- The Science Behind CBDA: How it’s Formed and How it Works
- CBDA vs CBD: Understanding the Differences and Connections
- The Potential Health Benefits of CBDA
- How Acidic Cannabinoids are Extracted from Cannabis Plants
- The Role of cannabidiolic acid CBDA in the Raw Cannabis Plant
- Methods of Consuming CBDA for Optimal Benefits
- Future Research and Potential Uses for CBDA
- Frequently Asked Questions about CBDA:
- 1. Does CBDA produce psychoactive effects?
- 2. How can I consume CBDA for optimal pain relief?
- 3. Is using CBDA legal?
- 4. What distinguishes raw cannabis from processed cannabis regarding CBDA?
- 5. What are the side effects associated with consuming CBDA?
- 6. How Does CBDA Function in the Body?
- 7. How Should CBDA Be Taken?
- 8. Is it possible for CBDA to interact with other medications?
- 9. What Is the Distinction Between CBDA and CBD?
- 10. Is CBDA Effective for Anxiety?
- 11. What is the Prospective of CBDA Research?
- 12. Can CBDA’s antibacterial qualities aid in the treatment of bacterial infections?
- 13. What are CBDA’s antioxidant properties?
- 14. Does CBDA interact with CB receptors (CB1 and CB2)?
- 15. What is the mechanism by which CBDA interacts with the 5-HT1A receptor?
- 16. What is the function of CBDA as a PPAR-agonist?
- 17. What is the antagonistic activity of CBDA at GPR55 receptors?
- 18. CBDA inhibits COX1/COX-2 enzymes in what way?
- 19. How does CBDA exert antibacterial activity?
- The Bottom Line
Cannabidiolic Acid, commonly known as CBDA, is a natural molecule produced by cannabis plants that is gaining popularity in the medical field due to its numerous potential health benefits. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of CBDA and other acidic compounds derived from olivetolic acid, exploring its benefits, potential and uses and looking into scientific research.
CBDA, also known as cannabidiolic acid, is a naturally occurring compound found in the raw form of the plant. This compound is a precursor to CBD, which means that it transforms into CBD when heated or processed. This transformation occurs through decarboxylation, where CBDA loses its carboxyl group and becomes CBD. Unlike CBD, CBDA is non-psychoactive and does not have any intoxicating effects. This makes it a popular choice among individuals who want to experience the potential health benefits of cannabis without the mind-altering effects of THC. Recent studies have shown that CBDA has a wide range of potential health benefits. One study found that CBDA has anti-inflammatory properties, which could make it a helpful treatment option for individuals suffering from chronic pain. Another study found that CBDA has potential anti-nausea and anti-emetic effects, which could make it a useful treatment option for individuals undergoing chemotherapy. Additionally, researchers believe that CBDA could offer effective treatment options for various ailments like anxiety, depression, and epilepsy. The potential health benefits of CBDA make it an essential element for medical development. It is important to note that while CBDA shows promising potential as a treatment option, more research is needed to understand its effects on the body fully. As the medical and wellness industry continues to explore the potential benefits of CBDA, we will likely see more products containing this compound on the market.

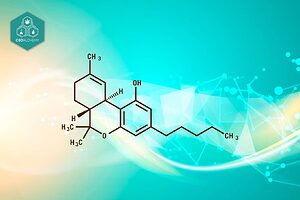
The Science Behind CBDA: How it’s Formed and How it Works
Cannabidiolic acid, or CBDA, is a non-psychoactive compound produced by the cannabis plant. It is a precursor to cannabidiol (CBD) and is believed to have therapeutic benefits for a variety of medical conditions.
The process of CBDA formation begins with olivetolic acid formation, then to cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), the primary cannabinoid produced by the cannabis sativa plant. CBGA is converted into other acidic compounds, such as tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) and cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), through a process called cannabinoid biosynthesis itself.
During the early growth stages of the plant, cannabigerolic acid CBGA is broken down into CBDA through decarboxylation. This process involves the removal of a carboxyl group from the CBGA molecule, which results in the formation of CBDA.
CBDA works by interacting with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS). The ECS is a complex network of receptors and neurotransmitters regulating various physiological functions such as appetite, pain, inflammation, and immune system responses.
CBDA binds with the receptors in the ECS, primarily CB1, and CB2, which enables it to influence pain, inflammation, and immune system responses. CBDA has been shown to have anti-inflammatory and anti-nausea properties and potential benefits for anxiety and depression.
