Introduction
Cannabis has been used by people for thousands of years because of its unique properties.
Traditionally employed in textiles due to its high strength, it has also been used for millennia to manufacture ropes, cloth, or paper, and its seeds are eaten as food in numerous civilizations due to their high nutritional content.
Cannabis was consistently associated with a range of pharmacological benefits from its first applications, so much so that it was a vital part of traditional Chinese medicine as early as 4,000 years ago, as various treatises of the time reveal.
Its use has been linked to treating chronic pain and muscle spasms, reducing nausea caused by chemotherapy, increasing appetite in patients with HIV/AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome), improving sleep quality, and eliminating tics in people with Tourette’s syndrome.
It is also recommended for severe anorexia, arthritis, glaucoma, and migraine headaches.
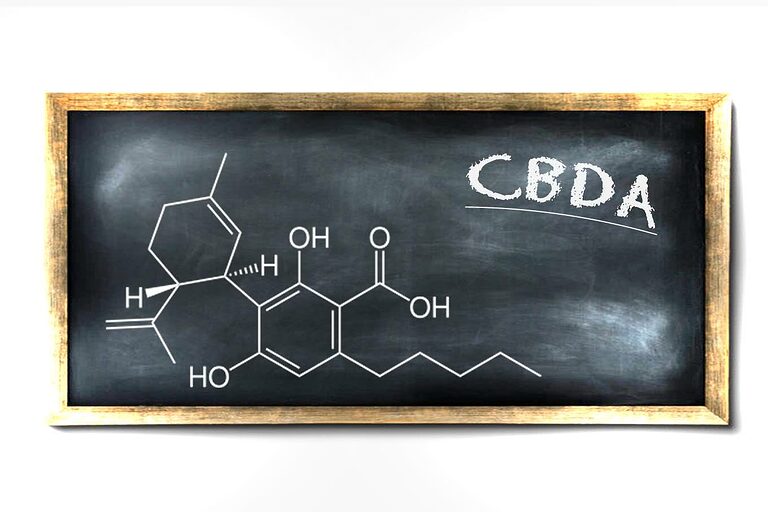
What exactly is Cannabidiolic Acid? (CBDA)
The Cannabis sativa L. plant naturally contains over 100 distinct chemicals known as cannabinoids, which protect the body from overstimulation by attaching to Endocannabinoid System (ECS) receptors and producing relaxing and anti-inflammatory effects.
Cannabinoids are produced primarily in glandular trichomes, which are most abundant in female inflorescences.
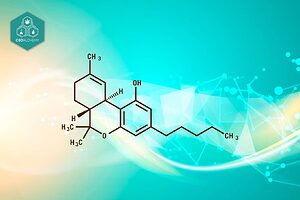
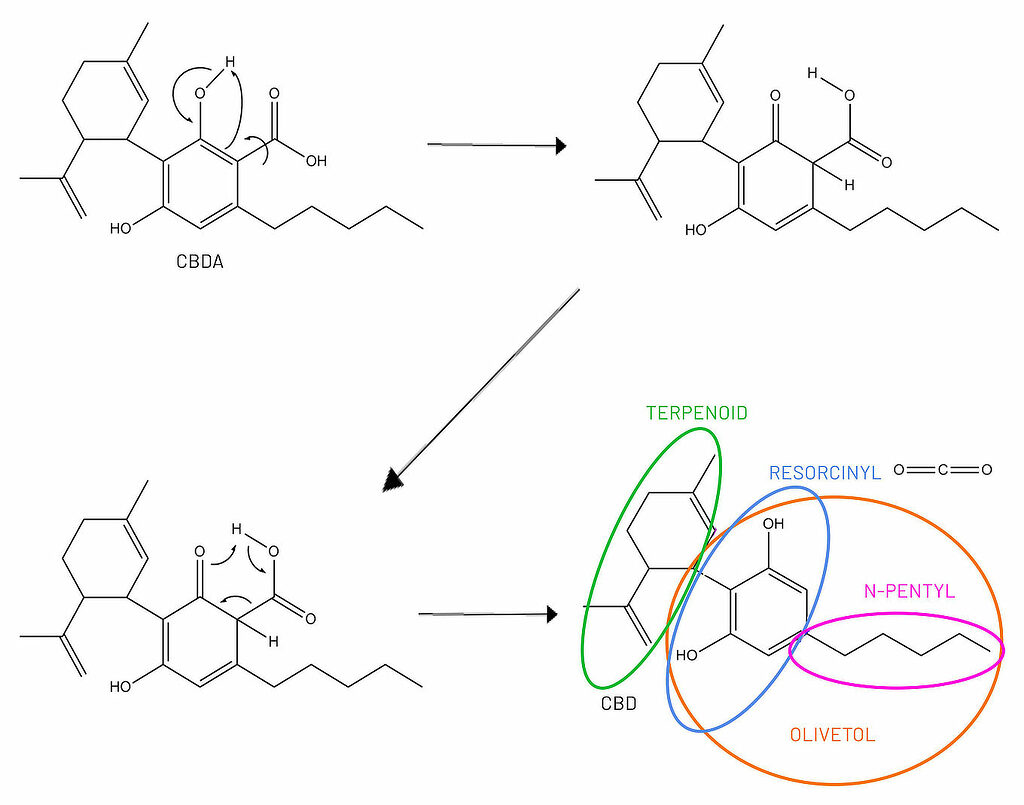
Among the cannabinoids present is Cannabidiolic Acid (CBDA), the ingredient from which CBD is derived through a conversion process (called decarboxylation) throughout plant development.
