1. What is CBG?
Introduction
Cannabigerol (CBG), a cannabinoid found in the hemp plant, is often referred to as the “parent” of other cannabinoids such as CBD and THC. Being part of the Cannabis sativa L. plant, CBG is present in smaller amounts compared to its counterparts.
Within cannabis plants, CBG is formed from cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), an acidic cannabinoid that serves as a precursor to other cannabinoids.
Transformation occurs through enzymes, leading to cannabinoids such as CBD and THC. Although the concentration of CBG in most hemp plants is less than 1%, its importance is undeniable.

2. History and Origin of CBG
Cannabigerol (CBG) is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid present in the genus Cannabis, which encompasses both hemp and marijuana. It was first identified in 1964 by Gaoni and Mechoulam. CBG is special because it acts as the chemical precursor to other cannabinoids, such as CBD and THC.
Olivetol, or olivetolic acid, is an essential precursor in the formation of cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) in the Cannabis sativa plant. CBGA is an acidic phytocannabinoid that serves as a precursor to other phytocannabinoids in the plant. The enzyme geranylpyrophosphate:olivetolate geranyltransferase (also known as CBGA synthase) catalyzes the binding of olivetolic acid to geranyl diphosphate to produce CBGA.
Within the cannabis plant, olivetolic acid combines with geranyl diphosphate to form CBGA. Specific enzymes then convert CBGA into CBCA, CBDA and THCA. Through drying and heating processes, THCA and CBDA can be transformed into THC and CBD, respectively.

3. Properties and Benefits of CBG
The benefits of CBG oil have piqued the interest of researchers in the medical field. Several studies have demonstrated the effects of CBG on diseases such as cancer, Crohn’s disease and Huntington’s disease.
3.1 Potential of CBG in Cancer Treatment
CBG may act as an agent that inhibits the growth of cancer cells. This aspect of CBG has led to continued research, especially its ability to target specific types of receptors.
3.2 CBG and Neurological Disorders
Research has shown that CBG’s properties can alleviate symptoms of neurological conditions.
CBG may offer relief in conditions such as Huntington’s disease, according to one study.
3.3 Other Medical Applications
The therapeutic benefits of CBG extend to other areas. CBG cannabinoid’s ability to stimulate appetite is one aspect, while its potential in treating infections is also notable. In addition, CBG’s effect on the endocannabinoid system has shown promise in the management of chronic pain.

4. Comparison of CBG with Other Cannabinoids
The uniqueness of CBG lies in its differences from other cannabinoids such as CBD and THC. Let’s take a look at these aspects:
4.1 CBG and CBD
CBG and CBD are both non-psychoactive compounds found in the cannabis plant. Although there are similarities between the two, CBG offers unique benefits that distinguish it from CBD.
For example, CBG’s potential in treating infections and appetite stimulation varies from CBD.

4.2 CBG and THC
The main differences between CBG and THC center on their effects. While THC is known for its psychotropic properties that cause feelings of euphoria, CBG does not have that psychotropic effect. This is because CBG does not bind to the CB1 receptor, unlike THC, which does and is what causes the “high” or “stoned” sensation.

4.3 CBG in the Context of Cannabis Regulation
The legal landscape for cannabis and cannabinoids such as CBG varies by region. In some places, hemp products containing CBG are subject to strict regulations, highlighting the need for transparent labeling.

5. Mechanism of Action and Pharmacodynamics
CBG’s Link to CB1R and CB2R Receptors
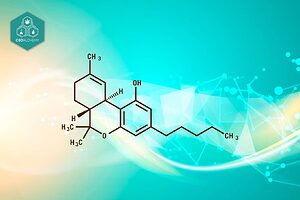
The molecular structure of CBG consists of 21 carbon atoms, with the total chemical formula of C21H32O2.
According to IUPAC nomenclature, the systematic name of cannabigerol is 2-[(2E)-3,7-dimethylocta-2,6-dienyl]-5-pentylbenzene-1,3-diol.
CBG has been found to have various therapeutic properties, such as antibacterial, antifungal and anti-inflammatory effects.
It has affinity and activity at CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors in vitro, as well as high affinity and activity at alpha-2 adrenergic receptors and moderate activity at serotonin (5-HT) 1A receptors.
CBG as a Modulator of the Endocannabinoid System
Cannabinoids such as CBG influence the endocannabinoid system, a complex network that regulates functions such as appetite, sleep, and immune response.
CBG can alter neurotransmitter release, acting as a reuptake inhibitor and modulating the concentration of endocannabinoids in the system.

Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Properties of CBG
In addition to its interaction with the endocannabinoid system, CBG exhibits anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
These properties may have significant implications in neuroprotection, offering potential for treating neurodegenerative diseases.

6. CBG Research and Studies
Current and Past CBG Research
The field of CBG research has grown exponentially over the past few decades.

Research Methods and Key Findings
Researchers have employed a variety of methods, from in vitro cell-based studies to mouse and human clinical trials.
These studies have revealed CBG’s potential to fight infections, reduce inflammation, and its neuroprotective ability.

Significance and Application of These Studies in Medicine and Industry
With each study, CBG is becoming more established in medicine and industry.
Its potential in pharmaceuticals, dietary supplements and cosmetics has led to increased investment and development of CBG-based products.

CBD Alchemy CBG Oil: A Revolution in the Wellness World
In the dynamic world of digital marketing, it is essential to highlight products that truly make a difference in people’s lives. One such product is CBD Alchemy’s CBG Oil.
CBG: what is it and why is it relevant?
CBG, one of the most recently discovered phytocannabinoids, has positioned itself as one of the most essential and natural components of the cannabis plant.

CBD Alchemy CBG Oil: A Perfect Match
CBD Alchemy’s CBG oil is not just another product on the market. Its unique blend of 5% CBG and 5% CBD captures the essence and potential of the cannabis plant.
With 20 mg of CBG in just 4 drops, this oil is ideal for those familiar with the world of CBG and looking for a potent and effective product.
A Safe and Conscious Choice
For those concerned about THC, Alchemy CBD CBG Oil is the perfect choice.
With no trace of THC, it is ideal for those sensitive to this component or living in regions with strict regulations.
In addition, its base of MCT oil and hemp extract guarantees a pure and natural experience.
The Future of Wellness with CBD Alchemy
In the digital age, where information flows fast and trends change in an instant, CBD Alchemy’s CBG Oil presents itself as a constant in the world of wellness.
Its combination of CBG and CBD, along with CBD Alchemy’s quality assurance, positions it as a star product in the cbg oil market.

Conclusion
CBG, with its broad spectrum of properties and benefits, stands as a jewel in the world of cannabinoids. As science advances, we are likely to see more applications and treatments based on this compound.
Bibliography and additional resources:
- Jastrząb, A., Jarocka-Karpowicz, I., & Skrzydlewska, E. (2022). The Origin and Biomedical Relevance of Cannabigerol. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(14), 7929. – DOI: 10.3390/ijms23147929
This study reviews the biological aspects and biomedical relevance of cannabigerol (CBG). The research examines how CBG interacts with the endocannabinoid system and highlights the therapeutic potential of CBG in various medical contexts.
- Navarro, G., Varani, K., Reyes-Resina, I., Sánchez de Medina, V., Rivas-Santisteban, R., Sánchez-Carnerero Callado, C., Vincenzi, F., Casano, S., Ferreiro-Vera, C., Canela, E. I., Borea, P. A., Nadal, X., & Franco, R. (2018). Cannabigerol Action at Cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 Receptors and at CB1-CB2 Heteroreceptor Complexes. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 9. – DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00632
This research focuses on the action of cannabigerol (CBG) on cannabinoid receptors and their heteroreceptor complexes. It is suggested that CBG has affinity for both receptors, which may have therapeutic implications in a variety of medical contexts.