Research has also suggested that CBDA may have anti-cancer properties. In a study conducted on breast cancer cells, CBDA was found to inhibit the migration of breast cancer cells and to reduce the expression of genes associated with breast cancer cells’ cell proliferation.
Overall, CBDA and other acidic cannabinoids are fascinating natural acidic compounds derived from olivetolic acid that are still being studied for its potential therapeutic benefits. Its formation through the decarboxylation of CBGA during the plant’s early growth stages is a complex process that is still not fully understood. However, its ability to interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system and influence various physiological functions makes it a promising area of research for the future.

CBDA vs CBD: Understanding the Differences and Connections
When it comes to plants, there are many different compounds that can be found within them. Two of these compounds are CBDA and CBD, which are both important in their own right. While they may sound similar, there are actually some important differences between the two.
What is CBDA? CBDA is short for cannabidiolic acid, and it is primarily found in raw plants. This means that if you were to eat or juice raw cannabis, you would be consuming CBDA. On the other hand, CBD is typically found in processed forms of cannabis, such as oils, tinctures, and edibles.
One interesting thing to note about CBDA is that it is actually a precursor to CBD. This means that when cannabis is heated or processed in some way, CBDA will transform into CBD. This is an important step in the creation of many CBD products that we see on the market today.
While both CBDA and CBD come from the same plant, they have different properties and effects on the body. Research has shown that CBDA has specific properties that are not found in CBD, such as anti-inflammatory and anti-nausea effects. This means that CBDA could potentially be used to treat different ailments than CBD.

However, when CBDA and CBD are consumed together, they can work together to produce even better results. This is known as the entourage effect, and it is a concept that has been gaining more attention in recent years. Essentially, the idea is that different compounds in cannabis can work together to produce a stronger effect than they would on their own.
So, while CBDA and CBD are different compounds with different properties, they are also connected in important ways. By understanding these differences molecular properties and connections, we can gain a better understanding of how cannabis works and how it can be used to treat various ailments and conditions.

The Potential Health Benefits of CBDA
CBDA, or cannabidiolic acid, is a non-psychoactive compound found in the cannabis sativa plant. It has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential therapeutic benefits. Medical researchers and product developers are exploring the possibilities of CBDA as a natural remedy for various health conditions.
One of the most promising benefits of CBDA is its anti-inflammatory properties. Inflammation is a natural response of the body to injury or infection, but chronic inflammation can lead to various health problems such as arthritis, heart disease, and even cancer. CBDA has been found to have a potent anti-inflammatory effect, which could help reduce swelling and pain in the body.
Another potential benefit of CBDA is its anti-nausea properties. Nausea and vomiting are common side effects of chemotherapy, and they can be debilitating for cancer patients. CBDA has been shown to have anti-nausea properties, which could help manage chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting.
CBDA also has potential cancer-fighting properties. Studies have shown that CBDA can inhibit the growth of specific types of cancer cells, including breast cancer and prostate cancer. While more research is needed in this area, CBDA could be a promising natural remedy for cancer patients.
In addition to its anti-inflammatory, anti-nausea, and potential cancer-fighting properties, CBDA also has antibacterial properties. It can help fight bacterial infections and promote overall health and well-being.
Finally, CBDA has antioxidant properties, which could help reduce oxidative stress and cellular damage in the body. Oxidative stress is a natural process that occurs when the body is exposed to toxins and pollutants, and it can lead to various health problems such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. CBDA’s antioxidant properties could help protect the body from oxidative stress and promote overall health.
Overall, CBDA has many potential health benefits that make it an exciting area of research for medical professionals and product developers alike. While more research is needed to fully understand its therapeutic potential, early research suggests that CBDA could be a natural remedy for various health conditions and promote overall health and well-being.
- CBDA’s interaction with CB receptors (CB1 and CB2) – acting as an inverse agonist or negative allosteric modulator.
- CBDA’s role as a 5-HT1A receptor agonist in vivo, either directly or indirectly.
- CBDA’s function as a PPAR-γ agonist, with lower affinity compared to THCA.
- CBDA’s antagonistic action at GPR55 receptors.
- CBDA’s ability to inhibit COX1/COX-2 enzymes.
- CBDA’s potent antimicrobial effects.