In reality, all cannabinoids begin their “life” as acids, and they all stem from a single cannabinoid “precursor,” Cannabigerolic acid (CBGa), which over time, owing to plant growth, heat, and exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light, converts into one of the three key cannabinoid precursors:
The plant’s major cannabinoids exist in acid form, but owing to aging, heat, and UV light exposure, both CBDA and THCA de-carboxylate into THC and CBD, which have different molecular structures and functions. CBDA is prevalent in living plants of chemotype III (CBD-dominant).
CBGA is converted into one of three primary cannabinoid precursors depending on which plant enzymes are triggered to drive synthesis:
- THCa stands for tetrahydrocannabinolic acid.
- CBCa stands for cannabicromenic acid.
- CBDA stands for cannabidiolic acid.
When the cannabis plant is decarboxylated by heat or sunlight, CBDA is transformed to CBD. In other words, CBDA is the raw or precursor form of CBD:
CBDA Applications
Because CBD is one of the most well-known and commonly utilized cannabinoids, it has been the focus of several studies and research that have analyzed practically all of its in-depth properties, but CBDA has garnered relatively little/less attention.
Because research on the potential health benefits of CBDA is limited and most studies are based on animal models, even though preliminary results are promising, more clinical studies in humans are required.
On the other hand, scientific research indicates that CBDA has many possible health and medicinal benefits.
CBDA, unlike other cannabinoids, does not bind directly to CB1 or CB2 receptors but instead operates directly on the endocannabinoid system by inhibiting the action of the enzyme cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2).
CBDA’s molecular structure was compared to that of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, which are commonly used to treat inflammation. Researchers found that their chemical structures were a lot alike, and that they both stopped COX-2 receptors from working.
Because COX-2 enzymes are associated with inflammation caused by injury or disease, CBDA showed promise as a potential anti-inflammatory by inhibiting these receptors.
In studies with rodents, it was found that CBDA affects the levels of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that nerve cells make to improve how they send and receive signals.
So, serotonin is needed for all basic human functions, like being able to move, sleep, eat, digest food, and feel emotions.
Radiation and chemotherapy are two examples of outside stressors that can cause the body to release too much serotonin, which can make you feel sick and make you throw up.
Drugs can often stop vomiting, but nausea is harder to deal with because it happens all the time. In fact, one in five cancer patients thinks about stopping treatment to stop feeling sick.
Scientists have shown that CBDA has a strong effect (almost 100 times stronger than CBD) on the serotonin 5-HT-producing receptors in the body. This suggests that it could be used as a medicine to treat nausea and vomiting caused by chemotherapy or other conditions that cause these symptoms.
Even though more research needs to be done, GW Pharmaceuticals’ recent tests suggest that CBDA may be an even better seizure medicine.
This same efficacy could imply that CBDA may play a role in successfully battling depression; after all, CBDA acts on 5-HT receptors in the same way that an antidepressant does.
Finally, while research on CBDA’s potential anti-cancer properties has so far only been conducted on isolated cells, preliminary results suggest that it may have favorable effects even in this field by reducing the migration of a very aggressive breast cancer cell type known as MDA-MB-231.
Potential side effects and interactions
CBDA, like CBD, has a relatively small number of potential negative side effects.
The following is a short list of the most common ones:
- Cottonmouth
- Drowsiness – Low blood pressure – Dizziness
- Moderate mood swings
These adverse effects are more likely to develop when CBDA is used in high dosages or periodically throughout the day; consult your doctor if you encounter troublesome or persistent side effects.
There is a list of prescription and over-the-counter medications that may interact with CBDA (and CBD); we always recommend talking with your doctor or pharmacist before mixing them with CBDA.
We recommend that you read a recently published paper to learn more about drug interactions:
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/17512433.2022.2142114
Is CBDA more effective than CBD?
The truth is that we don’t know yet.
Although it is unknown whether CBDA is more useful than CBD, the acid cannabinoid has shown significant promise for human health.
We will learn more about the efficacy of this cannabis as researchers go beyond animal models and into other clinical investigations.
CBDA and CBGA (Cannabigerolic acid) have recently been researched for their ability to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 virus infection. The study was made using cells in a laboratory and would need to be confirmed by human clinical trials. Cannabinoids, on the other hand, are not a common cure or treatment for COVID-19.
Link to the study:
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.1c00946
Additional references:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7321064/pdf/molecules-25-02638.pdf