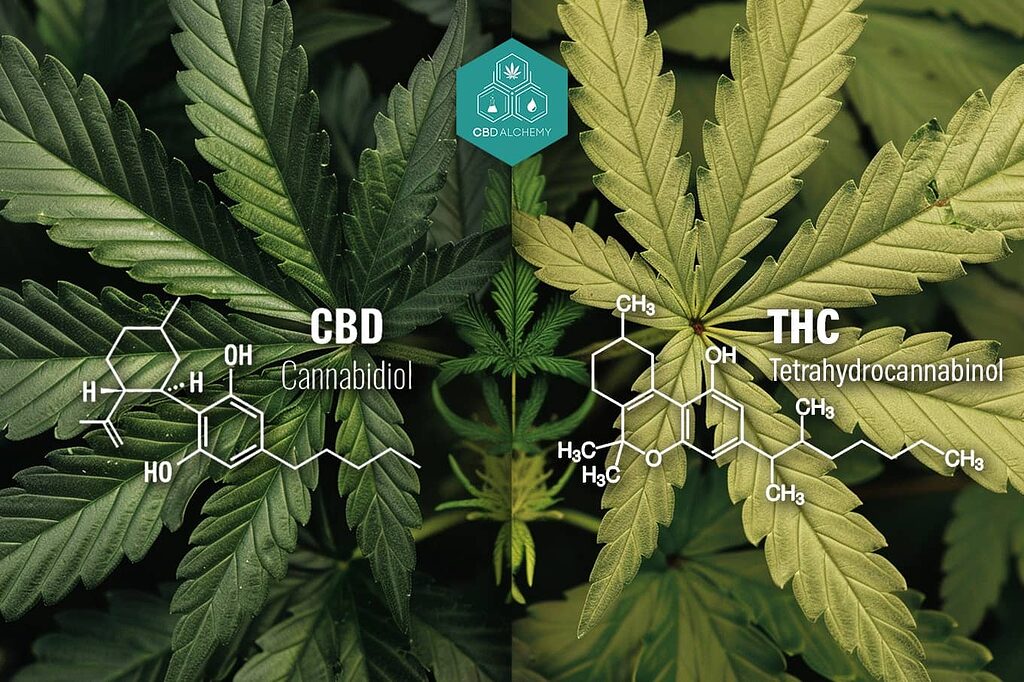
Although THC and cannabidiol (CBD) are both cannabinoids present in the cannabis plant, their effects are notably different. THC is known for its psychoactive effects, which alter mental function and perception, while CBD does not produce a “high” and is used therapeutically without these effects.
CBD has gained popularity for its therapeutic benefits without the side effects associated with THC. This fundamental difference has generated a great deal of controversy surrounding the legalization of cannabis, particularly with regard to THC and its effects on memory and perception.
THC use and drug testing
THC consumption can be detected in the body for several days, depending on the frequency of use. In occasional users, THC can be detected 1-3 days after use, while in regular users, it can be detected for more than 20 days. Drug tests are commonly used to detect the presence of THC in the body.
These tests are particularly relevant for people who must undergo regular testing, such as in the work or sports environment. It is important to be aware of the duration of THC in the body and how it can affect the results of these tests.
Methods of THC consumption
There are several methods of consuming THC, each with its own characteristics and effects. Smoking cannabis allows for rapid absorption of cannabinoids into the bloodstream, with effects felt within minutes and can last up to three hours. However, this method can be irritating to the lungs.
Vaporizers offer a less harmful alternative, heating cannabis at controlled temperatures to release cannabinoids without combustion. Dabbing, which involves heating cannabis concentrates on a hot nail, produces much more intense effects with smaller amounts than smoking flower.
Cannabis edibles require THC to pass through the digestive system, becoming a more potent metabolite. The effects of edibles can last up to 12 hours, offering a prolonged but slower experience compared to smoking.
Legality of THC in different countries
The legality of THC varies significantly between countries and regions. In many places, THC is more restricted than CBD due to its psychoactive effects. For example, in some European countries such as Malta and Germany, possession of small amounts of cannabis is decriminalized. This approach allows for some permissiveness while maintaining regulation.
In contrast, in countries such as Canada and Uruguay, recreational use of cannabis is completely legal. However, in some Asian nations such as Singapore and Malaysia, penalties for cannabis trafficking can be extremely severe, up to and including the death penalty. This diversity in laws reflects the global controversy surrounding the use of THC and cannabis.
In Spain, Law 17/1967 on Narcotic Drugs prohibits the recreational use of THC. However, the sale of products with low THC concentrations (0.2% to 0.6%), labeled as ‘cannabis light’, is permitted in some states. This legal complexity underscores the need to be well informed about local laws before consuming or possessing cannabis products.
Summary
In summary, THC is a key component of marijuana with a wide range of effects and applications. From its psychoactive and therapeutic effects to the risks associated with its use, it is essential to understand both the benefits and potential dangers. THC interacts with the endocannabinoid system, affecting bodily and mental functions significantly.
As the legality of THC continues to evolve around the world, it is crucial to stay informed and consider all aspects of its use. While it can offer relief for various medical conditions, it can also present health risks, especially with prolonged use. At the end of the day, being mindful and responsible in its consumption is the best way to reap its benefits while minimizing adverse effects.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is THC?
THC is the main psychoactive component of marijuana, responsible for causing high effects and is found in the trichomes of the cannabis sativa plant.
How does THC act in the body?
THC acts in the body by interacting with the endocannabinoid system, impacting functions such as behavior, memory and perception of time. This can lead to significant psychoactive effects.
What are the short-term effects of THC?
The short-term effects of THC include increased sensory perception, relaxation, euphoria, anxiety, as well as dry mouth and increased heart rate. These effects can vary depending on the dose and form of consumption.
Is THC legal in all countries?
No, the legality of THC is not uniform in all countries; some allow its recreational use, while others apply strict penalties.
What are the therapeutic benefits of THC?
THC offers significant therapeutic benefits, including treating chronic pain, reducing nausea and improving appetite, as well as alleviating symptoms in conditions such as multiple sclerosis. These effects make it a valuable option in medicine.