How Acidic Cannabinoids are Extracted from Cannabis Plants
Cannabis sativa plants are known for their therapeutic properties, and CBDA is one of the many compounds found in these plants that offer a wide range of health benefits. CBDA, or cannabidiolic acid, is the acidic precursor to CBD, which is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid that is known for its anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and anti-anxiety properties.
CBDA is commonly extracted from plants using various methods, including CO2 extraction, liquid solvents, and olive oil. Each of these methods has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of method depends on the desired outcome and the resources available.
One common method of CBDA extraction is through CO2 extraction, which involves passing supercritical CO2 through the raw cannabis plant. This method is preferred since it ensures maximum purity and preserves the natural efficiency of the CBDA extracts. Supercritical CO2 is a form of carbon dioxide that is heated and pressurized to a point where it becomes a liquid and a gas at the same time. This state allows it to act as a solvent, which can extract the CBDA from the plant material.
Another method of CBDA extraction is through liquid solvents, such as ethanol or butane. This method involves soaking the raw hemp or plant biomass in the solvent, which dissolves the CBDA and other cannabinoids and terpenes. The resulting solution is then evaporated to remove the solvent, leaving behind a concentrated extract that is rich in CBDA.
Olive or hemp oil extraction is another method that is commonly used to extract CBDA from raw cannabis flowers or growing cannabis plants themselves. This method involves heating the raw cannabis plant in olive oil, which decarboxylates the CBDA and converts it into CBD. The resulting hemp oil, is then strained and used for various purposes, such as cooking, topical application, or oral consumption.
In conclusion, CBDA extraction from plants is a complex process that requires specialized equipment and expertise. The choice of extraction method depends on various factors, such as the desired outcome, the resources available, and the level of purity required. Regardless of the method used, CBDA extracts offer a wide range of health benefits and are becoming increasingly popular among health enthusiasts and medical practitioners.

The Role of cannabidiolic acid CBDA in the Raw Cannabis Plant
CBDA, or cannabidiolic acid, is a naturally occurring cannabinoid produced by cannabis plants. While it may not be as well-known as its counterpart, CBD, CBDA plays a significant role in the functioning of the raw cannabis plant, with other acidic cannabinoids.
One of the most important roles of CBDA is its function as a precursor to other cannabinoids in the plant. When the raw cannabis plant is heated or exposed to light, CBDA is converted into CBD through a process called decarboxylation. This process is what allows the plant to produce the various cannabinoids that are so sought-after by consumers.
But CBDA’s benefits don’t stop there. Its acidic chemical composition enables it to preserve the freshness and potency of the cannabis plant. This is because CBDA is a powerful antioxidant, which means it can help prevent the breakdown of other compounds in the plant, such as THC and CBD.
CBDA is also responsible for the plant’s anti-inflammatory properties. In fact, studies have shown that CBDA may be even more effective at reducing inflammation than CBD. This makes CBDA a sought-after element in various medical treatments, particularly those that aim to treat conditions such as arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and Crohn’s disease.
Furthermore, CBDA has been shown to have anti-nausea and anti-emetic properties, which means it can help alleviate symptoms of nausea and vomiting. This makes it a valuable tool in the treatment of conditions such as chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting.
In conclusion, while CBDA may not be as well-known as other cannabinoids, its role in the functioning of the raw cannabis plant is crucial. From its function as a natural precursor to other cannabinoids, to its ability to preserve the freshness and potency of the plant, to its anti-inflammatory and anti-nausea properties, CBDA is a valuable element in the world of cannabis.

Methods of Consuming CBDA for Optimal Benefits
Consuming CBDA offers many health benefits, including reducing inflammation, relieving pain, and improving mood. However, it is crucial to use the correct method for maximum benefits. The methods of consumption include:
- Raw cannabis juice: One of the easiest and most natural ways to consume CBDA is by juicing raw cannabis leaves and buds. This method allows you to consume CBDA in its purest form, without any heat or processing that can destroy the compound. Raw cannabis juice can be added to smoothies or other drinks for a refreshing and healthy boost.
- Tinctures and oils: Tinctures and oils are another popular way to consume CBDA. These products are made by extracting CBDA from the cannabis plant and mixing it with a carrier oil, such as coconut or olive oil. Tinctures and oils are easy to use and can be added to food or drinks for a discreet way to consume CBDA.
- Topical creams and balms: CBDA can also be applied topically in the form of creams and balms. These products are designed to be absorbed through the skin and can provide localized relief for pain and inflammation. Topical CBDA products are particularly useful for people with skin conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis.
- Capsules and tablets: For a more convenient and precise way to consume CBDA, capsules and tablets are a good option. These products contain a pre-measured dose of CBDA and can be taken orally like any other supplement. Capsules and tablets are a good choice for people who want to ensure they are getting a consistent dose of CBDA.
The method you choose will depend on your preferences and the specific health benefits you are targeting. It is important to talk to your healthcare provider before using CBDA, especially if you are taking other medications or have a medical condition. With the right method of consumption and proper guidance, CBDA can be a safe and effective way to improve your health and well-being.

Future Research and Potential Uses for CBDA
The use of CBDA in medicine and wellness is gaining traction, and researchers are exploring new ways to utilize the compound. Some of the potential uses include:
- Alternative treatment for anxiety and depression
- Cancer treatments
- Anti-inflammatory treatments for pain and swelling
- Pain management for migraines and chronic pain
One potential use for CBDA is as an alternative treatment for anxiety and depression. These conditions are often treated with pharmaceuticals that can have negative side effects, such as addiction and withdrawal symptoms. CBDA has been shown to have anxiolytic and antidepressant effects in animal studies, indicating that it could be a natural alternative to these medications.
Another area of early research used for CBDA is in cancer treatments. Some studies have shown that CBDA can inhibit the growth of certain types of cancer cells, including breast cancer and leukemia. While more research is needed to determine the full extent of CBDA’s anti-cancer properties, these findings are promising for the development of new cancer treatments.
CBDA also has anti-inflammatory properties, which could make it a useful treatment for pain and swelling. Inflammation is common in many chronic pain conditions, such as arthritis and multiple sclerosis. CBDA has been shown to reduce inflammation in animal studies, suggesting that it could be a natural alternative to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and other pain medications.
Finally, CBDA could be a potential treatment for migraines and other types of chronic pain. Migraines are a debilitating condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Some studies have shown that CBDA can reduce the frequency and severity of migraines, and it may also have analgesic effects that could make it a useful treatment for other types of chronic pain.
With more research, CBDA could offer a natural alternative to current treatments and medications for various conditions other mood disorders. Its unique properties make it a promising area of study for the future of medicine and wellness.
Frequently Asked Questions about CBDA:
1. Does CBDA produce psychoactive effects?
CBDA, a compound found in raw cannabis plants is non-psychotropic and does not produce the “high” associated with THC or other cannabinoids. Instead, it serves as a chemical precursor to CBD, another non-psychotropic compound that is touted for its possible therapeutic benefits.
2. How can I consume CBDA for optimal pain relief?
There isn’t a consensus on how to consume CBDA for pain relief since it depends on ones personal preferences, medical conditions and desired speed of relief. The forms available include oils, tinctures, capsules, and topical creams.
However before starting any new treatment or supplement regimen, its essential to seek guidance from a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable approach.
3. Is using CBDA legal?
The legality of using CBDA varies by location and local laws and can sometimes be complicated.
Often legally permissible are cannabinoids originating from industrial hemp containing low levels of THC. Still yet you should consult with an expert in the field regarding legalities surrounding CBDA per your specific location.
4. What distinguishes raw cannabis from processed cannabis regarding CBDA?
Raw cannabis contains acid form cannabinoids such as THCA and CBDA that undergo heat induced decarboxylation during processing into CBD and THC variants, resulting in processed strains having higher concentrations of CBD than raw strains.
5. What are the side effects associated with consuming CBDA?
Current research around potential side effects related to consuming this compound remains limited although similarities may exist with common side effects found through consuming similar compounds such as drowsiness, heightened dry mouth sensations, or lowered blood pressure. You should always consult up to date scientific literature or healthcare providers for precise information and questions pertaining to the use of any supplement.
One area where researchers are focusing their attention is how CBDA can relieve seizures among patients who suffer from them frequently. A pharmaceutical company that studied how CBDA compared with CBD in reducing seizure activity previously reported finding promising results about its potential efficacy and overall usefulness in treating epileptic episodes.
6. How Does CBDA Function in the Body?
CBDA, like other cannabinoids, acts in the body by interacting with the endocannabinoid system. The endocannabinoid system is essential for maintaining homeostasis in your body by regulating many physiological activities such as mood, sleep, appetite, pain, immunological response, and more.
CBDA, unlike THC or CBD, does not bind directly to the CB1 and CB2 receptors in the endocannabinoid system. Instead, CBDA inhibits the Cox-2 enzyme, which interacts with serotonin receptors in the endocannabinoid system indirectly. This is what makes CBDA non-psychoactive, allowing it to provide potential health advantages without producing a “high.”
7. How Should CBDA Be Taken?
Because CBDA research is still in its early stages, no official dose guidelines are available as of today. However, with cannabis, the usual rule of thumb is to start with a low dose and gradually increase until you find the quantity that works best for you. It is always advisable to seek individualized counsel from a healthcare expert based on your specific health situation and needs.
8. Is it possible for CBDA to interact with other medications?
CBDA’s ability to interact with other drugs has not been well researched. However, because it is related to CBD, it may share some medication interactions. CBD has the ability to inhibit specific enzymes in the liver, potentially altering the metabolism of other medicines. As a result, if you’re considering utilizing CBDA and are currently taking other medications, you should always contact a healthcare expert first.
9. What Is the Distinction Between CBDA and CBD?
CBDA and CBD are cannabinoids that are similar yet have unique characteristics. CBDA, or cannabidiolic acid, is CBD’s acidic precursor, and CBDA itself is synthesized in the cannabis plant from a compound called olivetolic acid in a reaction with geranyl pyrophosphate. These acidic compounds are present in unheated, plant raw material. When cannabis is heated or exposed to sunshine, CBDA in its acidic form is transformed into CBD via a process known as decarboxylation. As a result, the characteristics and possible advantages of these two substances may differ.
While CBD has been extensively investigated and is known for its potential therapeutic properties such as pain relief, anxiety reduction, and improved sleep, CBDA research is still in its early phases. However, preliminary research suggests that CBDA may have distinct health advantages that are distinct from, or perhaps more strong than, CBD.
10. Is CBDA Effective for Anxiety?
Early study reveals that CBDA may have anxiety-relieving properties. CBDA, like CBD, interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system, which regulates mood and stress response. More research is needed, however, to grasp CBDA’s potential as an anxiety medication fully. Always get the advice of a healthcare provider before using CBDA or any other anxiety supplements.
11. What is the Prospective of CBDA Research?
While CBDA research is still in its early phases, preliminary data indicate that this chemical has a lot of promise. Scientists are currently investigating how CBDA could be utilized to treat a variety of illnesses ranging from inflammation and pain to anxiety and seizures. As additional scientific research is completed and our understanding of CBDA grows, we should expect to see a rise in the number of CBDA-based products on the market. As with all fields of medical research, it is critical to speak with healthcare specialists and stay up to date on the most recent results.
12. Can CBDA’s antibacterial qualities aid in the treatment of bacterial infections?
According to preliminary research, CBDA may have antimicrobial effects. This could imply that CBDA could aid in the battle against bacterial infections, although additional research is required to understand this process and its efficiency fully.
13. What are CBDA’s antioxidant properties?
Antioxidants are essential in the fight against oxidative stress, a process that can cause cellular damage and a variety of health problems such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. CBDA has antioxidant capabilities, which means it can help lower oxidative stress in the body, protecting cells from harm and potentially aiding to overall health and well-being, according to the research team.
14. Does CBDA interact with CB receptors (CB1 and CB2)?
CBDA, unlike THC and CBD, does not bind directly to the CB1 and CB2 receptors. Instead, some study suggests that CBDA may function as an inverse agonist or negative allosteric modulator on these receptors, reducing rather than boosting their activity. This could result in a unique set of effects when compared to other cannabinoids.
15. What is the mechanism by which CBDA interacts with the 5-HT1A receptor?
5-HT1A receptors are a subtype of serotonin receptors, which play an important role in mood, anxiety, and stress regulation. According early evidence and to certain studies, CBDA may act as an agonist of the 5-HT1A receptor, either directly or indirectly. This implies that CBDA may activate these receptors, potentially providing advantages such as reduced anxiety and depression. More research, however, is required to comprehend this mechanism completely.
16. What is the function of CBDA as a PPAR-agonist?
The nuclear receptor PPAR- (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma) regulates genes involved in energy storage, insulin sensitivity, and inflammation. CBDA has been proven to be a PPAR- agonist, however with less affinity than THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid). This shows that CBDA may have benefits for metabolic health and inflammation.
17. What is the antagonistic activity of CBDA at GPR55 receptors?
The GPR55 receptor is hypothesized to be involved in pain perception, bone health, and blood pressure regulation. According to some early research, CBDA may function as an antagonist at GPR55 receptors, which means it may block or limit their action. However, additional further research suggests it is required to comprehend this connection’s ramifications properly.
18. CBDA inhibits COX1/COX-2 enzymes in what way?
COX-1 and COX-2 cycloxygenase enzymes are engaged in the inflammatory process in the body. According to some study, CBDA may block these enzymes, potentially reducing inflammation and providing relief from ailments such treat inflammation such as pain and edema.
19. How does CBDA exert antibacterial activity?
According to new studies, CBDA may have potent antibacterial properties. This implies that it has the potential to kill or impede the growth of bacteria and other microbes. This expands CBDA’s potential medicinal applications, although further research is needed to investigate its antibacterial efficiency properly.
There are various factors to consider when it comes to CBDA consumption, and it is essential to seek medical advice before using it for medical purposes.
The Bottom Line
CBDA has many potential benefits and is gaining popularity in the medical and wellness industry. Its anti-inflammatory and anti-nausea properties, as well as its potential cancer-fighting and pain-relief benefits, make it an essential element in various therapies. While research is ongoing, seeking medical advice before using CBDA for medical purposes is crucial.

Bibliography and additional resources:
- Martinenghi, L.D. et al. (2020): This study discusses the extraction, purification, and antimicrobial characterization of Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) and Cannabidiol (CBD) from Cannabis sativa L. The research demonstrates the substantial inhibitory effect of CBD on Gram-positive bacteria, including multi-drug resistant strains like MRSA, and explores the potential of these compounds as alternative antimicrobial agents:
Martinenghi, L.D.; Jønsson, R.; Lund, T.; Jenssen, H. Isolation, Purification, and Antimicrobial Characterization of Cannabidiolic Acid and Cannabidiol from Cannabis sativa L. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060900
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023): This source provides a comprehensive overview of CBDA. It is the chemical precursor to CBD and is most abundant in the glandular trichomes on the female seedless flowers of the cannabis plant. The decarboxylation process transforms CBDA into CBD:
National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023). PubChem Compound Summary for CID 160570, Cannabidiolic acid https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Cannabidiolic-acid
- Formato M. et al. (2020): This review paper offers an in-depth look at the bioactive properties of CBDA, the main phytocannabinoid in fiber and seed-oil hemp. Despite CBDA’s multiple bioactive effects, the review notes that efforts to purify the compound have been limited. It suggests that CBDA could be a valuable product of industrial hemp processing:
Formato M, Crescente G, Scognamiglio M, Fiorentino A, Pecoraro MT, Piccolella S, Catauro M, Pacifico S. (‒)-Cannabidiolic Acid, a Still Overlooked Bioactive Compound: An Introductory Review and Preliminary Research. Molecules. 2020 Jun 5;25(11):2638. doi: 10.3390/molecules25112638 PMID: 32517131; PMCID: PMC7321064
- De Petrocellis et al. (2011) investigate the effects of cannabinoids and cannabinoid-enriched Cannabis extracts on several receptors and enzymes involved in the endocannabinoid system. They find that CBDA has a potent inhibitory effect on an enzyme that degrades endocannabinoid:
De Petrocellis L, Ligresti A, Moriello AS, Allarà M, Bisogno T, Petrosino S, Stott CG, Di Marzo V. Effects of cannabinoids and cannabinoid-enriched Cannabis extracts on TRP channels and endocannabinoid metabolic enzymes. Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Aug;163(7):1479-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01166.x PMID: 21175579; PMCID: PMC3165957
- Takeda et al. (2017) explore the anti-cancer potential of CBDA in a highly aggressive breast cancer cell line. They show that CBDA reduces the expression of a gene that is associated with tumor progression and invasion:
Takeda S, Himeno T, Kakizoe K, et al. Cannabidiolic acid-mediated selective down-regulation of c-fos in highly aggressive breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells: possible involvement of its down-regulation in the abrogation of aggressiveness. Journal of Natural Medicines. 2017 Jan;71(1):286-291. DOI: 10.1007/s11418-016-1030-0 PMID: 27530354
- Citti et al. (2018) analyze the cannabinoid content of commercial hemp seed oil and study the decarboxylation kinetics of CBDA, which converts to CBD under heat. They find that hemp seed oil contains low levels of cannabinoids and that CBDA decarboxylation is influenced by temperature and time:
Citti C, Pacchetti B, Vandelli MA, Forni F, Cannazza G. Analysis of cannabinoids in commercial hemp seed oil and decarboxylation kinetics studies of cannabidiolic acid (CBDA). J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 Feb 5;149:532-540. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2017.11.044. Epub 2017 Nov 20. PMID: 29182999
- Franco et al. (2020) discuss the pharmacological potential of a variety of understudied phytocannabinoids, including varinic acids, minor cannabinoids, and acidic minor cannabinoids. Their anti-inflammatory, analgesic, neuroprotective, and anticancer properties are highlighted, and future research directions are suggested:
Franco R, Rivas-Santisteban R, Reyes-Resina I, Casanovas M, Pérez-Olives C, Ferreiro-Vera C, Navarro G, Sánchez de Medina V, Nadal X. Pharmacological potential of varinic-, minor-, and acidic phytocannabinoids. Pharmacol Res. (2020) May 13;158:104801. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104801.
- Navarro et al. (2020) investigate the pharmacological information of cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabigerol (CBG) as well as their derivatives on cannabinoid CB1, CB2, and CB1/CB2 heteromer receptors. Comparing the major cannabinoid and compounds, their binding affinities, functional activities, and signaling pathways reveals both similarities and differences:
Navarro G, Varani K, Lillo A, Vincenzi F, Rivas-Santisteban R, Raïch I, Reyes-Resina I, Ferreiro-Vera C, Borea PA, Sánchez de Medina V, Nadal X, Franco R. Pharmacological data of cannabidiol- and cannabigerol-type phytocannabinoids acting on cannabinoid CB1, CB2 and CB1/CB2 heteromer receptors. Pharmacol Res. (2020) Sep;159:104940. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104940.
- Zagzoog et al. (2020) describe the pharmacological activity of four secondary cannabinoids isolated from Cannabis sativa: cannabidivarin (CBDV), cannabichromene (CBC), cannabigerol (CBG), and cannabigerovarin (CBGV). They discover that their effects on models of pain, inflammation, anxiety, mood disorders and seizures vary in terms of efficacy and potency:
Zagzoog A, Mohamed KA, Kim HJJ, Kim ED, Frank CS, Black T, Jadhav PD, Holbrook LA, Laprairie RB. In vitro and in vivo pharmacological activity of minor cannabinoids isolated from Cannabis sativa. Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 23;10(1):20405. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-77175-y
- In a mouse model of Huntington’s disease, Nadal et al. (2017) investigate the neuroprotective effect of tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA), a precursor of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). THCA is a potent agonist of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR), a nuclear receptor that controls inflammation and neurogenesis. In addition, they demonstrate that THCA enhances motor function and decreases neuroinflammation in rodents:
X. Nadal, C. del Río, S. Casano, B. Palomares, C. Ferreiro-Vera, C. Navarrete, C. Sánchez-Carnerero, I. Cantarero, M.L. Bellido, S. Meyer, G. Morello, G. Appendino, E. Muñoz, Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid is a potent PPARγ agonist with neuroprotective activity, Br. J. Pharmacol. 174 (2017) 4263–4276, https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.14019.
- Ben-Cnaan et al. (2022) assess the metabolic efficacy of a synthetic derivative of cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), a precursor of CBD, in the treatment of diet- or genetically-induced obesity in mice. By activating PPAR and PPAR receptors, the CBDA derivative reduces body weight, fat mass, hepatic steatosis, insulin resistance, and inflammation:
Ben-Cnaan E, Permyakova A, Azar S, Hirsch S, Baraghithy S, Hinden L, Tam J. The Metabolic Efficacy of a Cannabidiolic Acid (CBDA) Derivative in Treating Diet- and Genetic-Induced Obesity. nt J Mol Sci. 2022 May 17;23(10):5610. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105610.
- In a breast cancer cell line, Hirao-Suzuki et al. (2022) investigate the molecular mechanism by which CBDA modulates the expression of PPAR/ target genes. By activating PPAR/ receptors, they demonstrate that CBDA increases the expression of genes implicated in fatty acid oxidation, mitochondrial biogenesis, and anti-inflammation. They also propose that CBDA and PPAR/ agonists may have a synergistic effect:
Hirao-Suzuki M, Takayuki K, Takiguchi M, Peters JM, Takeda S. Cannabidiolic acid activates the expression of the PPARβ/δ target genes in MDA-MB-231 cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2022 Nov 30;731:109428. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2022.109428.